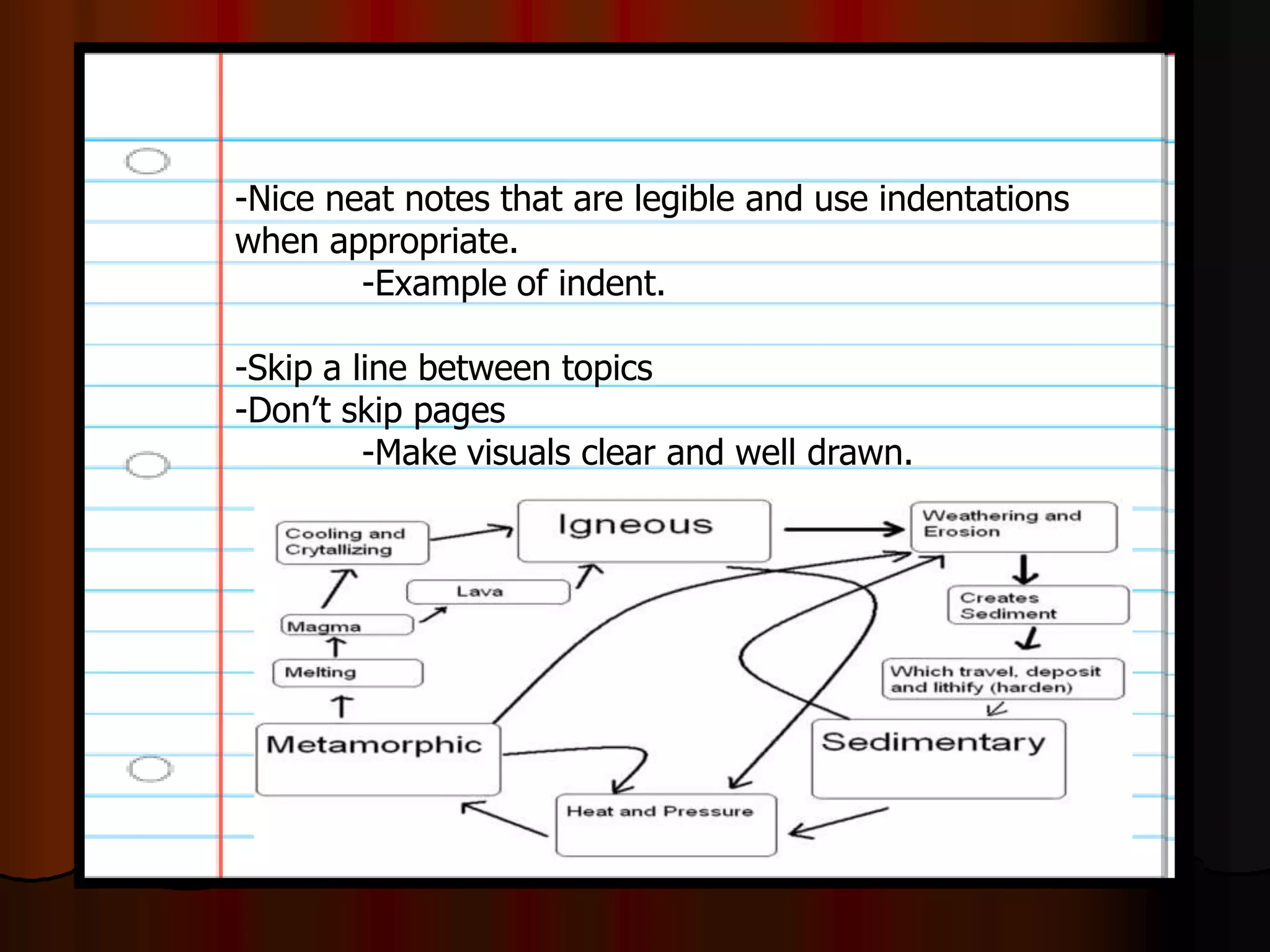
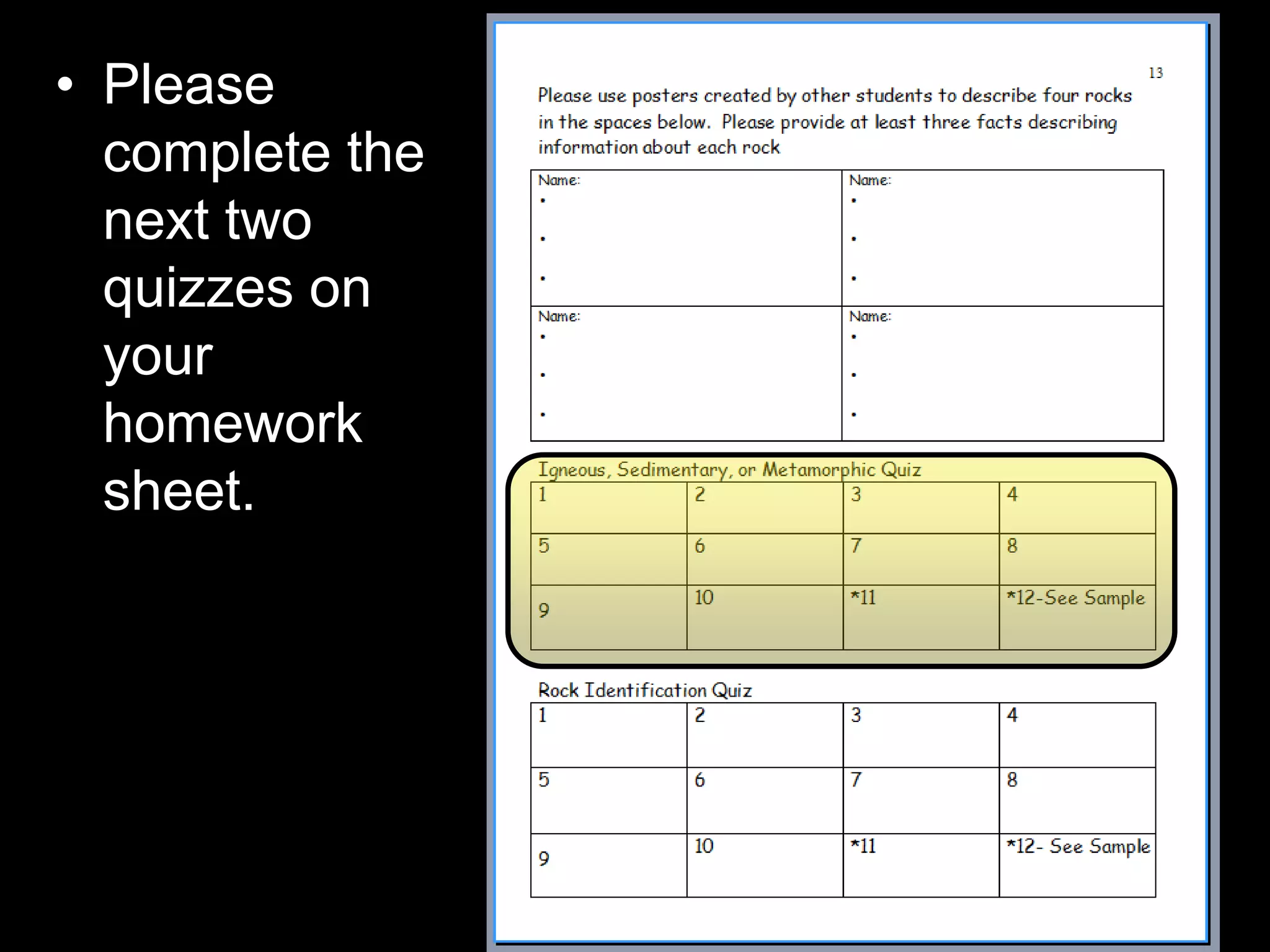
