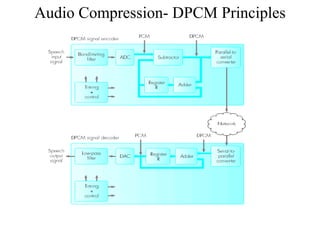
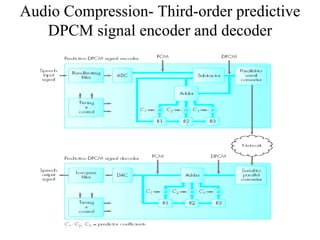
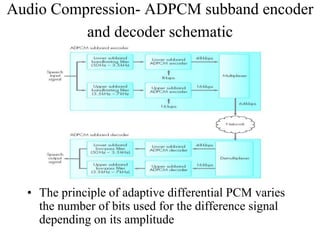
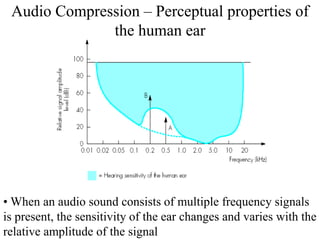
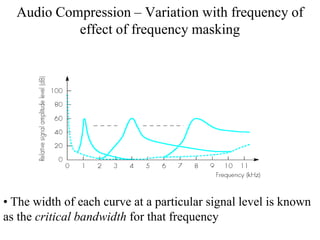
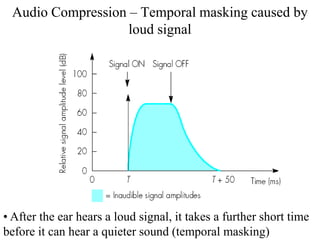
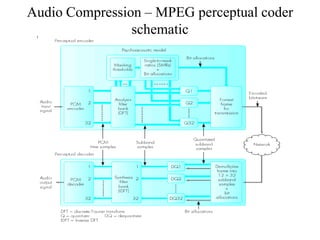
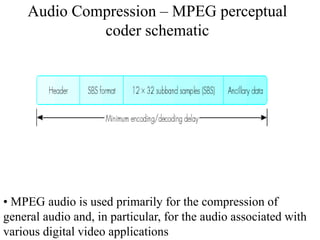
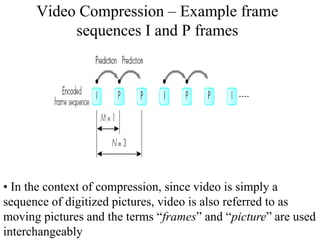
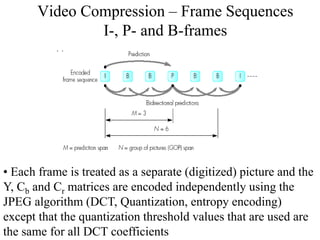
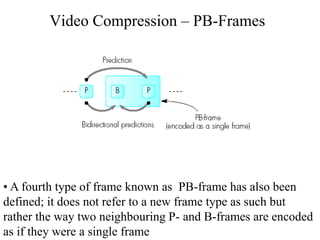
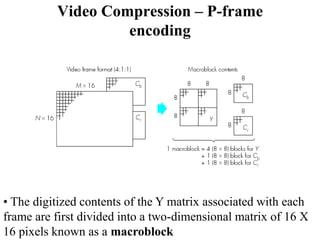
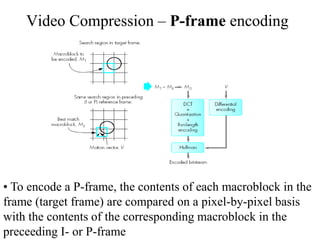
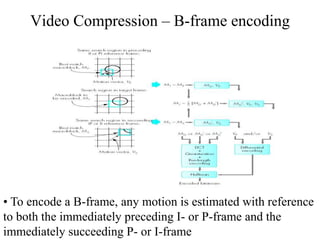
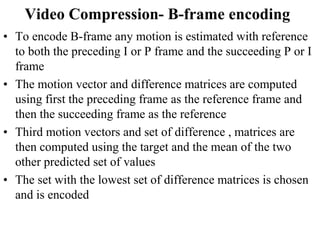
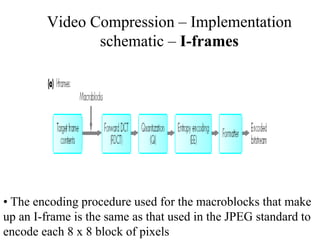
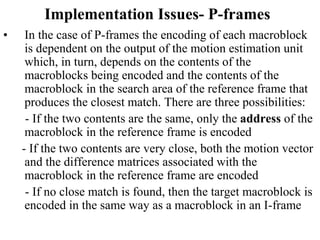
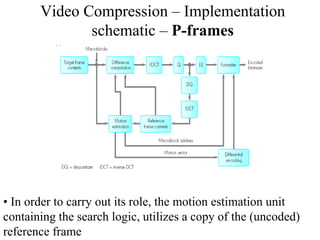
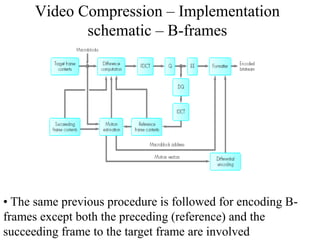
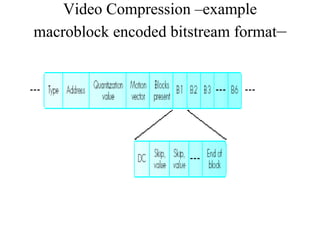
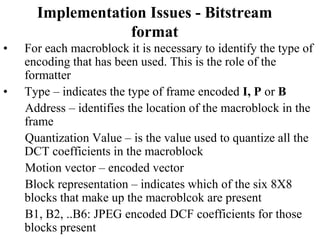
