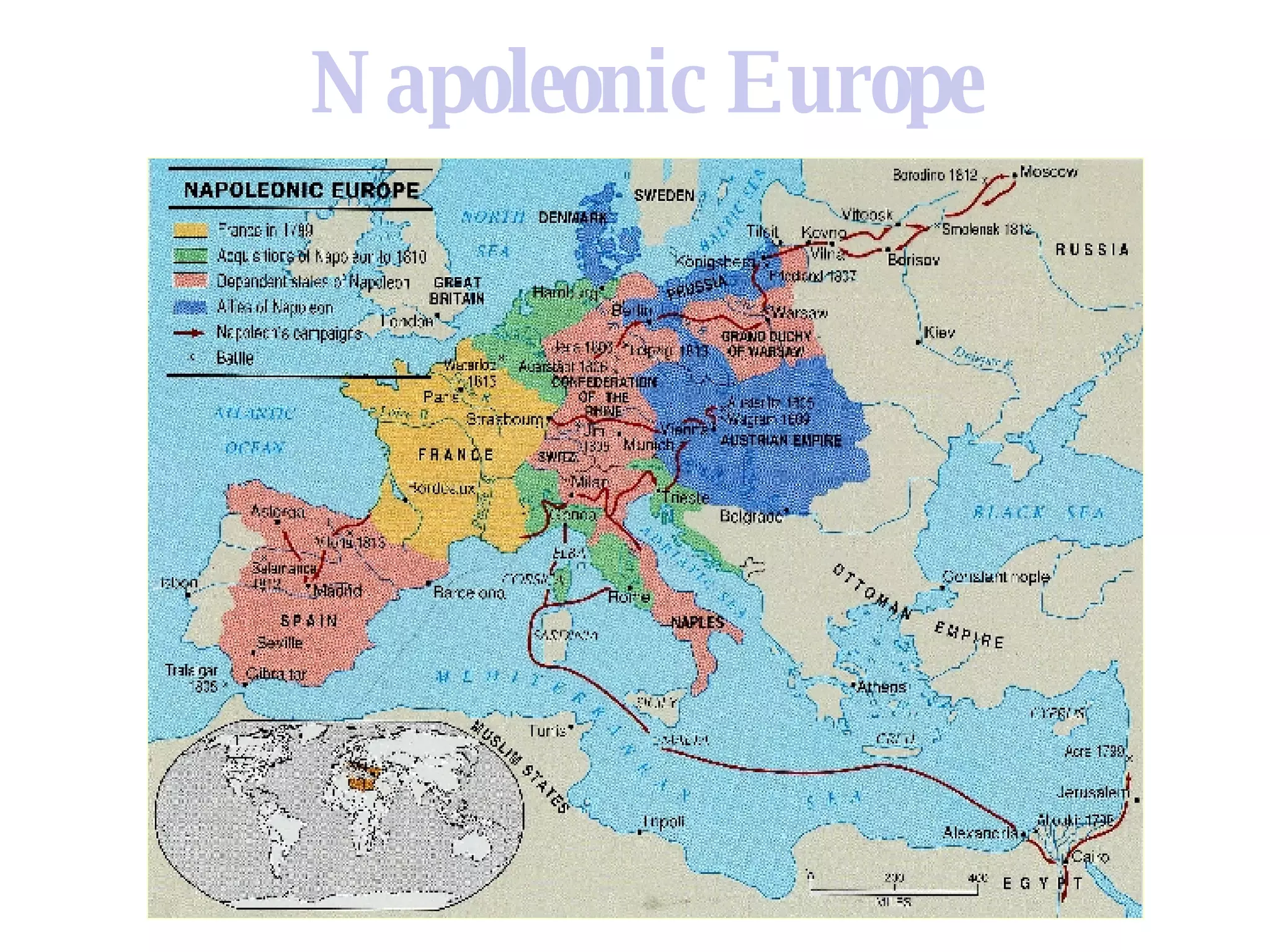
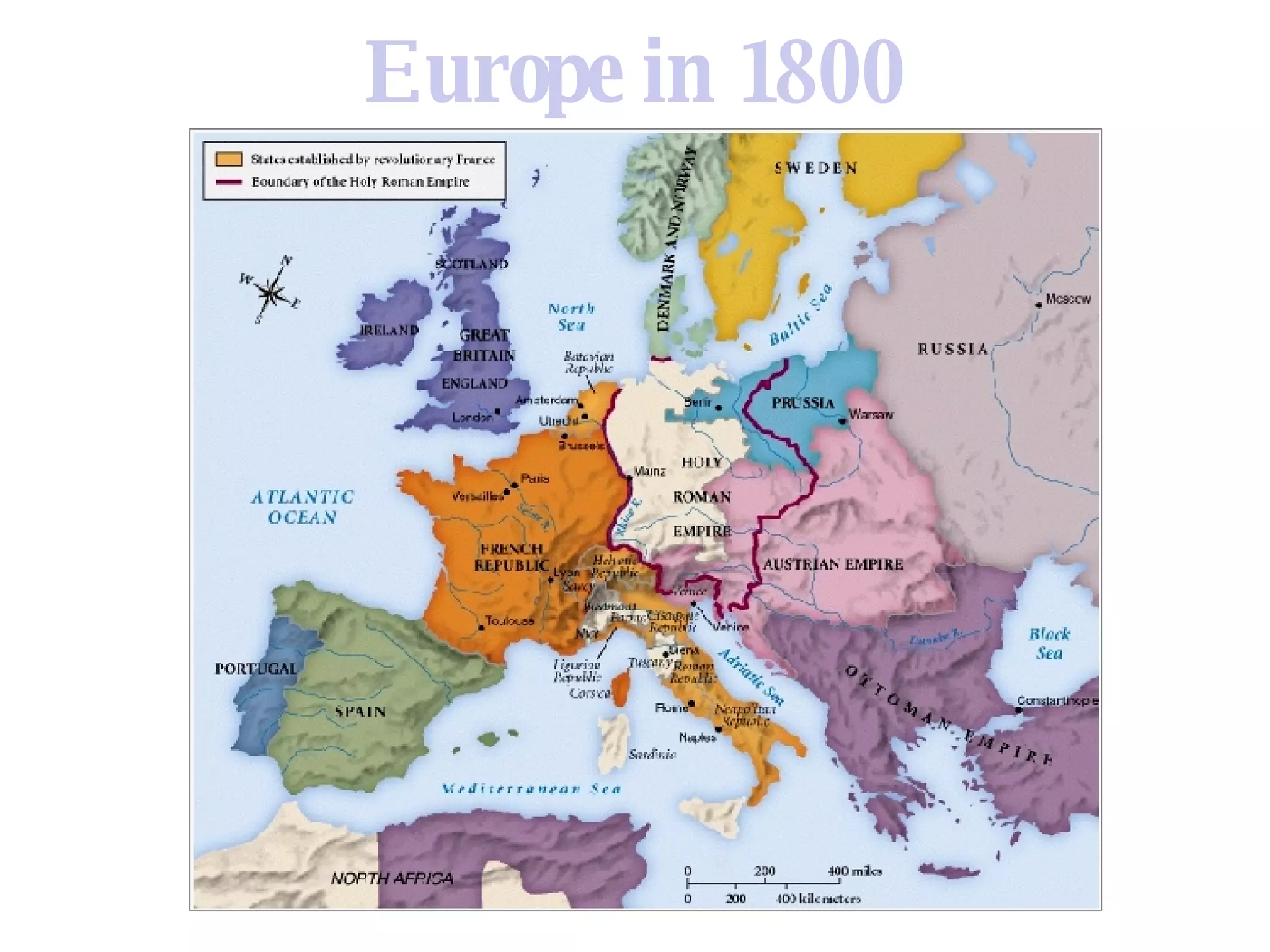
1) Napoleon rose to power in France but overreached with his vast continental empire, leading to major military defeats in Russia in 1812 and Germany in 1813.
2) At the Congress of Vienna in 1814-1815 after Napoleon's defeat, European leaders redrew borders and established a new balance of power to prevent future French domination, weakening France and increasing the power of Prussia and Austria.
3) While Napoleon's empire was dismantled, his legacy lived on through the spread of revolutionary ideals like nationalism and the Napoleonic Code of laws across Europe.