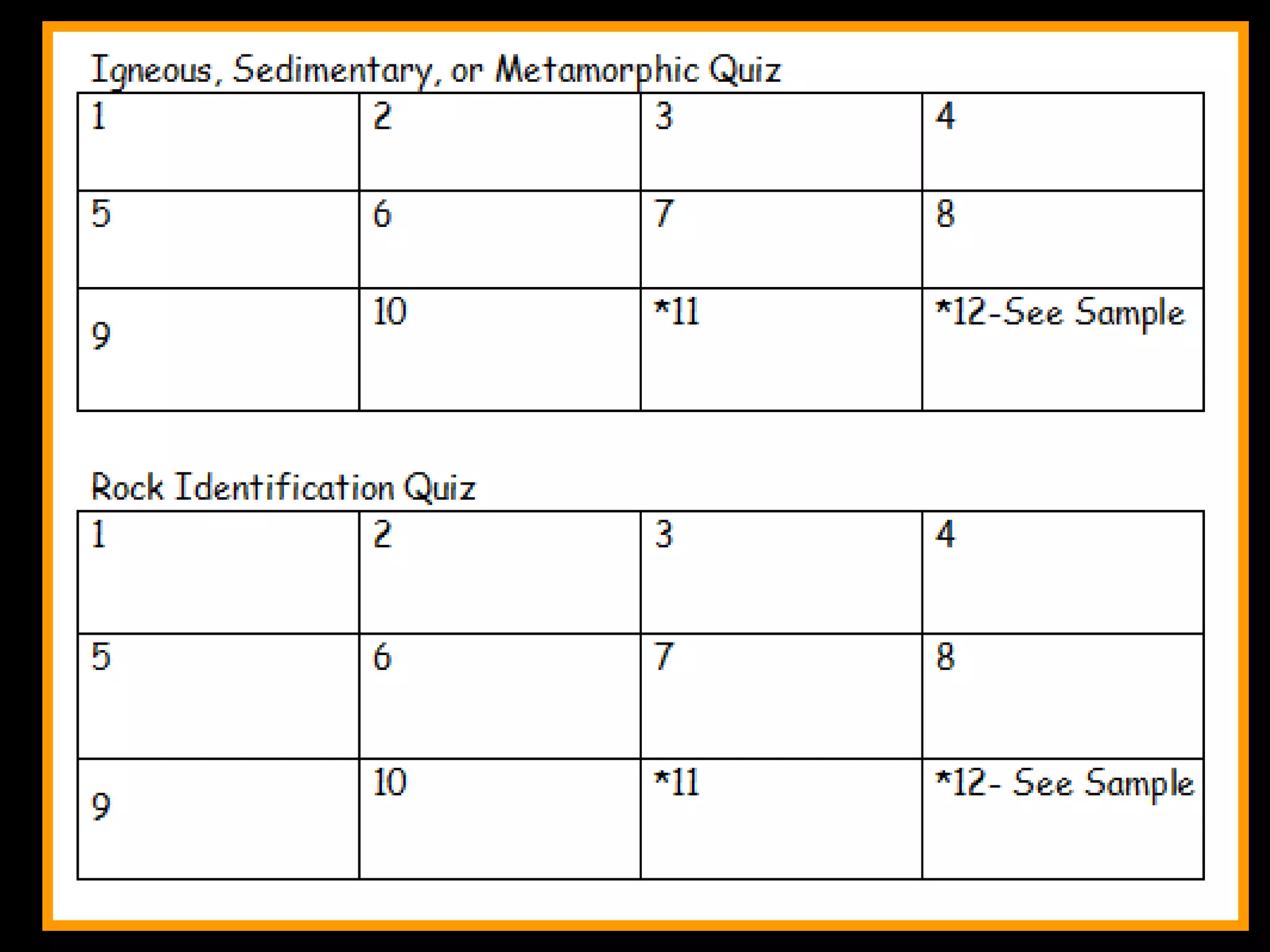
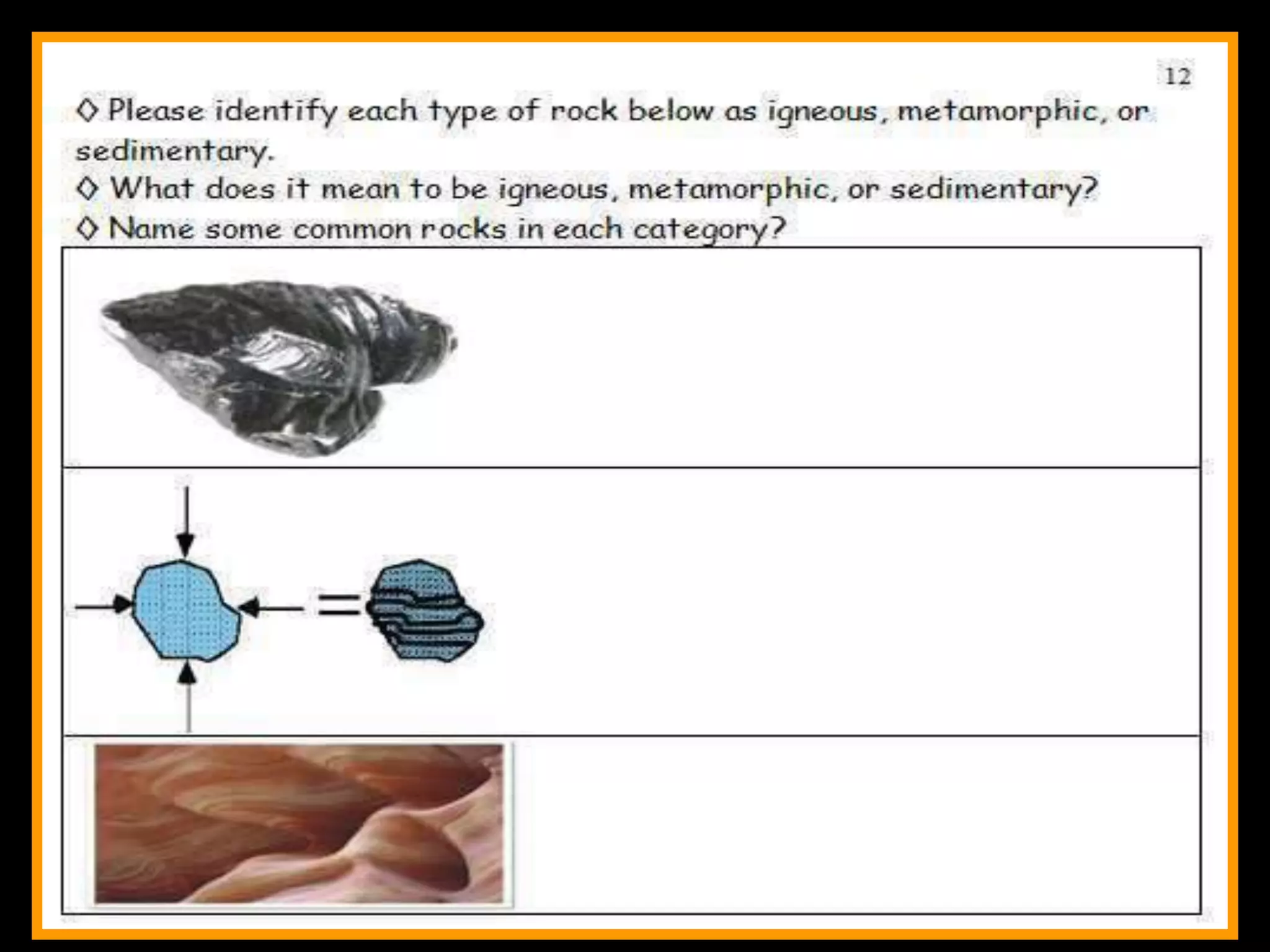
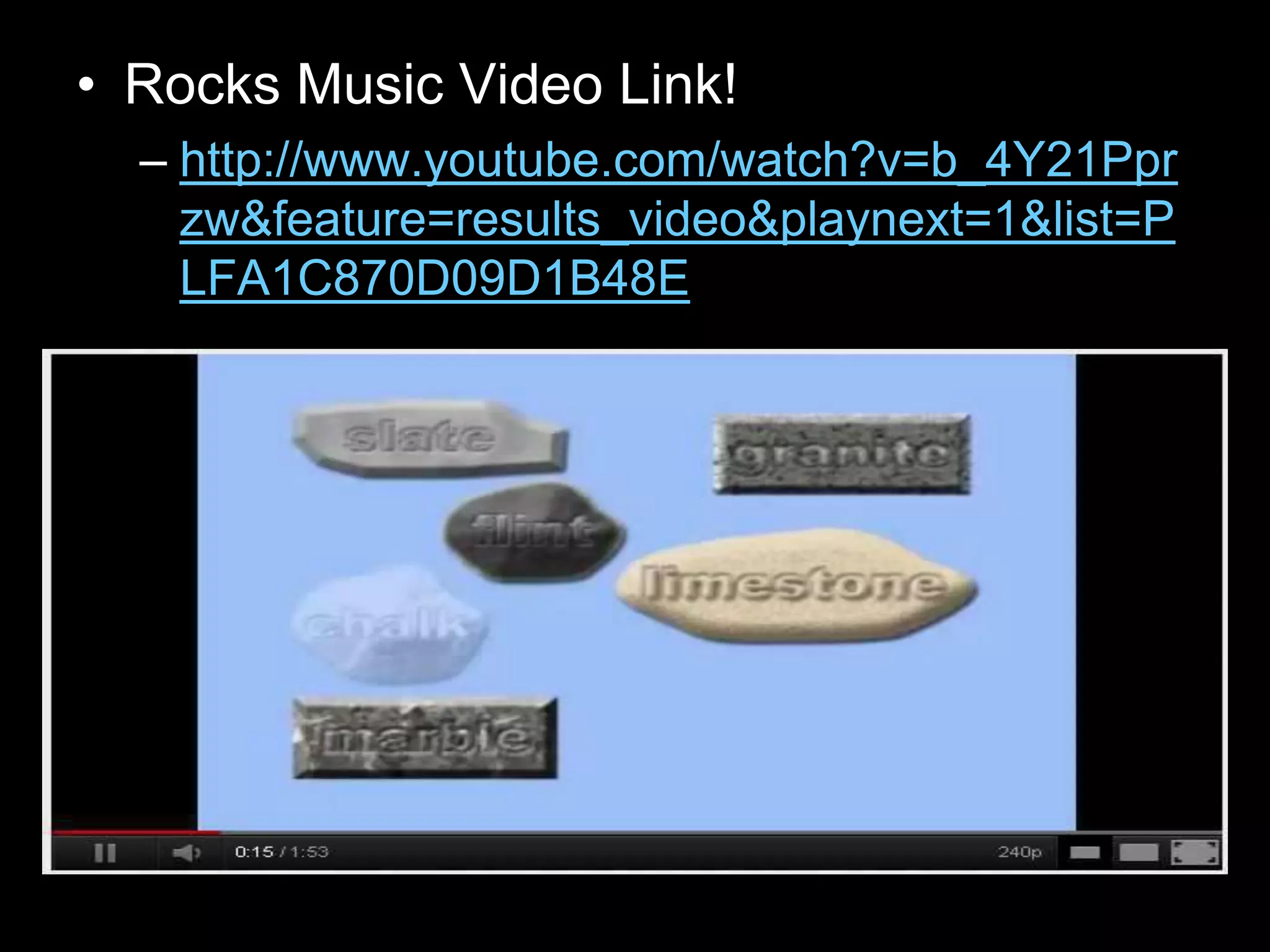
