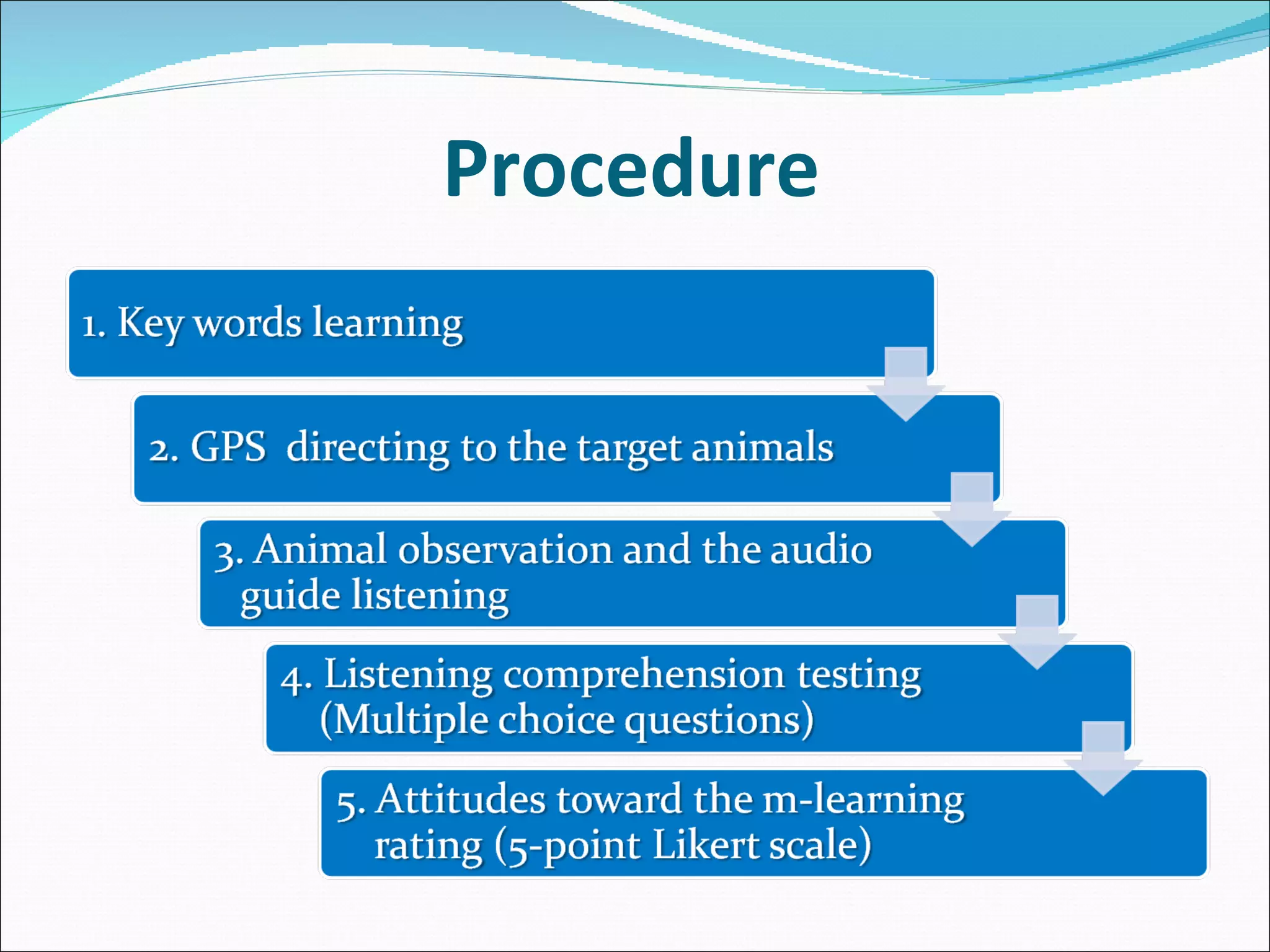
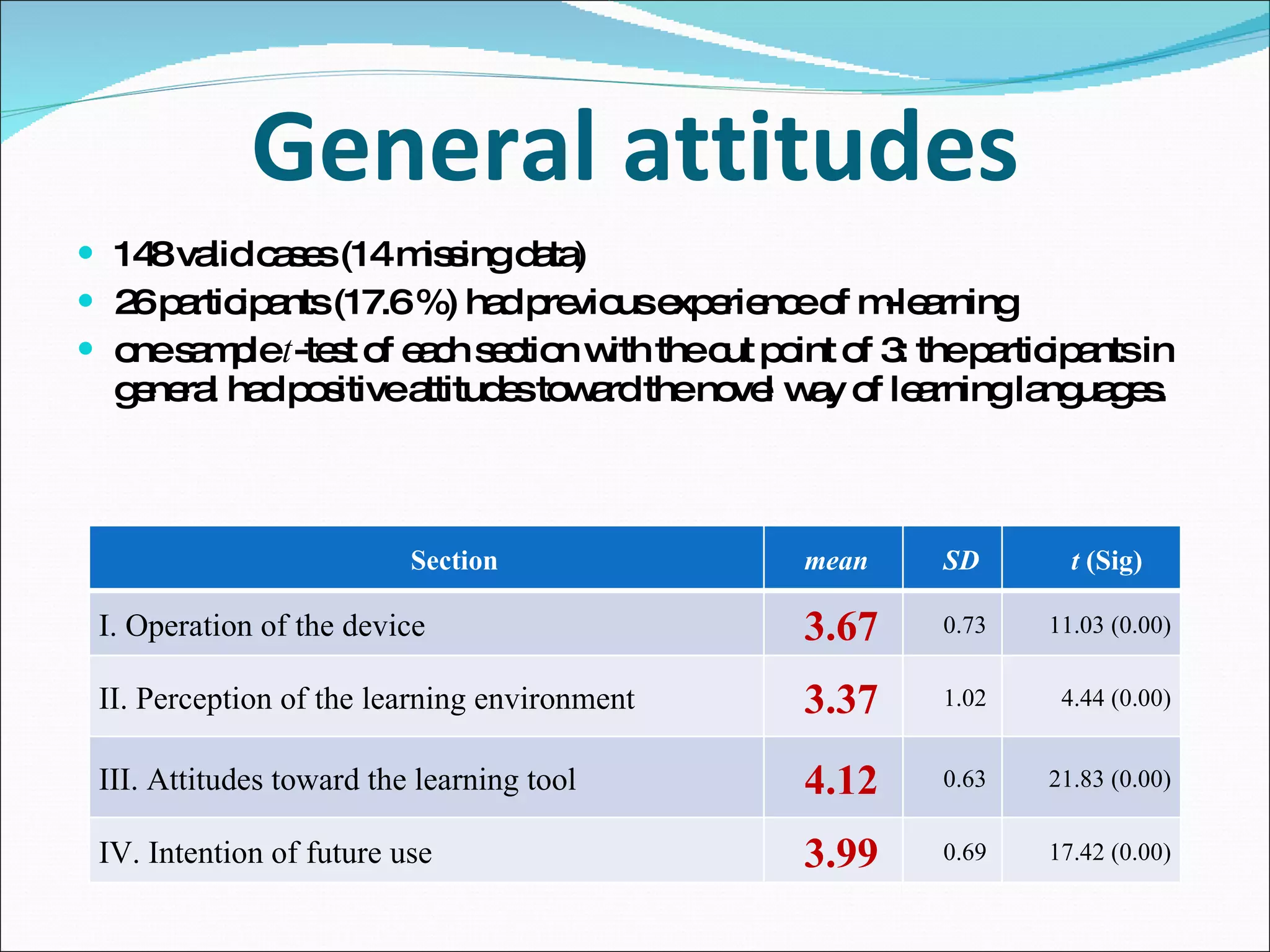
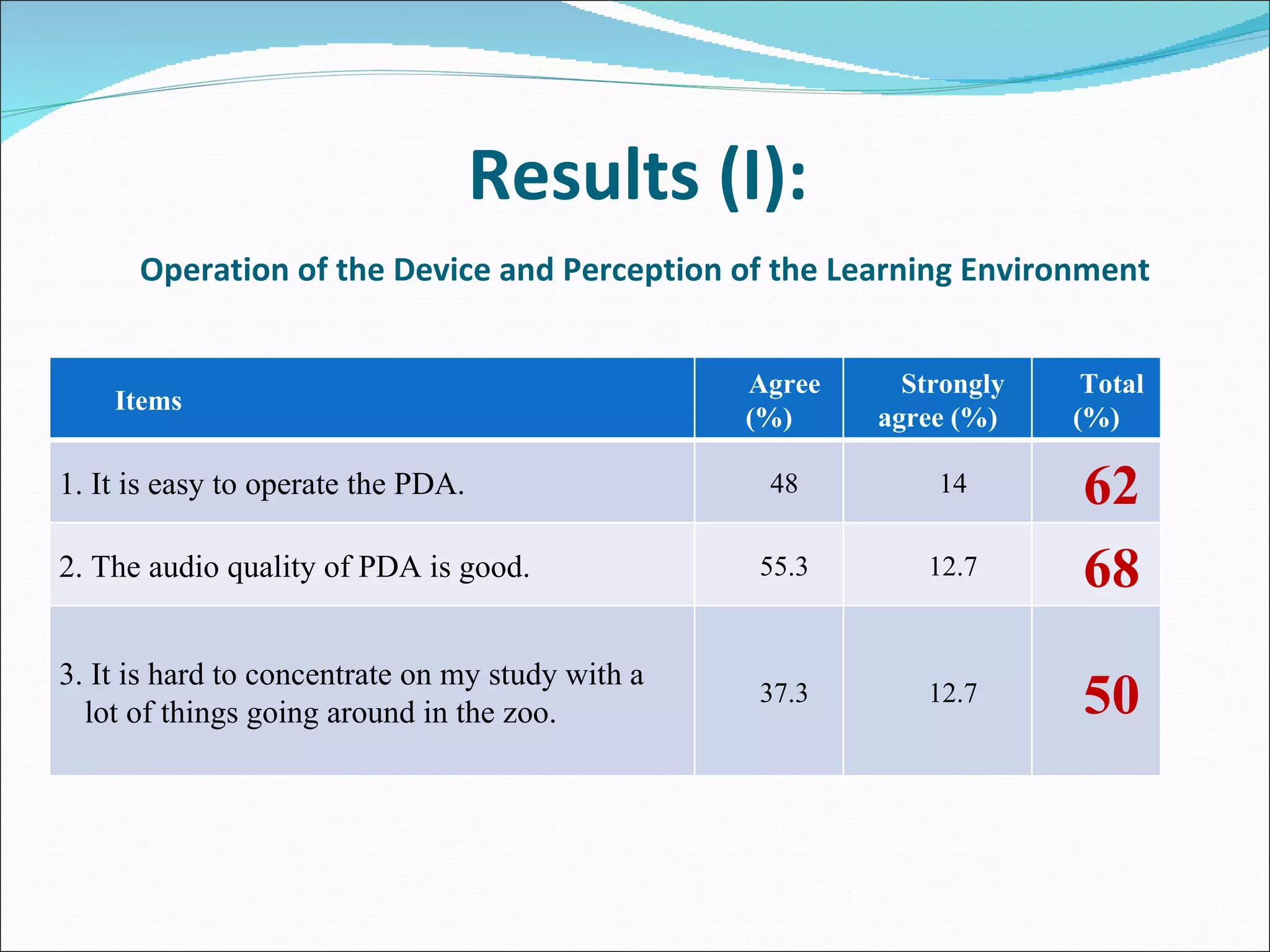
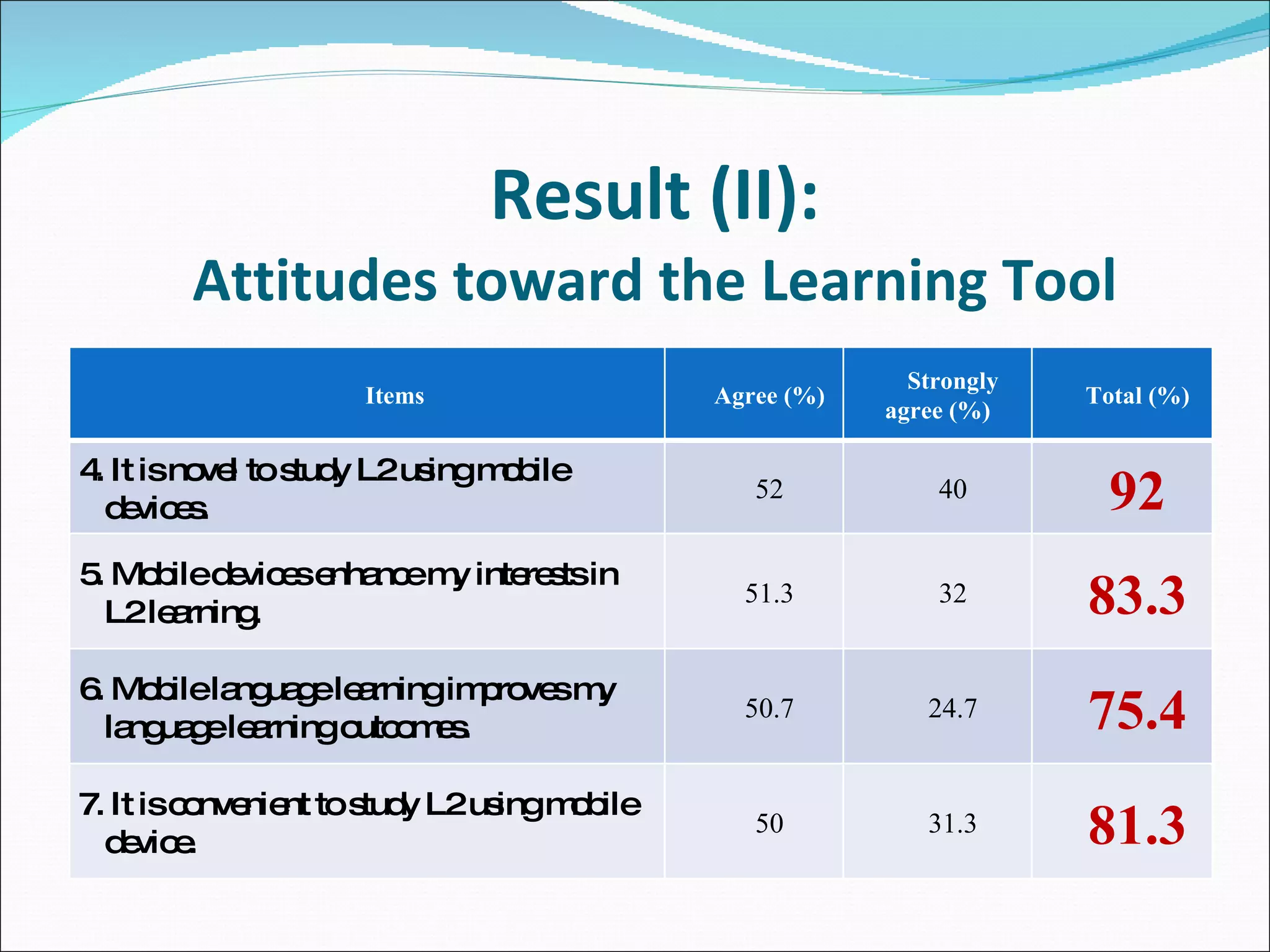
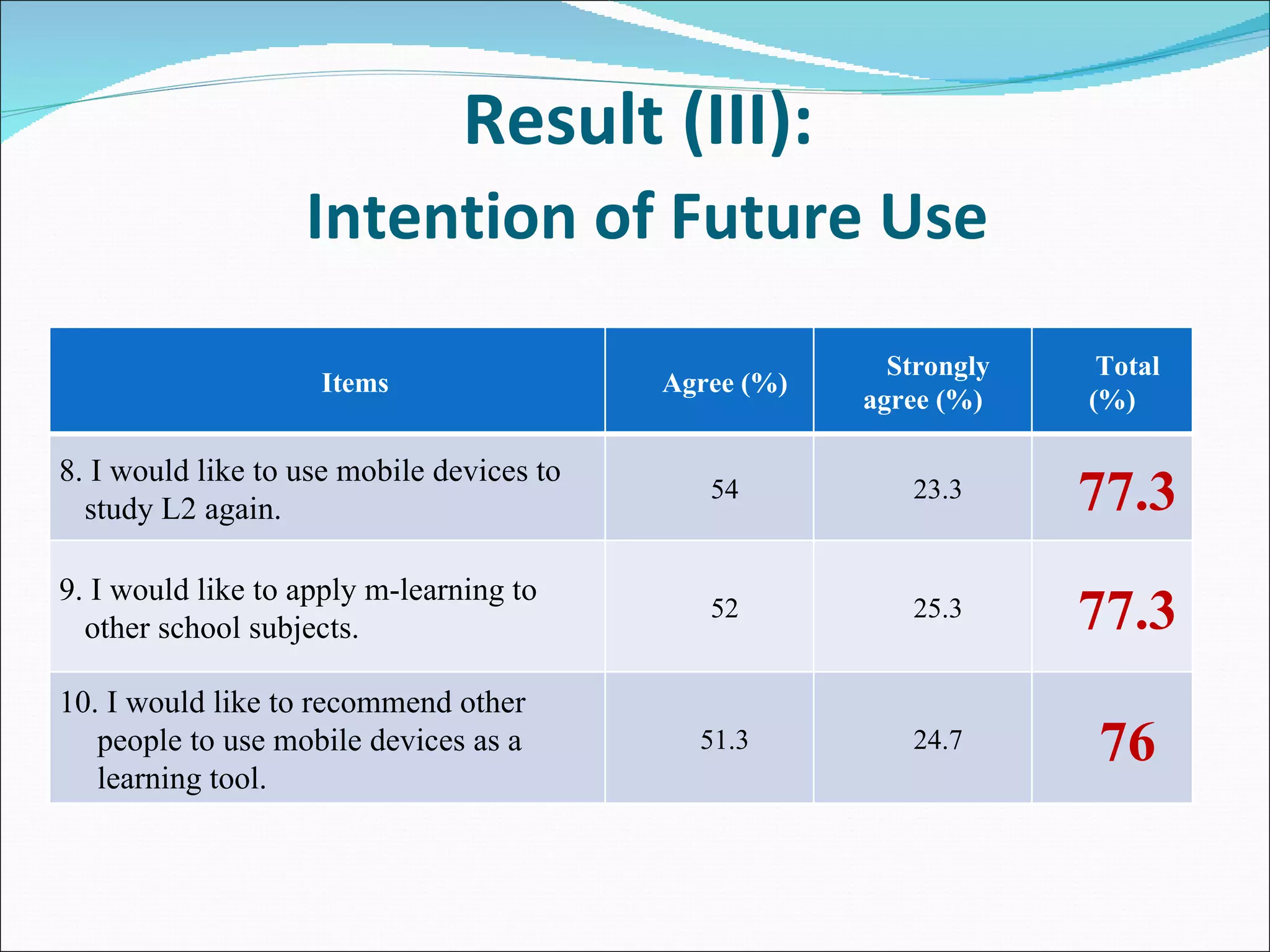
