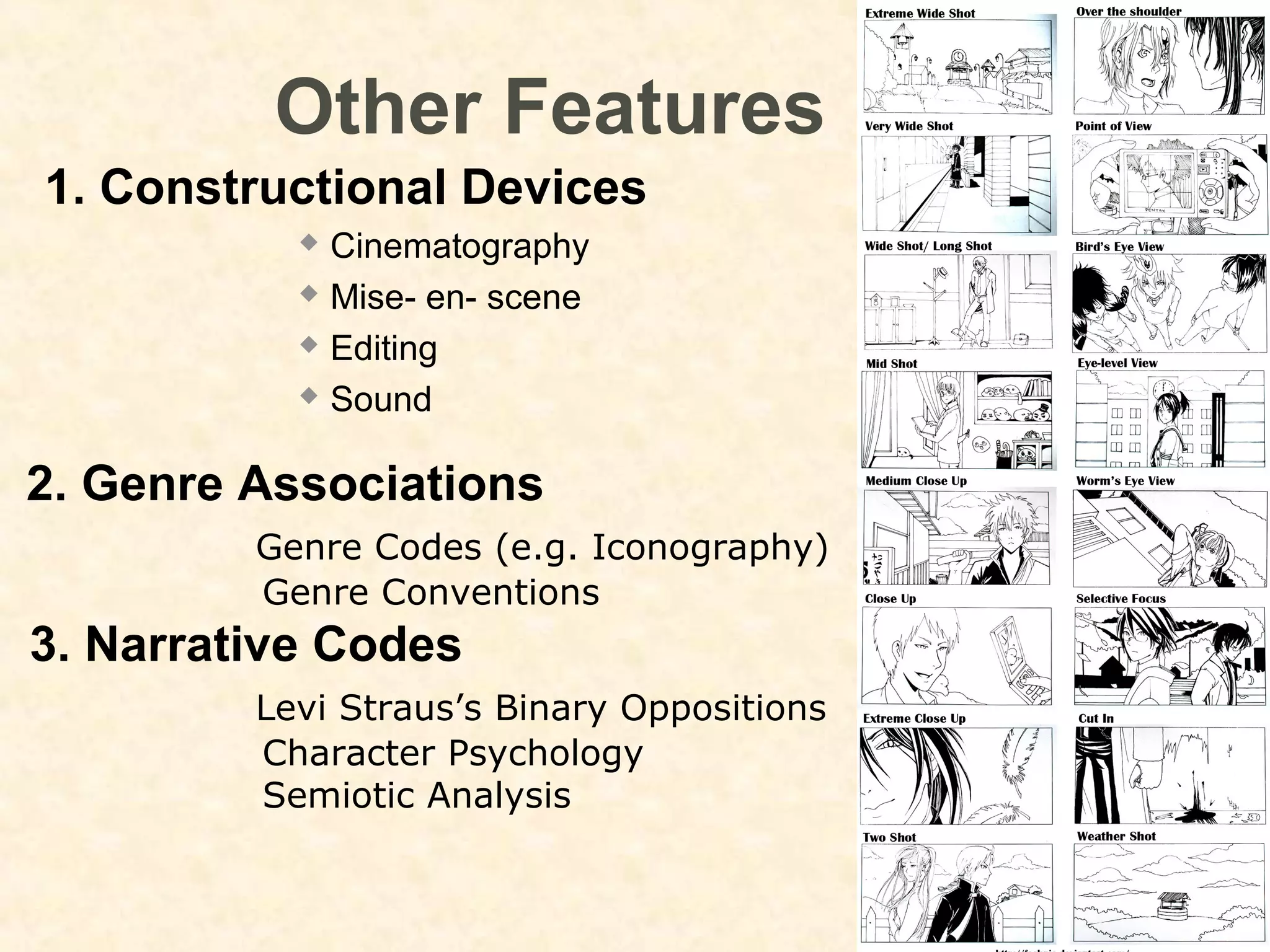
This document discusses various concepts and theorists related to narrative structure in media. It outlines Aristotle's beginning, middle, end structure. Todorov's equilibrium, disequilibrium, re-equilibrium structure is presented. Propp is discussed for identifying 31 narrative functions and 7 character archetypes based on Russian folktales. Other concepts covered include plot vs story, cause and effect, Levi-Strauss's binary oppositions, and Barthes' codes for how audiences decode narratives. Examples are given like Propp's archetypes in Star Wars and definitions from Bordwell and Thompson.