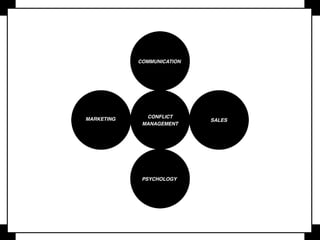
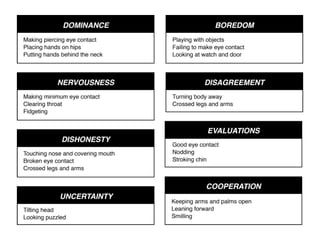
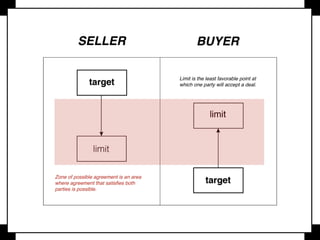
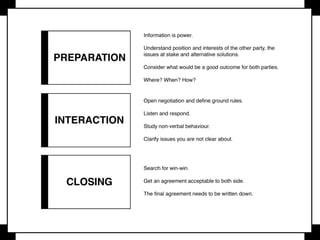
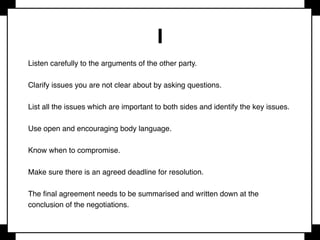
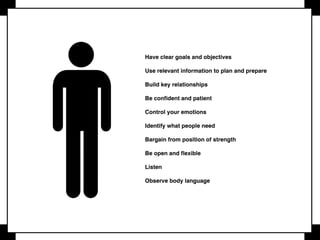
Negotiation is a communication process where parties with different objectives aim for a mutually agreeable solution, relying on effective communication, active listening, and clear goals. Key strategies include evaluating alternatives, understanding body language, and knowing when to compromise, while maintaining composure and assertiveness. Successful negotiators prepare well, leverage their strengths, and understand their best alternatives to reach favorable outcomes.