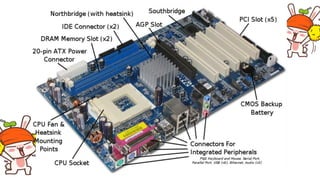
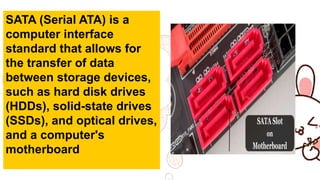
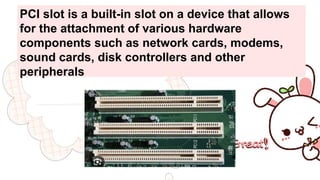
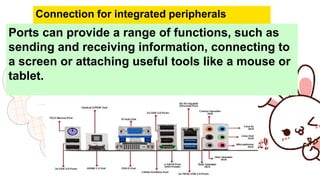
A motherboard connects all the crucial components of a computer system. It contains sockets and slots for the CPU, RAM, graphics card, storage drives, expansion cards, and ports. Key components include the CPU socket, DIMM slots for RAM, power connection, CPU fan socket, IDE and SATA ports for storage, PCI and PCIe slots for expansion cards, chipset components like the northbridge and southbridge, CMOS battery, and BIOS chip. The motherboard allows communication between these internal components and external peripherals.