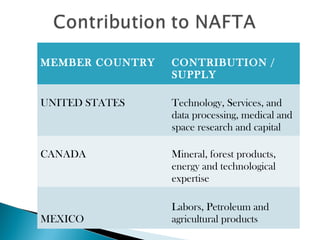
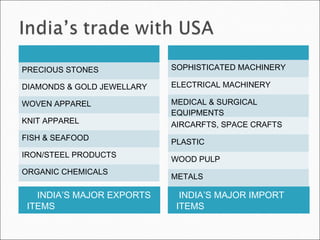
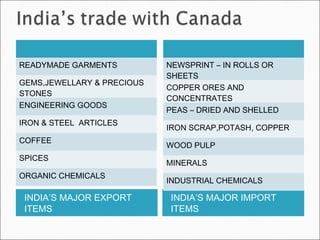
The document discusses the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) which established rules for free trade between Canada, the United States, and Mexico. NAFTA systematically eliminated tariff and non-tariff barriers to trade and investment. It aims to promote fair competition, increase investment opportunities, protect intellectual property rights, and establish frameworks for cooperation. NAFTA has increased trade, investment, and economic growth in North America but has also been criticized for negative impacts on some workers and farmers.