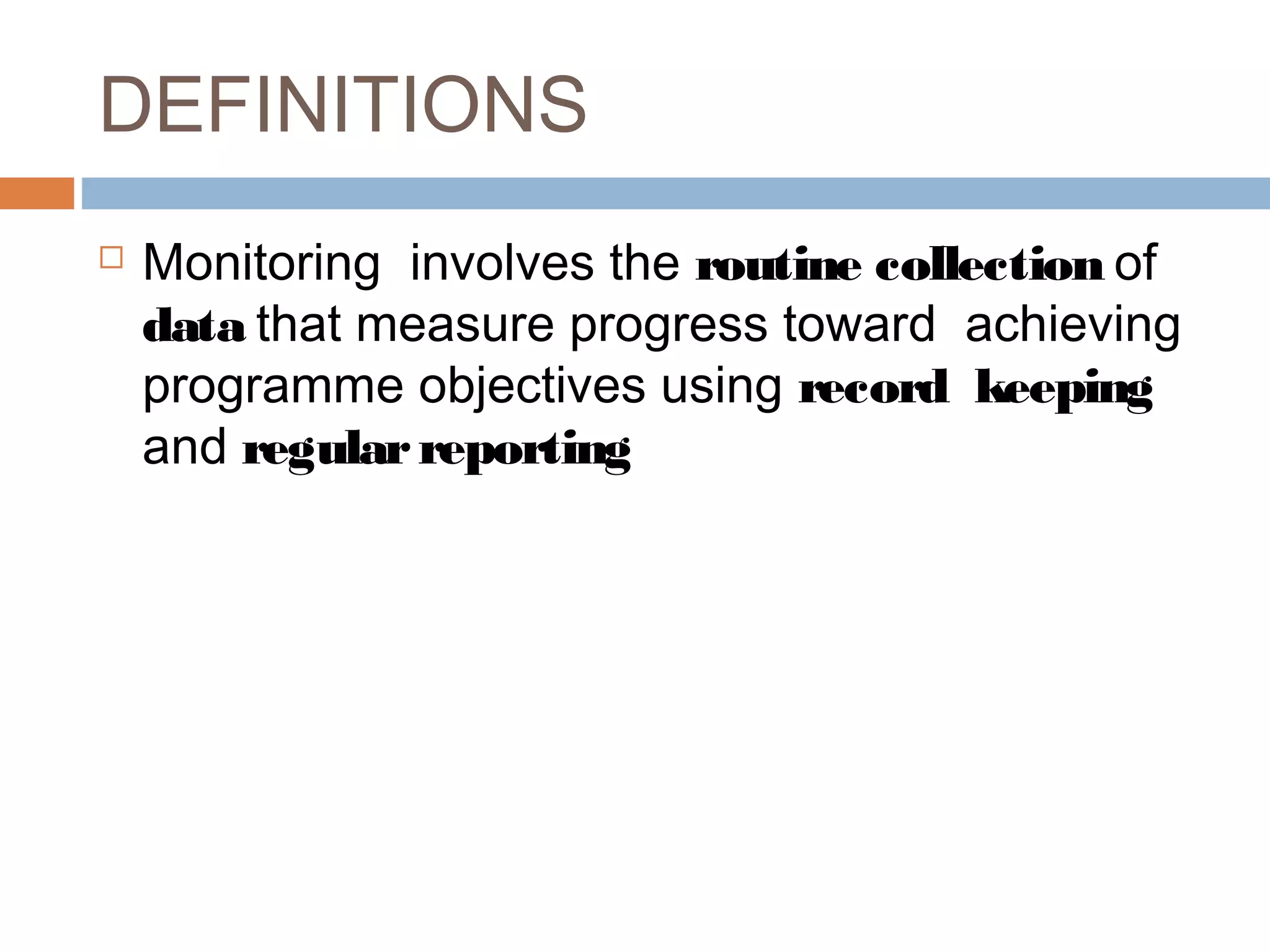
