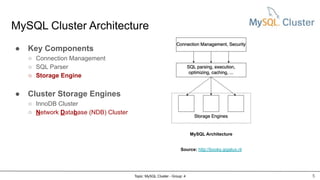
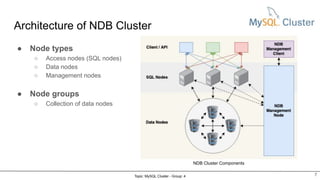
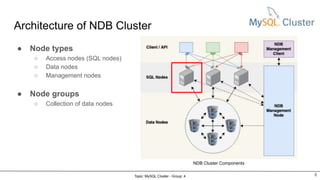
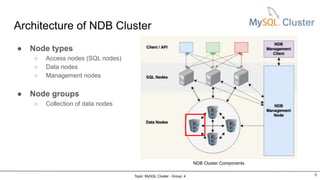
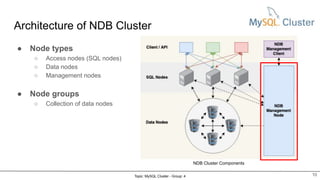
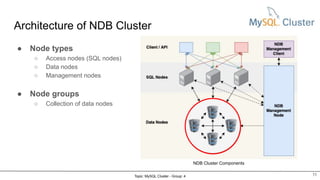
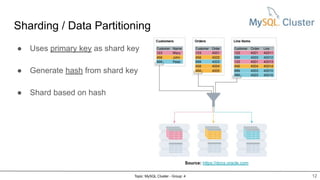
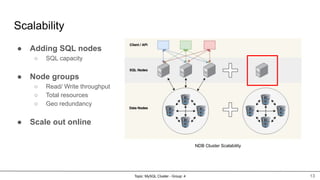
MySQL Cluster is a distributed, highly available, and scalable version of MySQL. It has key components like connection management, SQL parser, and storage engines. The two main types of MySQL Clusters are InnoDB Cluster and Network Database (NDB) Cluster. NDB Cluster uses different node types and data partitioning across nodes to provide scalability and high availability. MySQL Cluster is used for applications that require high performance, scalability and availability.



![History
● Developed by Ericsson in the late 90’s [1,2]
● Initially designed for Telecommunication Applications
Paper: "Design and Modeling of a Parallel Data Server for Telecom Applications" [3]
○ High availability and reliability – downtime less than 30 seconds / year [2]
○ High throughput and linear scalability when adding more servers [2]
● Later Acquired by MySQL
● Incorporated as a Storage Engine
[1] https://web.archive.org/web/20040202195548/http://www.mysql.com/press/release_2003_30.html
[2] https://downloads.mysql.com/presentations/3_MySQL_Use_Case_for_TELCO_Europe.pdf
[3] Ronström, M., & Ab, E. U. (1998). Design and Modelling of a Parallel Data Server for Telecom Applications. Computer and Information Science, Linköping University.
4
Topic: MySQL Cluster - Group: 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cs550topicpresentation-211108052625/85/MySQL-NDB-Cluster-4-320.jpg)