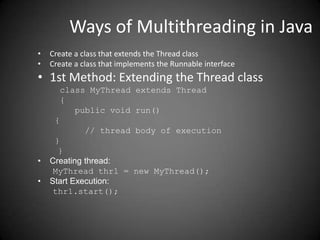
This document discusses multithreading in Java. It defines threads as pieces of code that run concurrently with other threads. It describes the life cycle of a thread as starting, running, and stopping. It also discusses how to create multithreaded programs in Java by either extending the Thread class or implementing the Runnable interface.







![class C extends Thread
{
public void run()
{
for(int k=1;k<=5;k++)
{
System.out.println("t From Thread C: k= "+k);
}
System.out.println("Exit from C");
}
}
class ThreadTest
{
public static void main(String S[])
{
new A().start();
new B().start();
new C().start();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mytheadpresentation-131116033033-phpapp01/85/Java-Multi-Thead-Programming-9-320.jpg)


![class theadrun
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
ththead f1=new ththead("one");
ththead f2=new ththead("Two");
ththead f3=new ththead("Three");
f1.t.start();
f2.t.start();
f3.t.start();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mytheadpresentation-131116033033-phpapp01/85/Java-Multi-Thead-Programming-12-320.jpg)