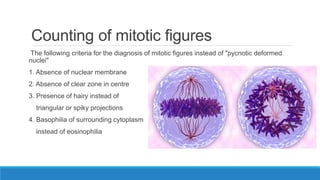
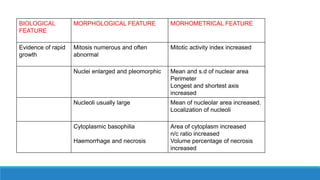
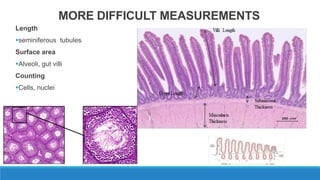
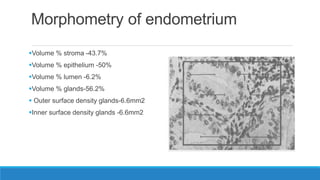
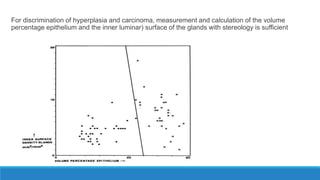
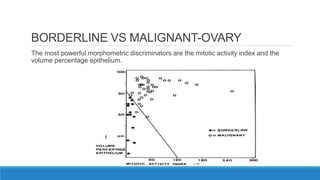
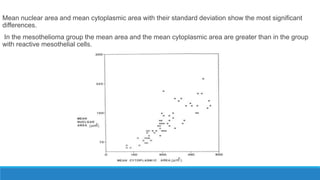
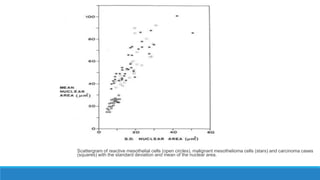
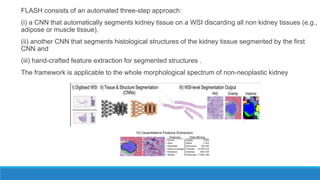
Morphometry involves obtaining quantitative information about biological tissue structures through measurements of their size, shape, and other metrics. It provides objective criteria that can improve reproducibility in histopathology. Key applications include tumor classification, diagnostic accuracy, and distinguishing conditions like hyperplasia vs carcinoma. Techniques include planimetry, point counting, pixel counting in digital images. Morphometry of features like nuclear size and shape correlates with biological behaviors and can aid diagnosis of conditions like endometrial hyperplasia vs cancer or malignant mesothelioma. Next-generation techniques continue advancing this quantitative approach.