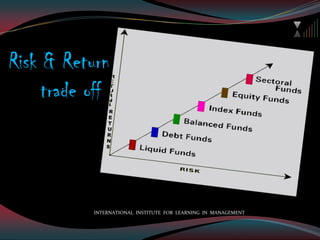
The document provides information about mutual funds in India. It defines mutual funds as a collective investment vehicle that pools money from investors to invest in stocks, bonds, and other securities. It describes the key participants in a mutual fund structure like sponsors, trustees, asset management companies, custodians, and more. It also outlines the various types of mutual funds like equity funds, debt funds, money market funds, gold ETFs, and others based on their investment objectives, asset classes, and risk-return profiles. The document emphasizes that mutual funds provide an avenue for investors to participate in financial markets through a professionally managed and diversified portfolio.

















![Good financial track recordsFinancial activities must have carried out at least last financial years.“net worth” is positive in the all immediately preceding five years.“net worth” is [fixed assets + current assets – current liabilities]Net worth of the immediately preceding year of the year of capital contribution to AMC must be more than its contribution.The sponsor must have had positive PAT[profit after tax] at least three out of immediately preceding five years.[As per chapter II of SEBI (Mutual fund) regulations Act 1996]INTERNATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR LEARNING IN MANAGEMENT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1212mutualfundshow-100826093343-phpapp01/85/mutual_fund-18-320.jpg)


![Asset ManagementCompany AMC is the face of a Mutual fund. AMC is appointed by Board of trustees to manage the fund of investors. Its issues prospectus, NFO[net fund offer, statements of offer documents [SID],invests investors money. In the market & so on behalf of Trustees. Minimum capital of an AMC is 10 core.AMC…..It’s the responsibility of AMC to appoint intermediaries, Bankers, Resister& transfer agents.It charges expenses for managing of funds which is borne by investors. maximum expenses charged is stipulated by SEBI. 50% of the directors should be independent. 75% of UNIT HOLDERS can terminate appointment of an AMC. The chair man of AMC cant be a trustee of any other AMC.INTERNATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR LEARNING IN MANAGEMENT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1212mutualfundshow-100826093343-phpapp01/85/mutual_fund-21-320.jpg)
![Distribution agent: ! Appointed by Asset management company. ! Helps to distribute mutual fund on behalf of AMC.Banker: ! Maintains all the bank accounts for all the schemes. ! Collection & Redemption of money. ! Appointed by Asset management company.Registrars & transfer agent[R&T agent]: ! It maintains accounts of each unit holder. ! Gives information regarding various circulars, NAV & so on. ! Appointed by AMC. RISK AHEAD!INTERNATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR LEARNING IN MANAGEMENT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1212mutualfundshow-100826093343-phpapp01/85/mutual_fund-22-320.jpg)




![Debt fund: fund is invested in a short term debt instruments such as Bonds, Treasury bills, Government securities, corporate debt papers etc. it is less risky than Equity funds, thus less return. since in debt instruments return is guaranteed, investors are assured of returns. “Slow but steady” --- what the investors believe in. How debt fund is priced?Debt fund is priced as per present value. Its valued based on present value of future flows of cash.Why Bond price & its interest have inverse relationship? If coupon rate[rate of interest on debt paper] is 10%Redemption value is Rs. 20000, time period for holding is 5 years.Present value?Redemption valuePV=5( 1 + rate of interest)2oooo12418.42=5(1+.10)INTERNATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR LEARNING IN MANAGEMENT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1212mutualfundshow-100826093343-phpapp01/85/mutual_fund-28-320.jpg)
![Various types of Debt fundCapital protection funds: invest equity as well as debt instruments. main objective is to protect the capital value of the investment.Fixed maturity funds: a close ended fund, invest in debt instruments whose maturity period is same as period of funds.Gilt funds: invest mainly in central Govt. securities as well as state Govt securities.Balance funds: its a hybrid fund which invests partly in equity & partly on debt instruments to hedge the risk of market volatility.Monthly income plans[MIP]: a hybrid plan which gives an option to the investors to reap monthly income.Children benefit plans: invested mainly 5 to 15 years time horizon, with minimum part invested in equity with the intension to have adequate fund needed for children’ higher education. INTERNATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR LEARNING IN MANAGEMENT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1212mutualfundshow-100826093343-phpapp01/85/mutual_fund-29-320.jpg)
![Money market fundMoney market fund is a type of fund that invests money in “money market”.Money market is a market[not necessarily a physical place, it can be a virtual place as well ] where transactions are made through cash or cash equivalent. It lasts for a maximum period of one year. It’s a well organized market that provides short term financial support . Money market fund are popularly known as “LIQUID FUND”Invests in commercial debt, treasury bills, certificate of deposits, interest rate swaps, collateralized borrowing & lending options for short period of time.The main advantage of liquid fund is its liquidity, i.e. it cant be sold & bought at any pint of time. How is it priced?If fund remains invested in money market instruments more than 182 days its valued as MARK-TO-MARKET & fund that remains invested in money market instruments for less than 182 days its valued as COST PLUS INTEREST ACCRUED METHOD. INTERNATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR LEARNING IN MANAGEMENT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1212mutualfundshow-100826093343-phpapp01/85/mutual_fund-30-320.jpg)
![MARK-TO-MARKET: a process to price fund at per the market price prevailing in the market. COST PLUS INTEREST ACCRUED METHOD:Cost price of fund is 25000, rate of interest of instruments where money invested in is 10% per month, invested for 90 days [less than 180 days]. total amount of interest is : 25000 * 10/100 *3/12 =Rs 625So interest per day will be= 625/90 = 6.944 approxPrice of fund=[cost price + days left for redemption * interest per day ]Price of fund as per the method before 60 days before redemption is [25000 + 60 * 6.944] =25416.66 before 30 days before redemption =25000+30* 6.944 =25208.32INTERNATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR LEARNING IN MANAGEMENT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1212mutualfundshow-100826093343-phpapp01/85/mutual_fund-31-320.jpg)


