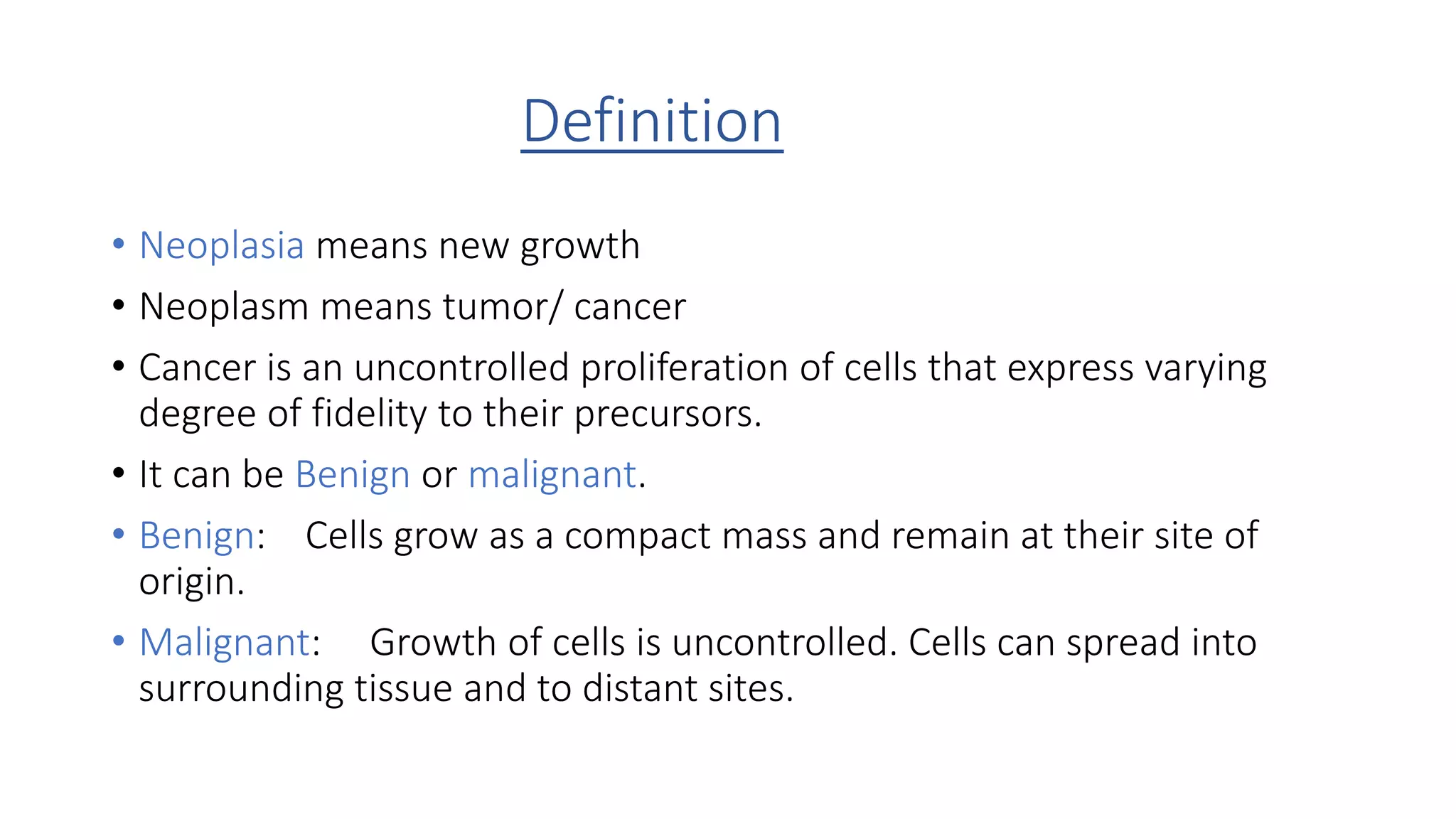
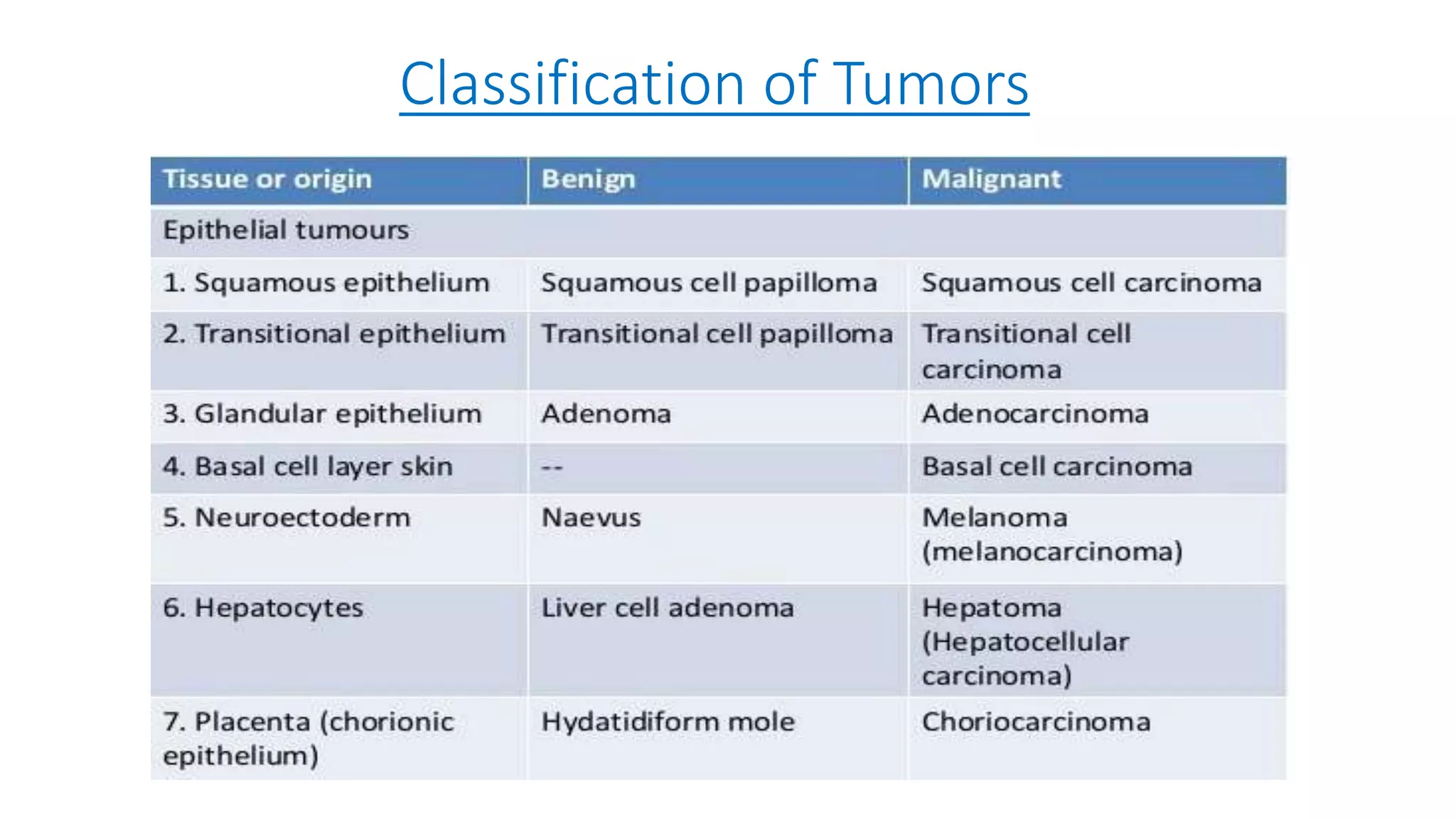
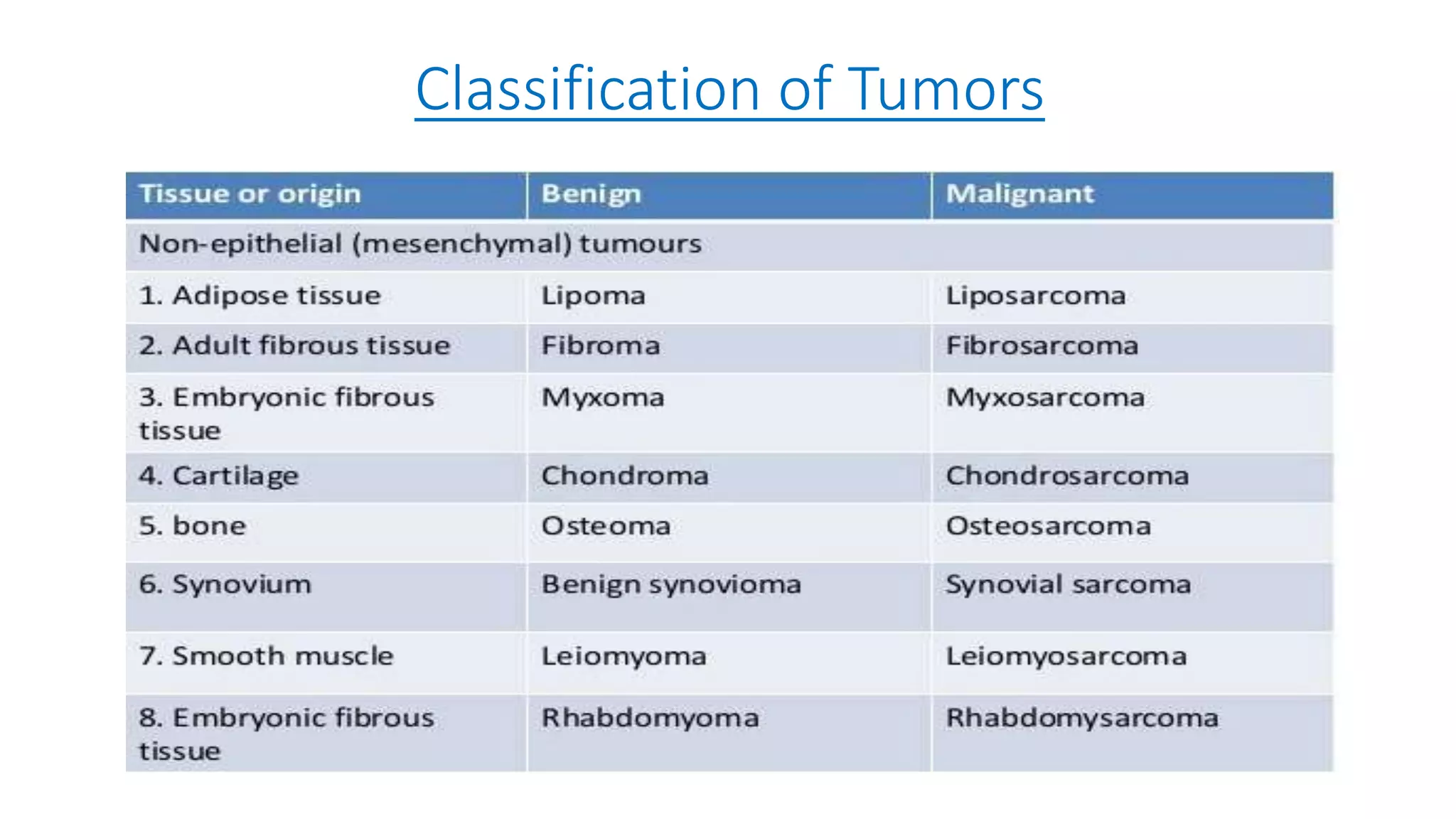