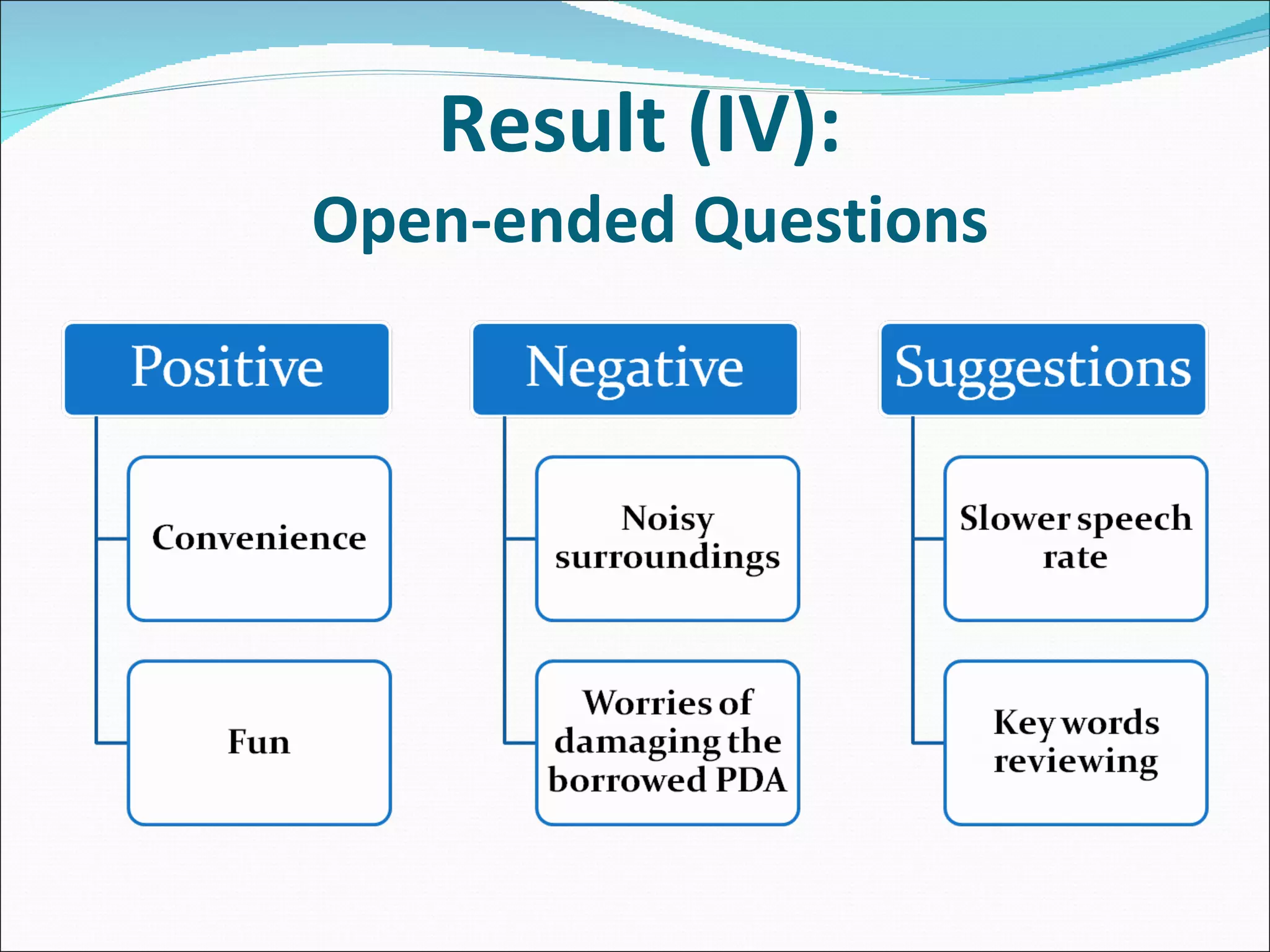
The document summarizes a study that used mobile devices to improve English listening comprehension for 162 university students in Taiwan. Students listened to 4 audio passages on animal guides using PDAs. A survey found students had positive attitudes toward mobile learning and the interface was easy to use. Results showed mobile devices enhanced interest in language learning and improved outcomes. Students wanted to use mobile learning for other subjects and recommend it to others. The study concluded mobile assisted language learning can provide meaningful and motivating learning when integrated with appropriate instructional design and strategies. Further research in different contexts was suggested.
![Chi-Cheng Chang 張基成 I-Jung Chen 陳怡容 , [email_address] Gina Wen-Chun Chen 陳玟君 UbiLearn 2010, April 12, Kaohsiung, Taiwan](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/morethanjustaudioguide-100412060202-phpapp02/75/More-Than-Just-Audio-Guide-1-2048.jpg)