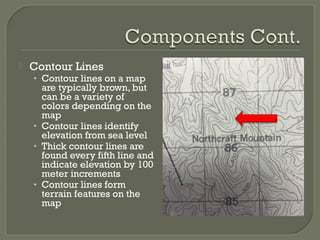
This document provides instruction on land navigation using topographic maps. It aims to teach students basic map reading skills and the ability to navigate using terrain association. The key topics covered include identifying the components of a map, common terrain features like hills, valleys, and ridges, and man-made symbols. Upon completion, students should be able to identify contour lines and legends, four terrain features, and four man-made symbols on a topographic map.