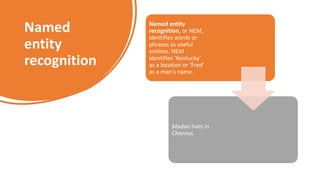
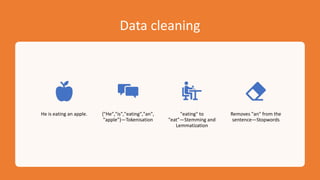
The document provides an overview of Natural Language Processing (NLP), explaining its integration of computer science, artificial intelligence, and linguistics to enable machines to understand and respond to human language. Key processes outlined include speech recognition, part of speech tagging, sentiment analysis, and named entity recognition, all of which contribute to the understanding and generation of text and voice data. The document also highlights essential techniques in NLP such as tokenization, stemming, and lemmatization for processing unstructured data.

















![Document
Term Matrix
corpus = ['This is the first document.', 'This
document is the second document.', 'And this is
the third one.', 'Is this the first document?']
['and', 'document', 'first', 'is',
'one', 'second', 'the', 'third',
'this']
[[0 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 1]
[0 2 0 1 0 1 1 0 1]
[1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 1]
[0 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 1]]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oanlp-220222094656/85/Natural-Language-Processing-from-Object-Automation-21-320.jpg)

![Sequence
to vector
models
"I love to eat" Positive sentiment
[0.10] bad [0.90] good](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oanlp-220222094656/85/Natural-Language-Processing-from-Object-Automation-23-320.jpg)