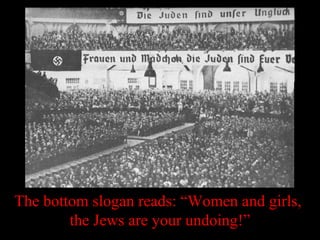
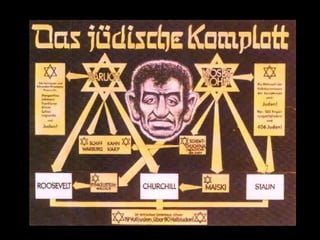
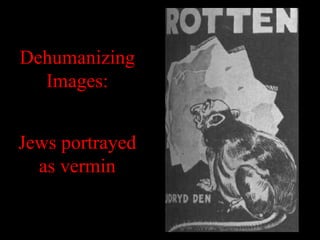
The document provides information about Nazi propaganda techniques and goals. It explains that Nazi propaganda had two main purposes: to create a positive image of Hitler and the Nazi party, and to create a negative view of enemies, particularly Jews. It describes several of Hitler's propaganda methods, including presenting simple repetitive themes, appealing to emotion, having broad mass appeal, and focusing on one main enemy. It also discusses how propaganda was pervasive in Nazi Germany through various media. Finally, it outlines the goals of both pro-Nazi and anti-Jewish Nazi propaganda, such as portraying Hitler as a savior and Jews as the source of all problems in Germany.