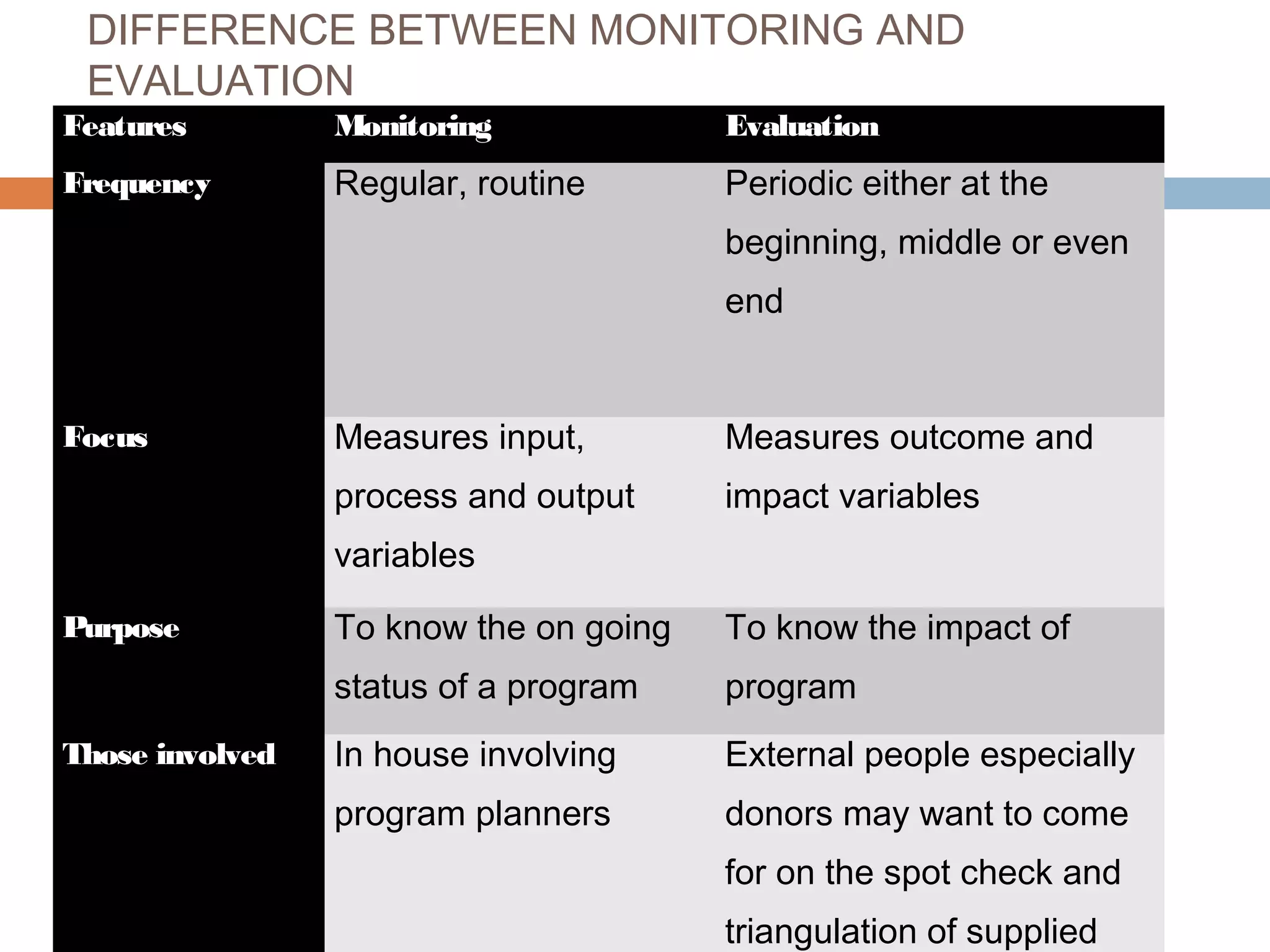
