Country Overview: Myanmar
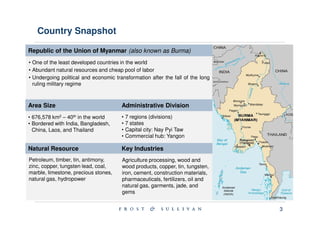
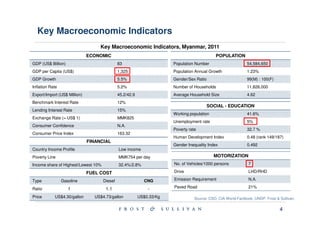
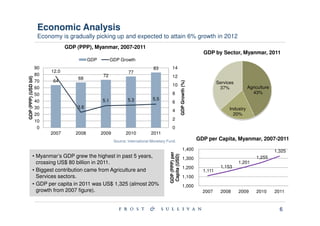
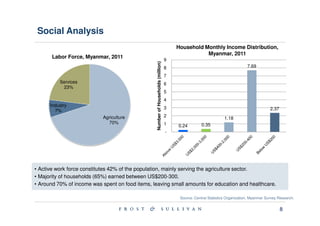
Myanmar is located in Southeast Asia and borders India, Bangladesh, China, Laos and Thailand. It has abundant natural resources and its economy is gradually growing after political reforms. However, Myanmar remains one of the least developed countries and faces issues like infrastructure development, human rights, and poverty reduction.