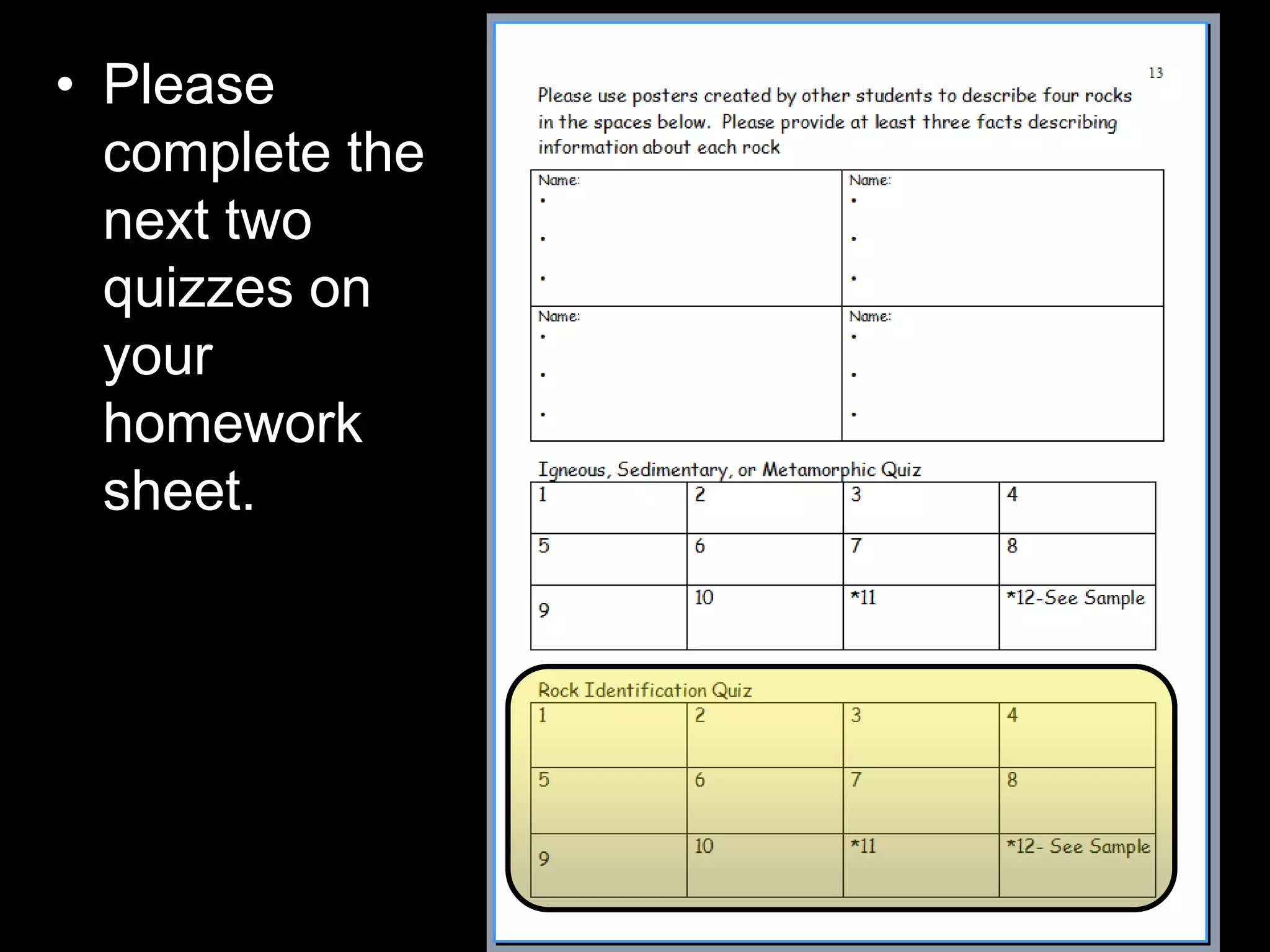
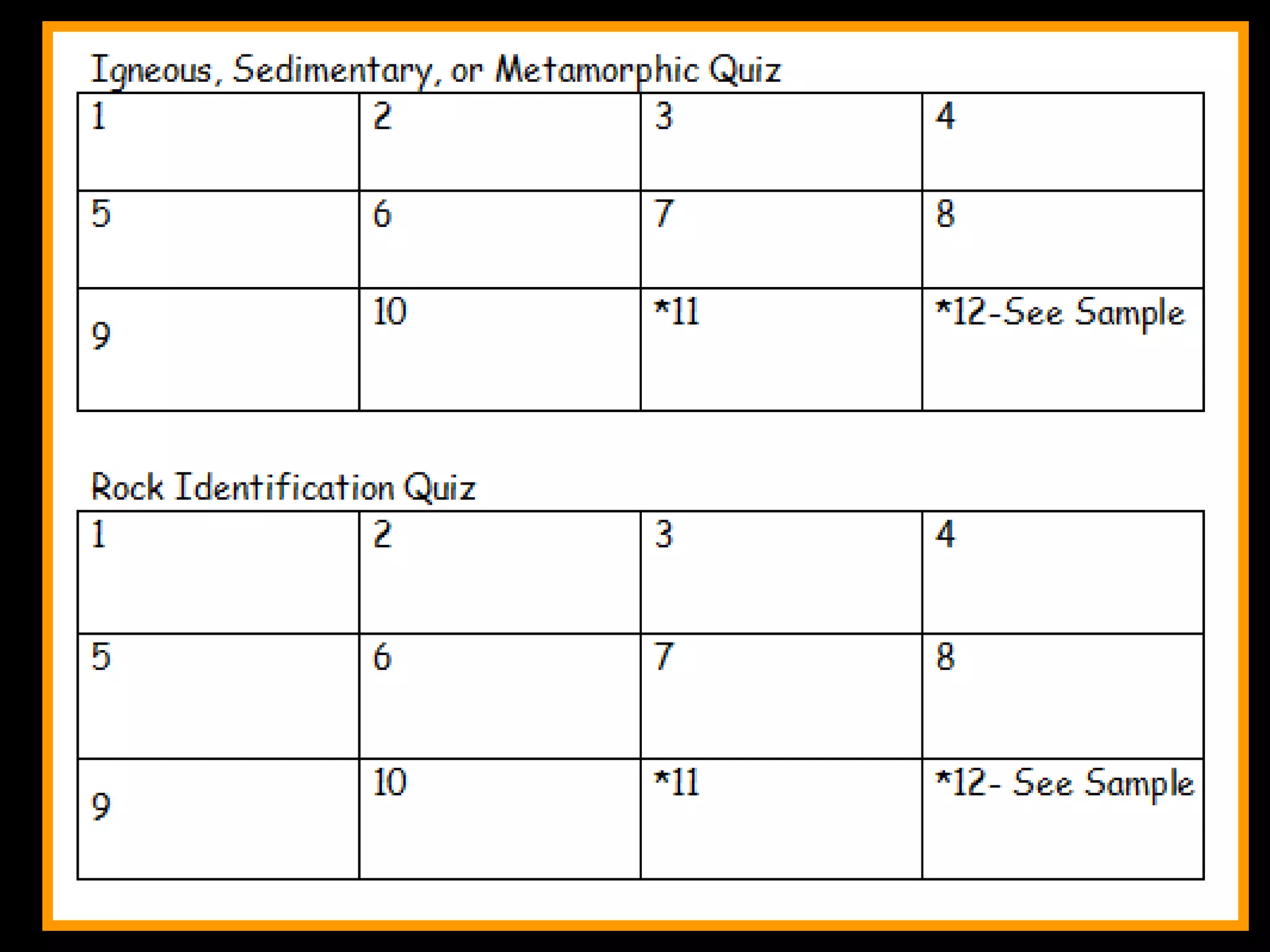
