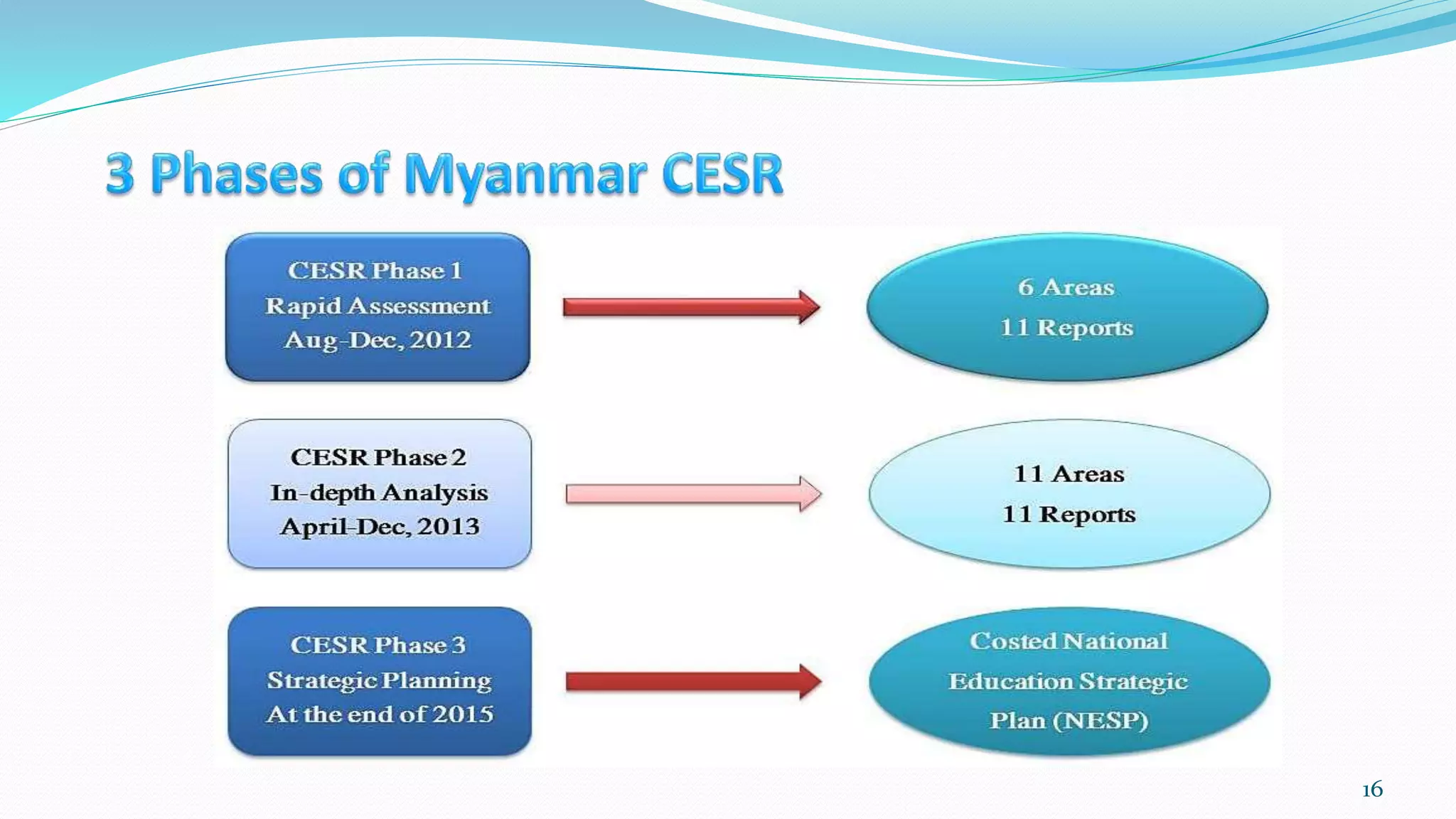
The document provides information about the education system in Myanmar. It discusses the following key points:
- Myanmar has a population of over 51 million and is located in Southeast Asia between China, India, Bangladesh, Thailand and Laos.
