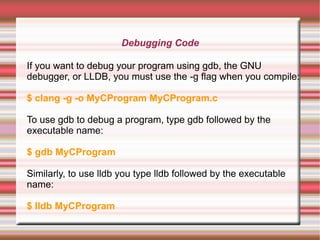
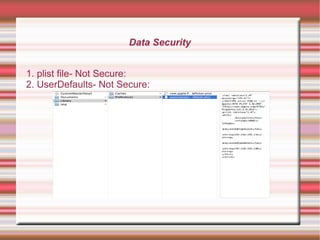
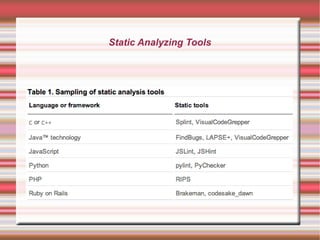
This 4-day training course covers iOS application development and security. Day 1 introduces iOS, Objective-C, and setting up development environments. Day 2 covers native, web, and hybrid mobile app types and the app development process. Day 3 discusses debugging, app store publishing, and iOS technologies. Day 4 focuses on application security best practices including data security, keychain usage, and penetration testing tools and techniques.

















![First Example Program (main.m)
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
int main (int argc, const char * argv[])
{
NSAutoreleasePool * pool = [[NSAutoreleasePool alloc] init];
NSLog (@"Programming is fun!");
[pool drain];
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/msriostraining-140115234846-phpapp01/85/MSR-iOS-Tranining-24-320.jpg)