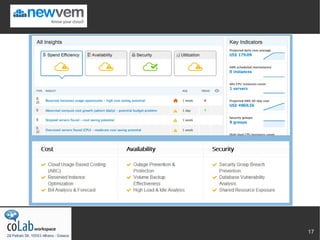
The document discusses the importance of monitoring cloud-hosted applications to manage availability and performance risks, emphasizing the need for proactive detection of issues, alerts, and data collection. It outlines various types of monitoring tools and techniques, including application, server, and end-user monitoring, as well as the significance of log aggregation and cloud analytics. The document also highlights the evolution towards holistic monitoring solutions that integrate multiple monitoring levels and the pitfalls of relying solely on custom application logging.