- The government is a democratic republic with a union government and state/regional governments. Elections are held every 5 years.
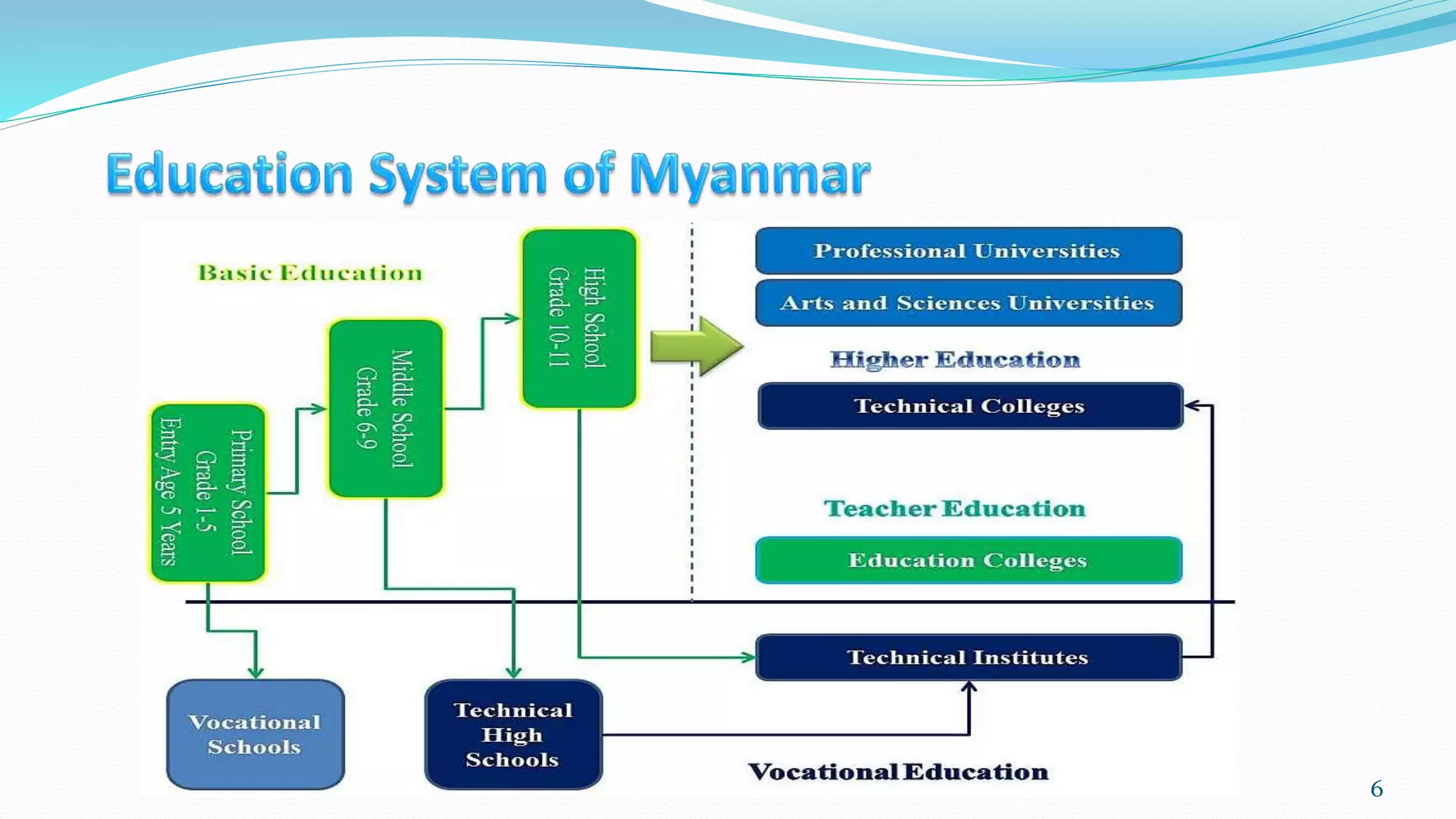
- The education system includes basic education from kindergarten through grade 12, higher education provided by 136 institutions, and vocational/technical education.