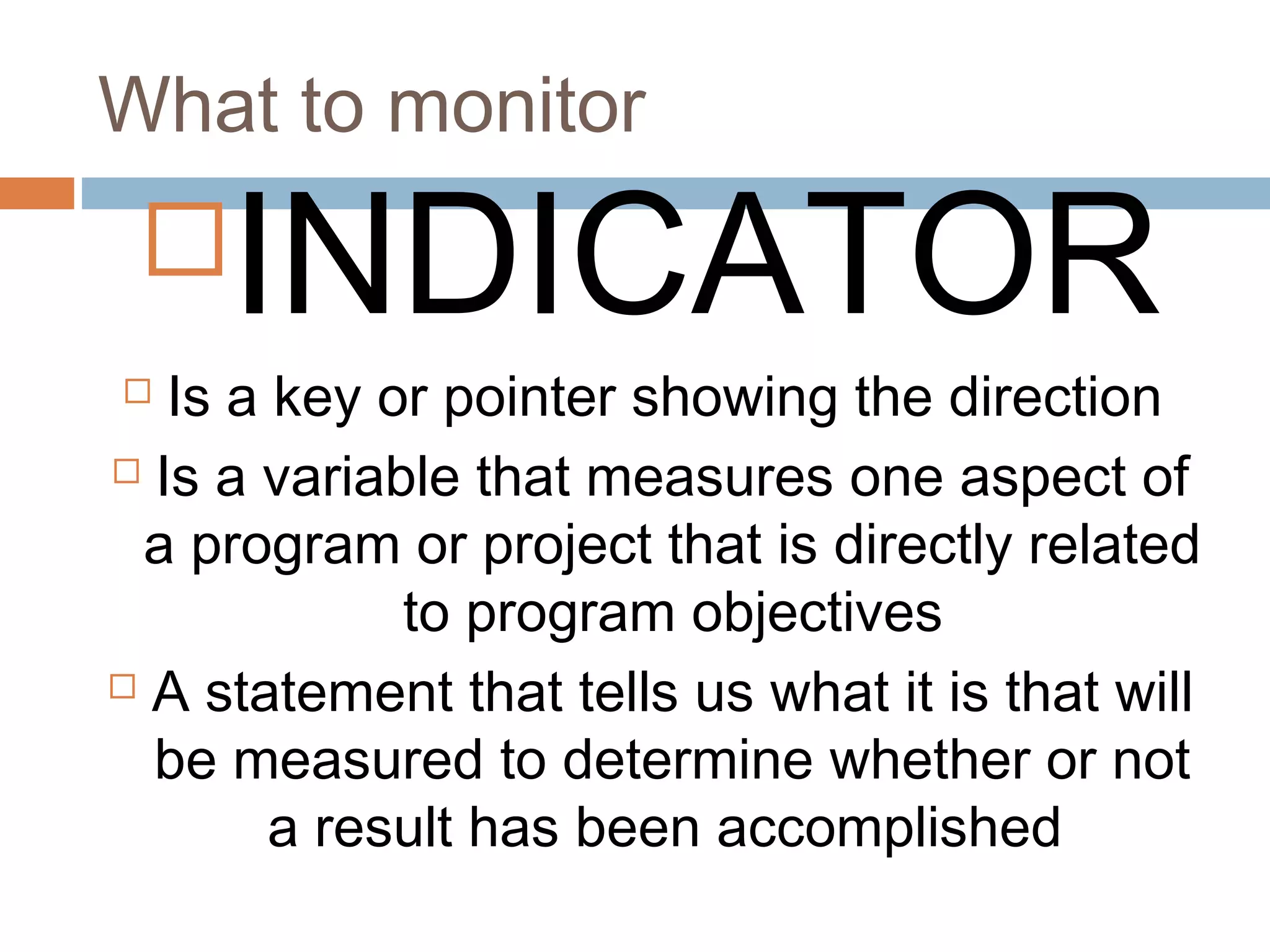