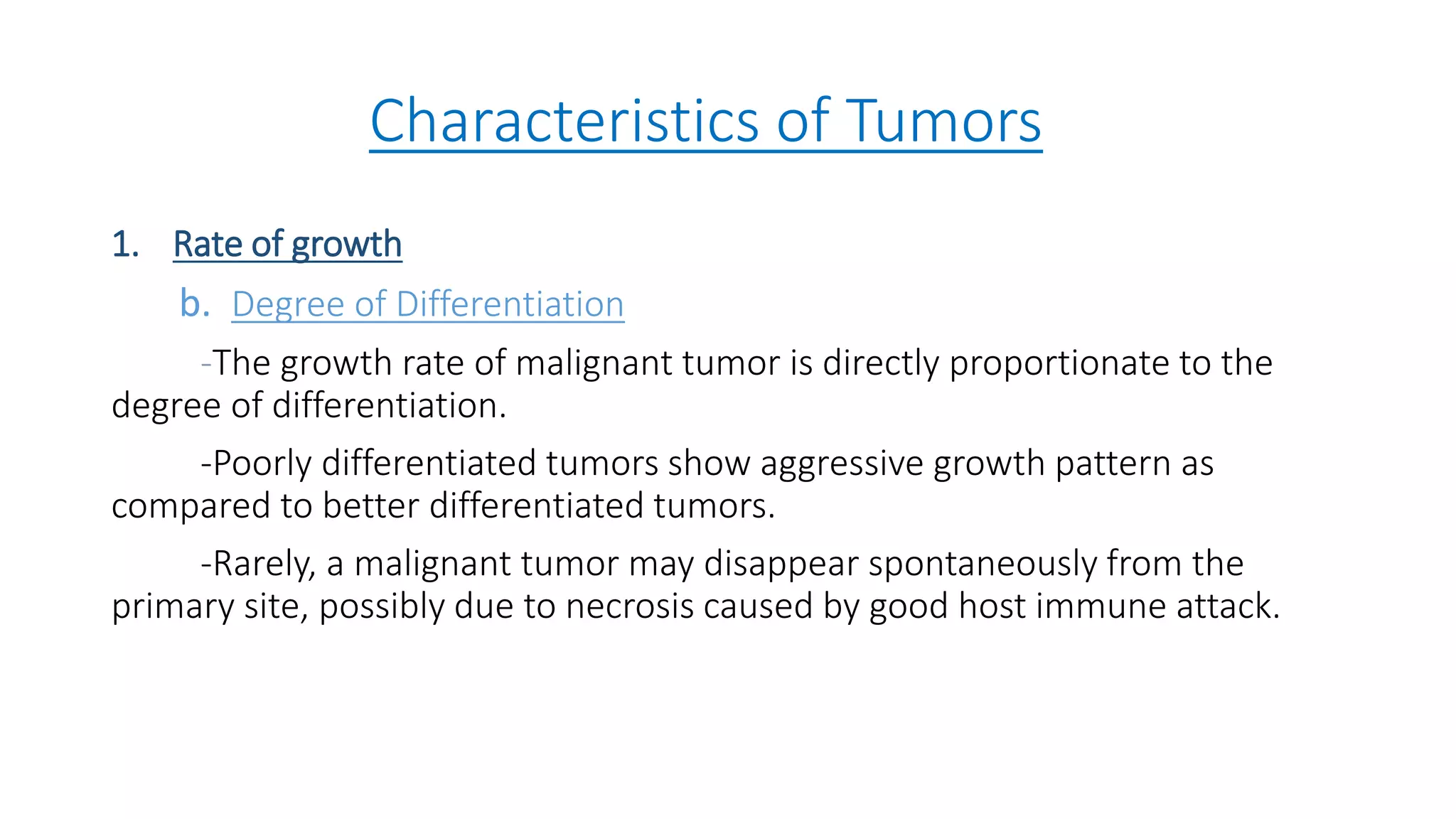
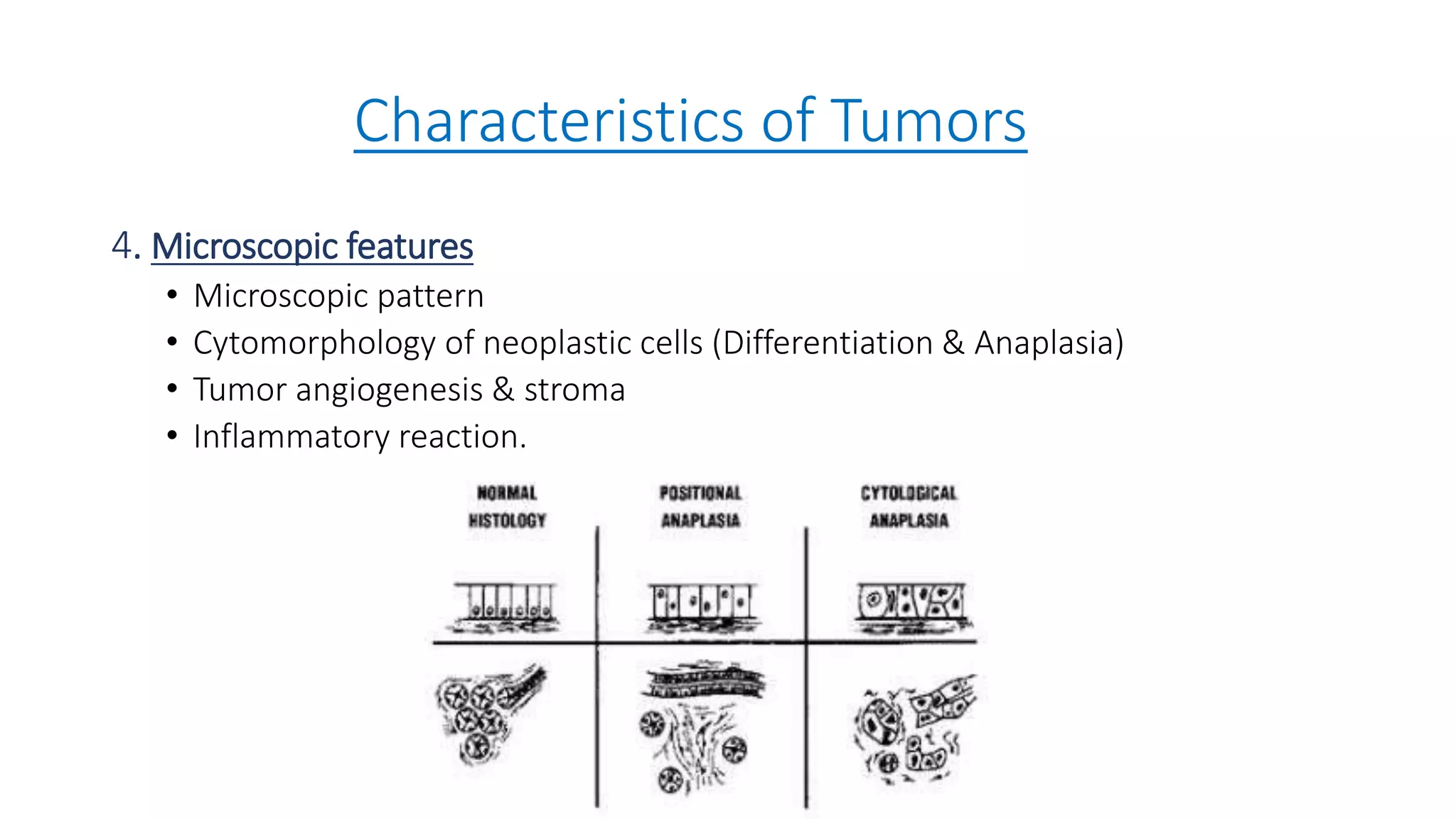
The document discusses the characteristics and classification of neoplasms, highlighting the distinction between benign and malignant tumors. It details various carcinogens responsible for cancer, the growth rates and differentiating features of tumors, and the behavior of cancer cells, including local invasion and metastasis. Additionally, it covers the clinical features and microscopic characteristics that differentiate benign from malignant neoplasms.