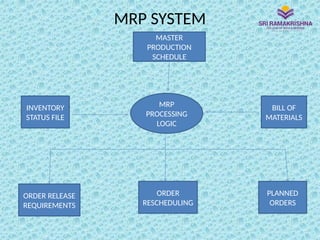
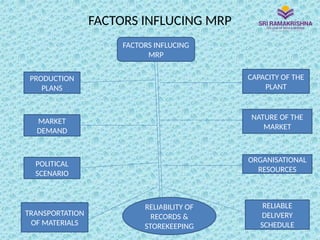
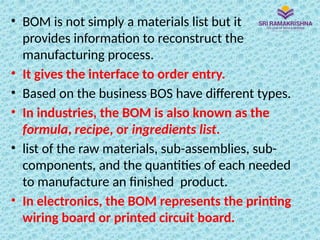
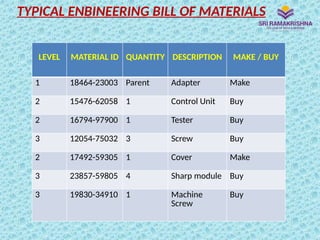
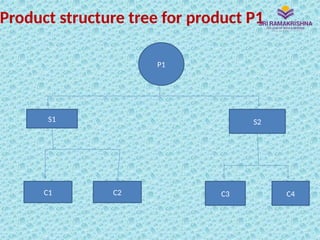
Material Requirements Planning (MRP) is a scientific technique for managing inventories, helping optimize manufacturing control by determining the quantity and timing of material requirements. It aims to reduce inventory and lead times while improving operational efficiency, but relies heavily on data integrity for accurate outputs. Issues such as incorrect data can lead to significant challenges in implementation and operation, particularly for manufacturers with complex product designs or multiple locations.