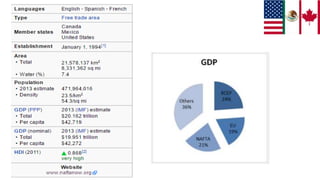
The document discusses the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), which created a trilateral trade bloc between Canada, Mexico, and the United States in 1994. NAFTA's objectives were to eliminate trade barriers and promote cross-border movement of goods and services. The agreement's members and their roles are described. Both pros and cons of NAFTA are provided, such as increased trade but also job losses in some industries. In conclusion, NAFTA has played an important role in developing the three nations' economies but also had some negative social impacts.