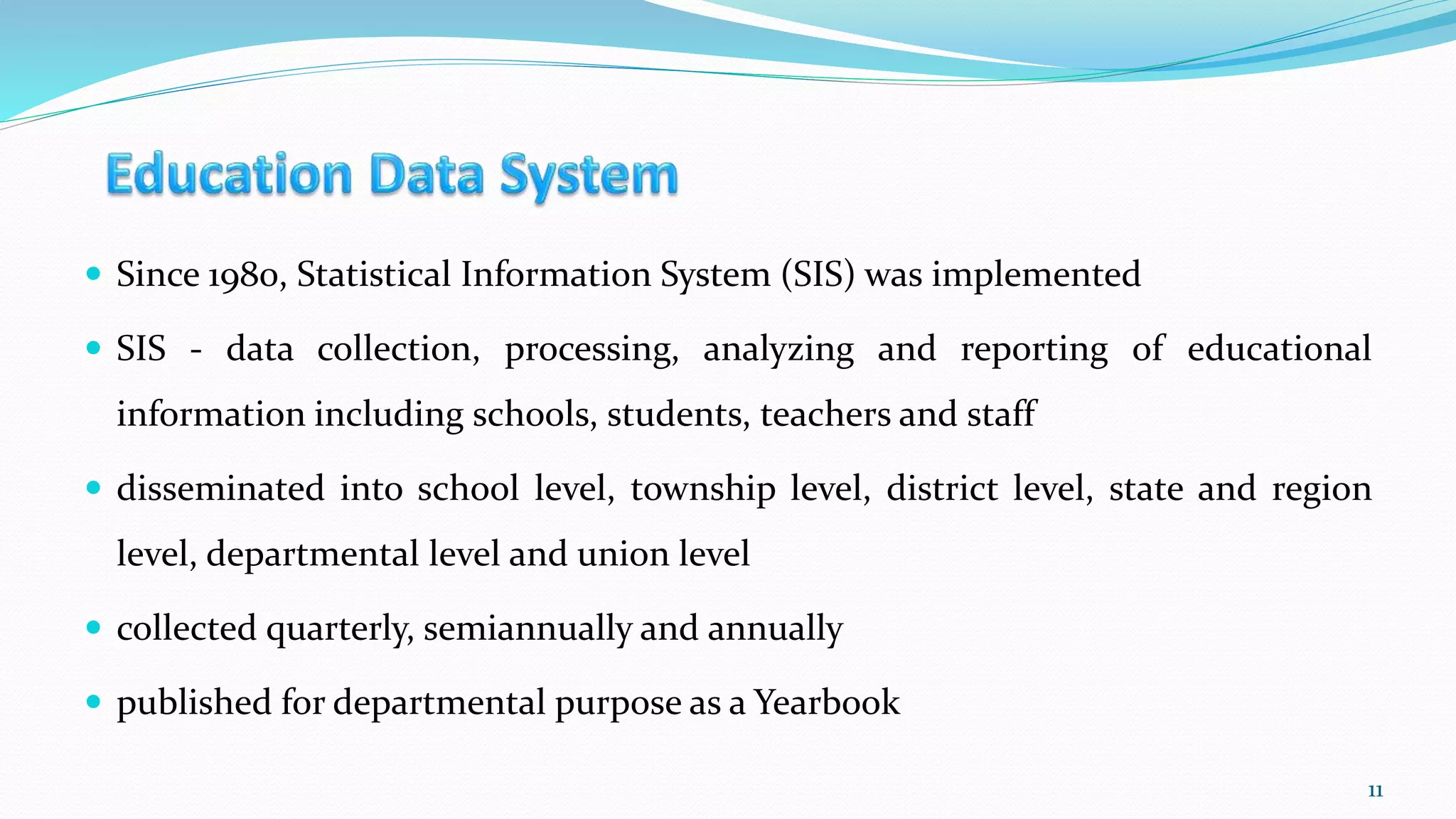
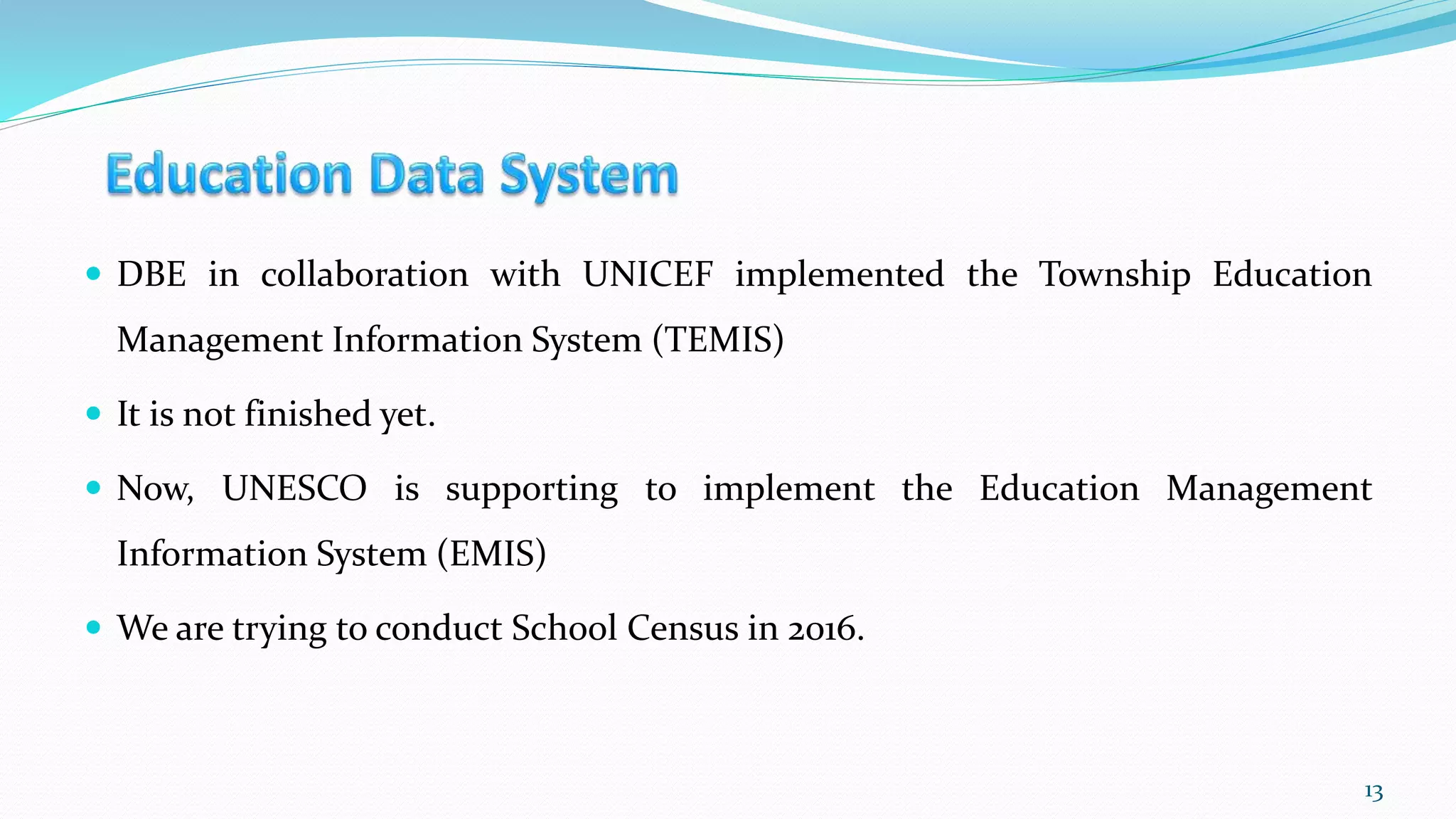
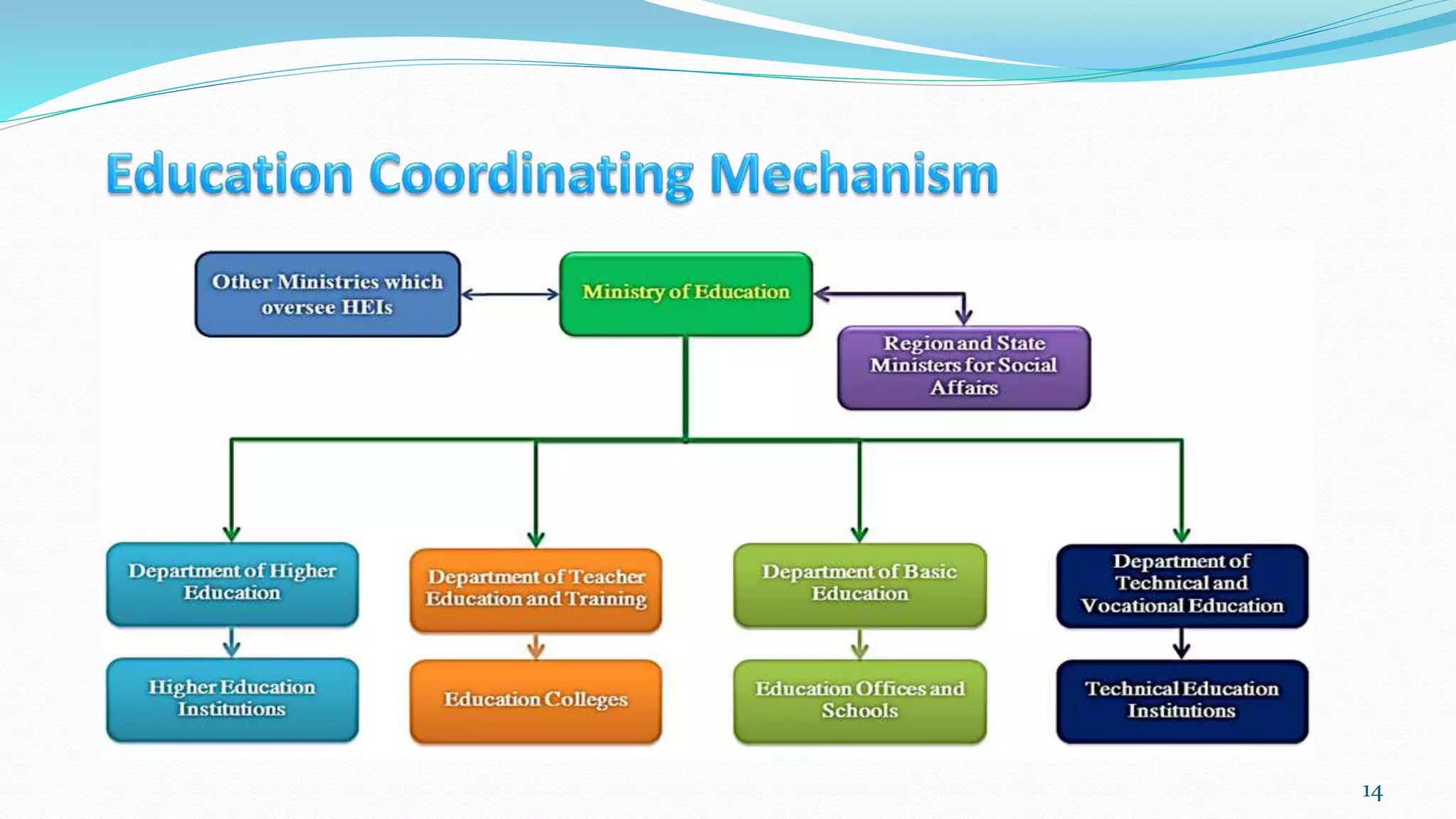
- The Ministry of Education oversees education and collects data on schools, students, teachers and staff to inform policy and planning. It is working to establish an effective Education Management Information System.