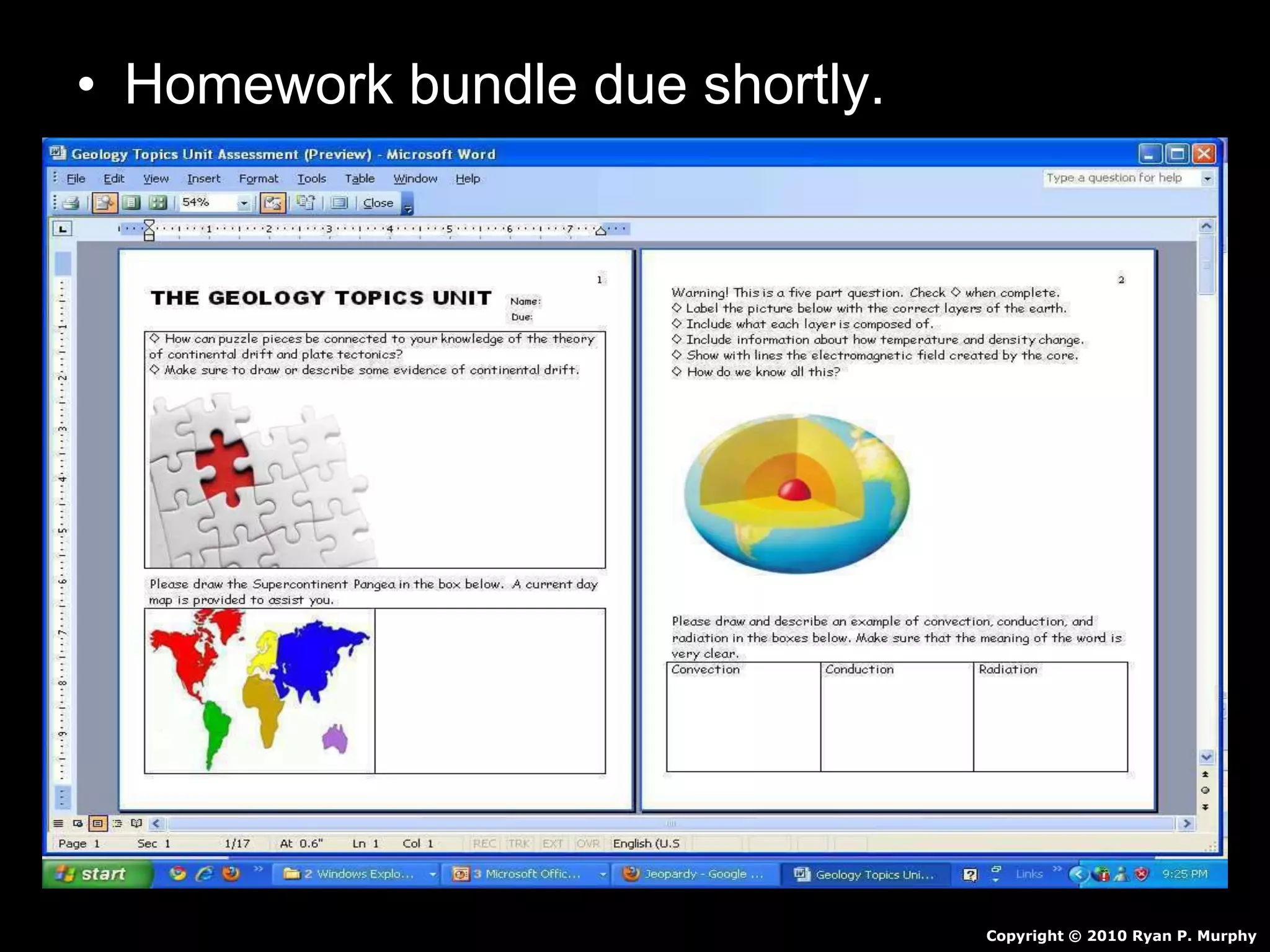
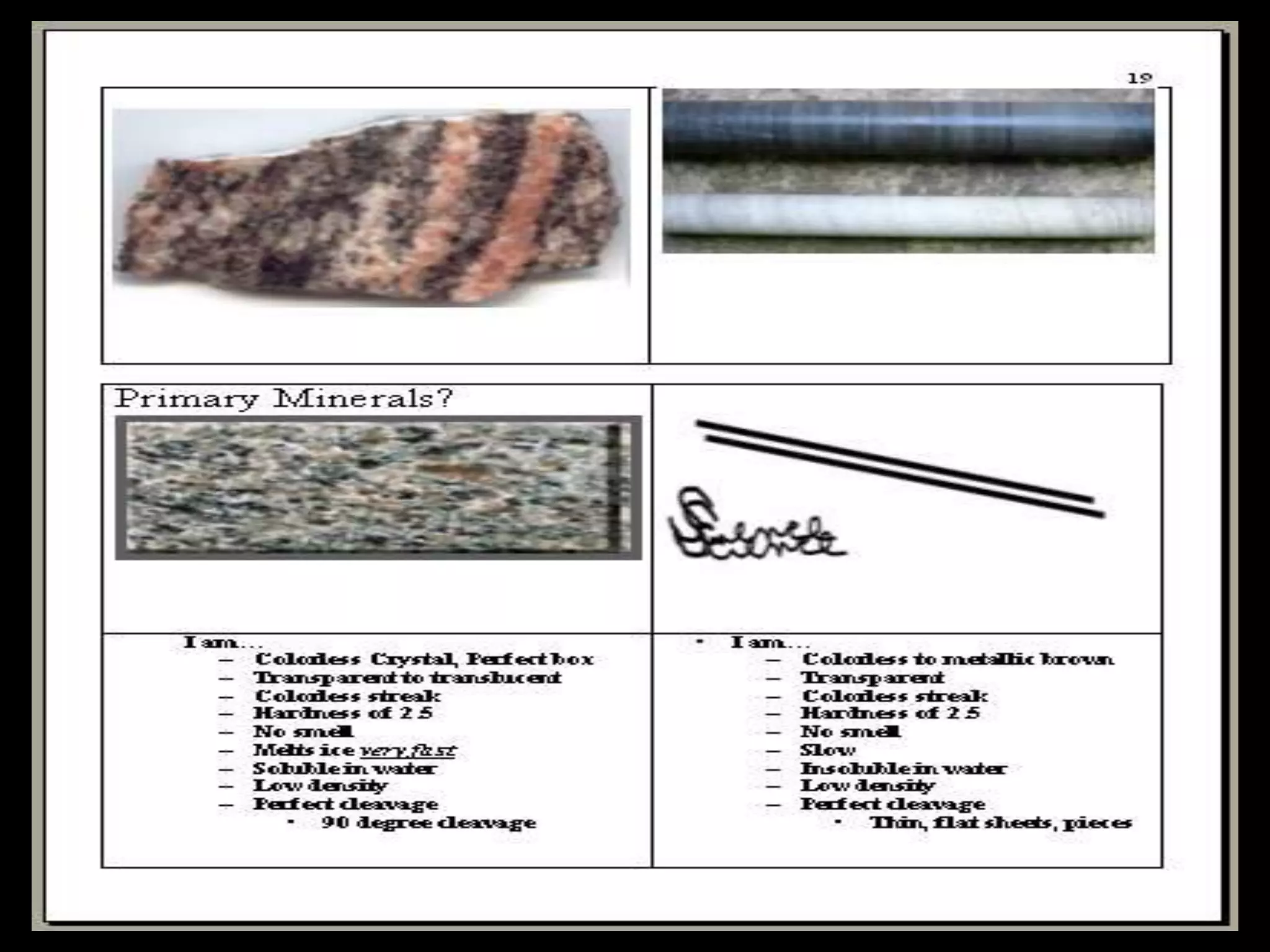
The document outlines a comprehensive geology unit, covering various rock types such as igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic, and their characteristics. It includes instructions for quizzes, homework assignments, and an auction project focused on different minerals. Additionally, it provides links for research and a curriculum guide for various science topics for students in grades 5-10.