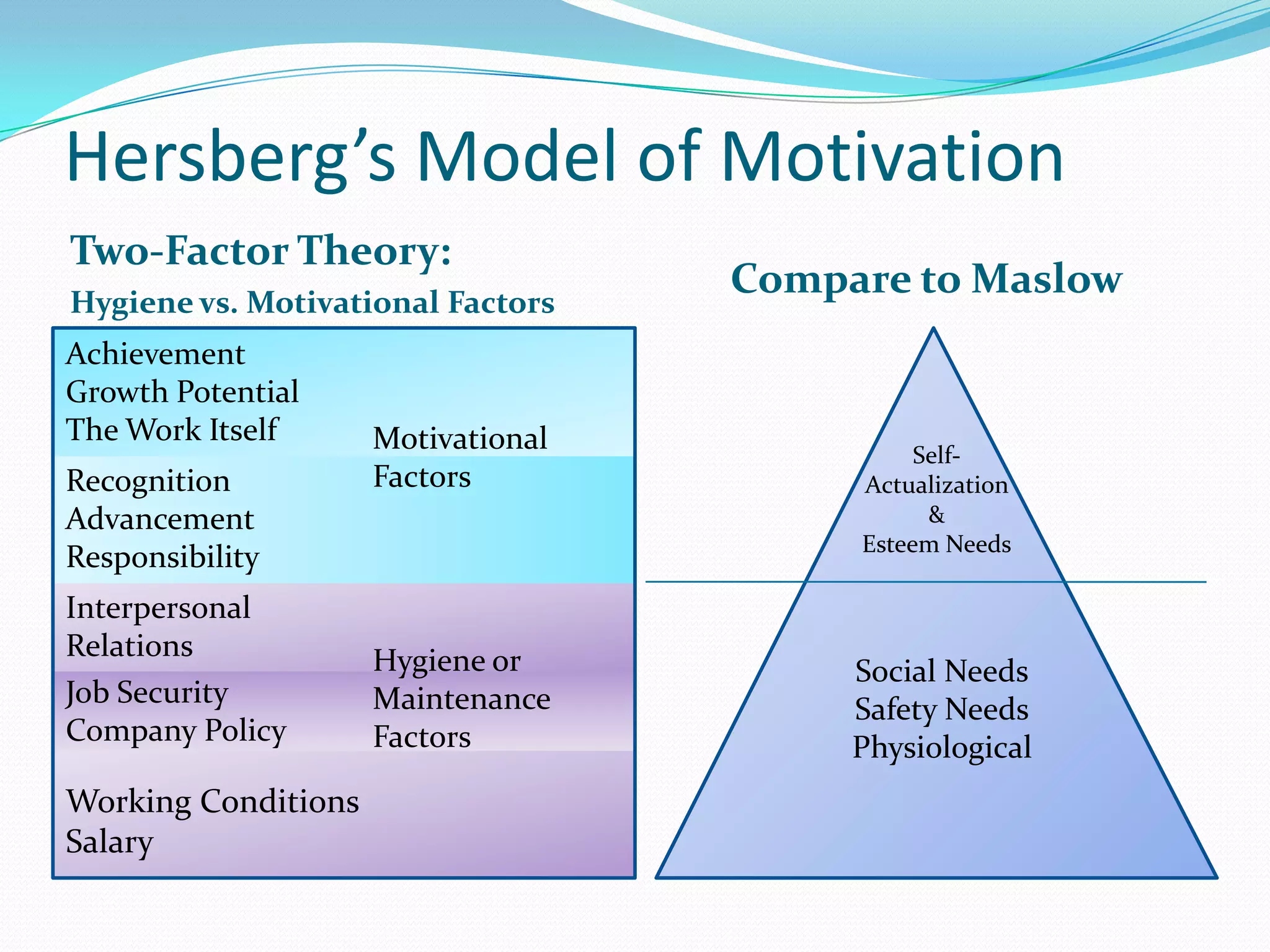
The document discusses motivation in the workplace. It defines motivation as the internal drive to accomplish goals. It then outlines several theories of motivation, including Maslow's hierarchy of needs and Herzberg's two-factor theory, and discusses factors workplaces can address to meet different needs, like physical comfort, job security, relationships, and opportunities for growth. It also covers contemporary motivational strategies like job design, incentives, and empowerment.