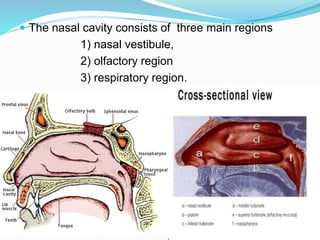
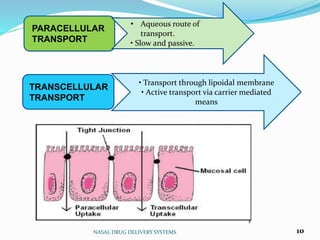
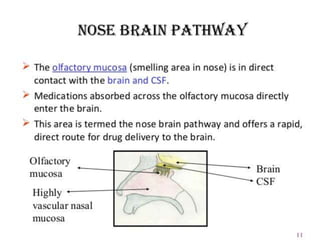
The document presents information on nasal drug delivery systems. It discusses the advantages of nasal delivery such as rapid drug absorption and avoidance of first-pass metabolism. Various formulations for nasal delivery are described such as drops, sprays, and gels. Barriers to nasal absorption like enzymatic degradation and strategies to improve absorption like permeation enhancers are also summarized. Applications include delivery of peptides, vaccines, and drugs to the brain. The anatomy and mechanisms of nasal absorption are briefly covered.