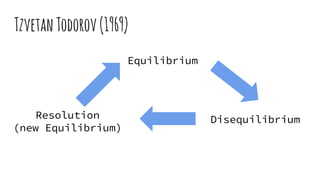
Narrative theory analyzes how media texts communicate meaning through stories. It can be applied to films, television, photographs, and magazines. Vladimir Propp identified 8 character roles that commonly appear in folk tales, such as heroes, villains, and helpers. Tzvetan Todorov suggested narratives follow a pattern of equilibrium, disequilibrium, and resolution. Roland Barthes described two codes - the action code which alerts audiences something is happening, and the enigma code which presents puzzles for audiences to solve. Technical codes like camera shots are also used to guide audience attention.