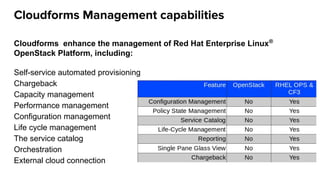
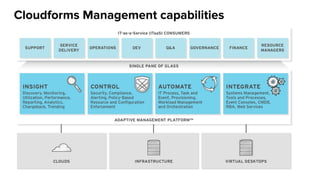
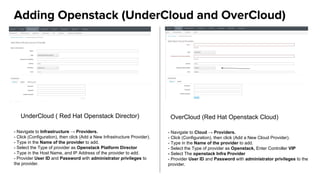
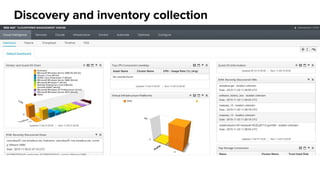
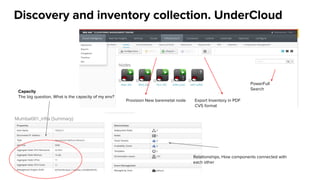
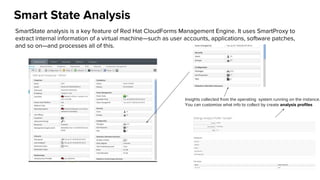
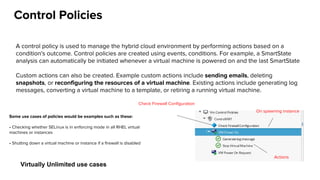
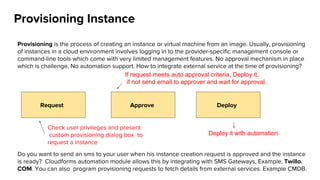
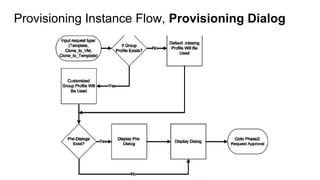
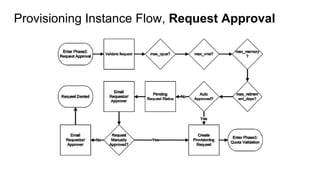
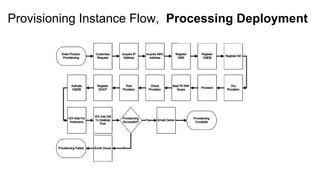
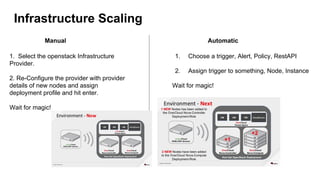
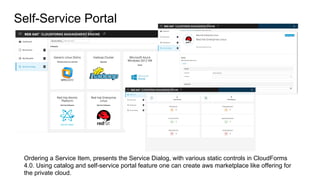
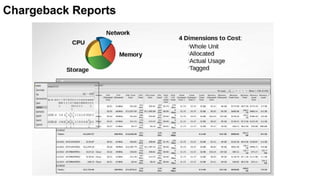
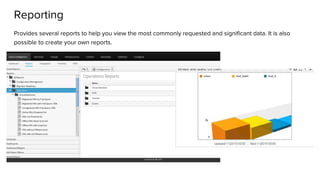
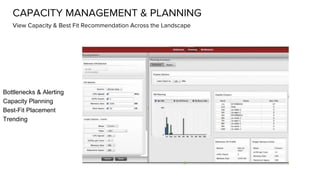
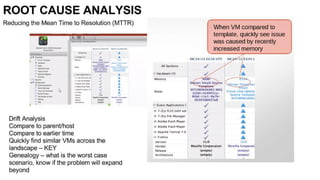
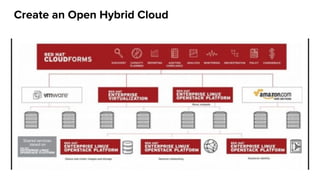
The document discusses OpenStack management and automation using CloudForms 4.0, highlighting its capabilities in provisioning, management, and compliance for cloud infrastructure. It addresses various challenges of OpenStack management, such as user control, capacity planning, and compliance enforcement, and outlines features like automated provisioning, smart state analysis, and policy management. CloudForms integrates with Red Hat OpenStack, providing tools for service catalog creation, reporting, and infrastructure scaling, enabling efficient cloud resource management.