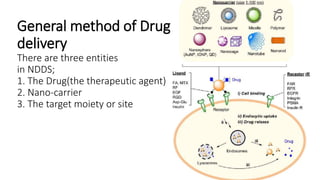
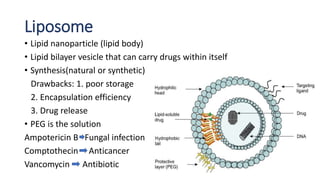
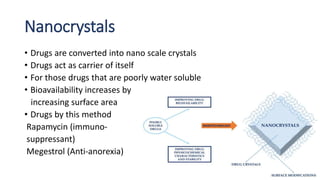
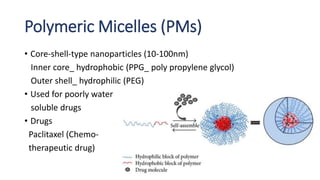
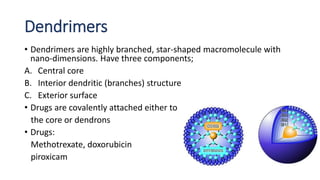
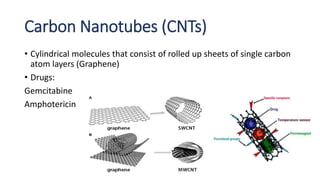
This document defines nano-based drug delivery systems as formulations that enable the controlled introduction of therapeutic agents into the body. Traditional drug delivery systems have problems like poor bioavailability, solubility, and stability. Nano-based delivery systems address these issues by allowing targeted and controlled drug release. Common nanocarriers discussed include liposomes, nanocrystals, polymeric micelles, dendrimers, and carbon nanotubes. The general method involves combining a drug with a nano-carrier and targeting moiety to improve drug properties and delivery.