![Special types of Mutual fundIndex fund:a. it’s a type of equity fund invests in stocks consist of benchmark indices like, Sensex, Nifty, Bse 500 etc. b. invests in stocks in the same proportion as they have on total capitalization of index. i.e. if RELIANCE ENERGY covers 20% of SENSEX[consists of 30 shares], fund manager invests 20% of its total fund in that share. c. as and when any scrip changes in benchmark index ,fund also changes its portfolio accordingly. d. Since fund manager has very little thing to do as far as selection of shares is concerned, its known as “passively maintained fund”. Gold ETF[exchange traded fund]: 1. ETFs are like shares , which requires DMAT & TRADING a/c for trading.2. Invests in gold & gold related securities , that gives an extra leverage to investors’ portfolio.3. Each Gold ETF has underlying gold of certain quantity somewhere. Usually one G-ETF consist of 10 gram gold as underlying assets.4. ETF is issued through authorized participants(APs). INTERNATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR LEARNING IN MANAGEMENT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1212mutualfundshow-100826093343-phpapp01/85/mutual_fund-34-320.jpg)

![Net Annual Value[NAV]What is NAV?NAV is the net amount of assets of a scheme of a MF that remain invested in market.NAV is actually the value of an unit. NAV=Net assets of a schemeNumbers of outstanding unitsNet assets = market value of investment + receivables +other accrued income + other assets – payables – outstanding liabilities .open ended fund issues 1000 units @ 10 each, NAV will be Rs 10. [1000* 10/1000]Now if market value of investment becomes Rs. 6000, previously it was Rs. 2ooo.So net increase in assets is [6000-2000]= Rs 4000. now the net assets will be Rs 14000. & NAV will be Rs. 14000/1000=Rs 14 per unit. Rs 4000 {14000-10000} is unrealized capital gain.INTERNATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR LEARNING IN MANAGEMENT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1212mutualfundshow-100826093343-phpapp01/85/mutual_fund-36-320.jpg)
![Regulations of MUTUAL FUNDInvest in debt securities[Rated] issued by single issuer max. 10% of scheme’s NAV, extendable to 15% with the permission of Trustee. No bar in Govt. securities[G-SEC].Invest max. 10% of scheme’s NAV in unrated securities issued by single issuer. total investment in that securities is max. 25% of NAV.Maximum investment in a single security is 10% of NAV of the scheme.No fund, under all its schemes cant hold 10% of paid up capital.No scheme can invest in any unlisted securities of the Sponsors or its group companies.It can invest max 25% of NAV of scheme in listed securities of Sponsors or its group companies.Scheme can invest in unlisted securities of companies other than Sponsors or its group companies max. 5% of NAV in case of open ended funds & 10% of NAV in case of close ended fund.If scheme invests in other schemes of same or different AMC, no fees will be charged, aggregate inter scheme transfer cant exceed 5% of NAV. INTERNATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR LEARNING IN MANAGEMENT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1212mutualfundshow-100826093343-phpapp01/85/mutual_fund-37-320.jpg)
![Various investment plansSystematic investment plans[SIP] 1.a plan of investment where same amount of money in each month is invested in buying MF unit as per the choice of investors. 2.the main advantage of SIP is average out the cost of investment. 3. SIP is generally made for meeting some particular goal of an investor. 4.investors buy more units when NAV of any fund is low[in Bear market] & vice-versa [in Bull market]with same amount of money that they invest in every month.INTERNATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR LEARNING IN MANAGEMENT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1212mutualfundshow-100826093343-phpapp01/85/mutual_fund-38-320.jpg)
