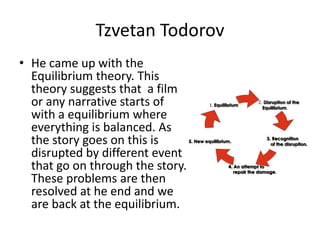
The narrative structure refers to both the content and form of a story. It is comprised of two main elements - the story, or raw chronological events, and the plot, which is how the story is structured and presented. The narrative structure also includes codes like action codes, which describe a causal chain of events, and enigma codes, which rely on clues and mysteries to drive the plot forward. Additionally, theorists have proposed concepts like equilibrium, where a story starts in balance and events disrupt it before resolution, and binary oppositions, where meanings rely on conceptual contrasts. Character roles and their functions are also important components of narrative analyzed by theorists.