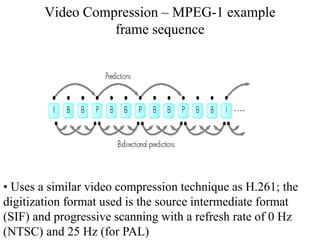
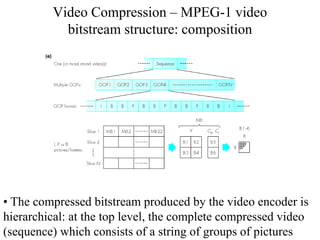
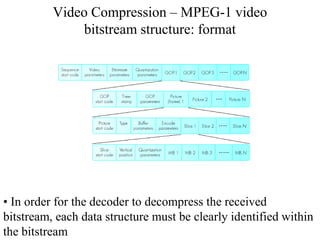
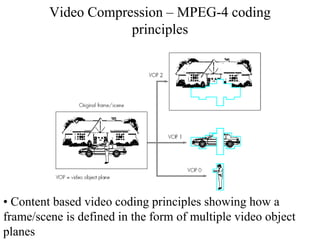
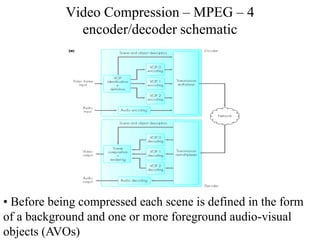
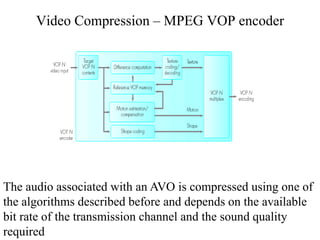
DPCM and ADPCM are audio compression techniques that exploit the fact that differences between successive audio samples are typically smaller than the sample amplitudes. DPCM encodes differences between original and predicted samples while ADPCM varies the number of bits used based on difference size. Higher compression can be achieved through predictive coding and linear predictive coding, which analyze audio to determine perceptual features like pitch, period, and loudness for encoding. Perceptual coding considers how the human ear perceives sound by exploiting frequency and temporal masking effects.