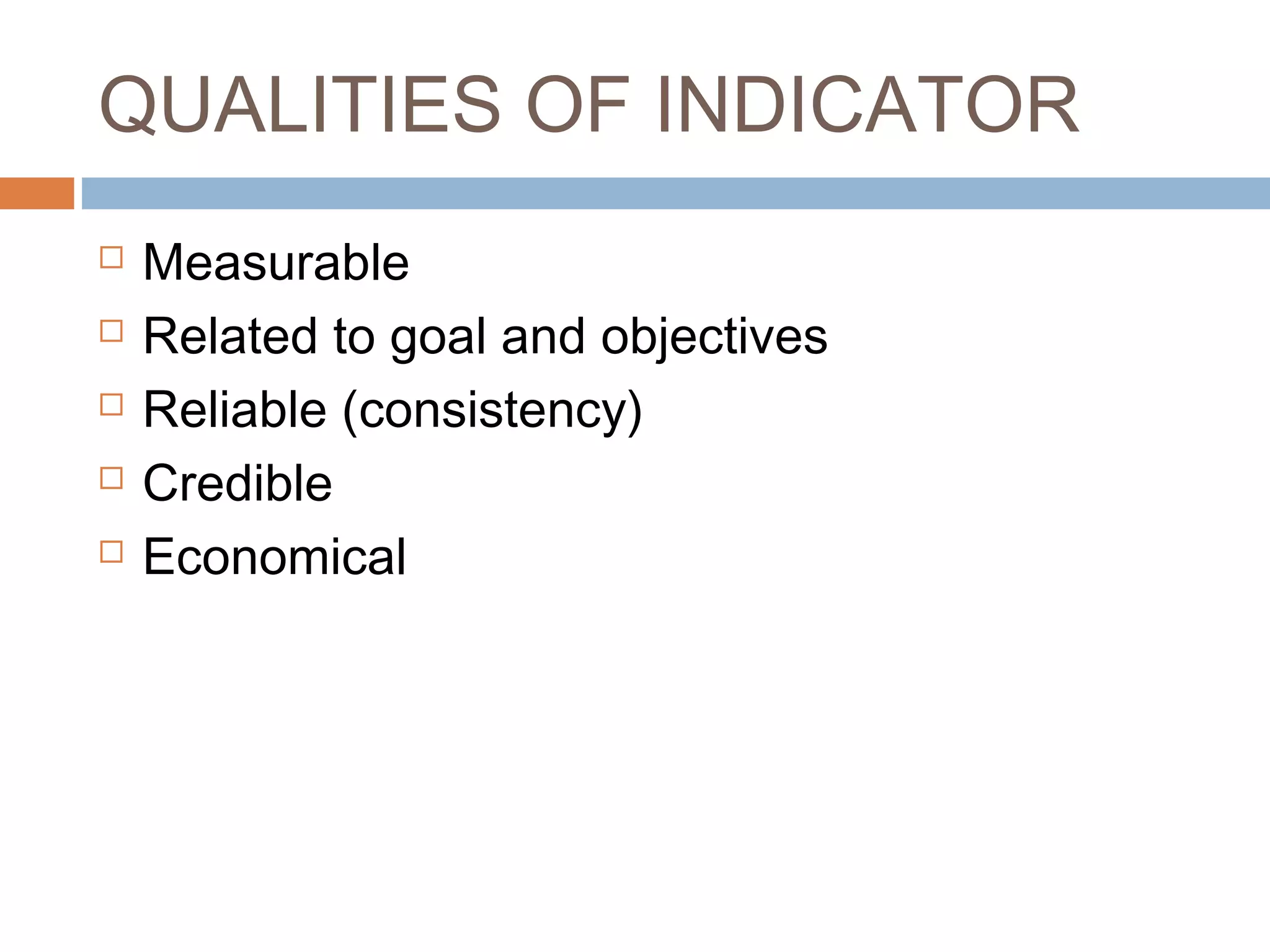
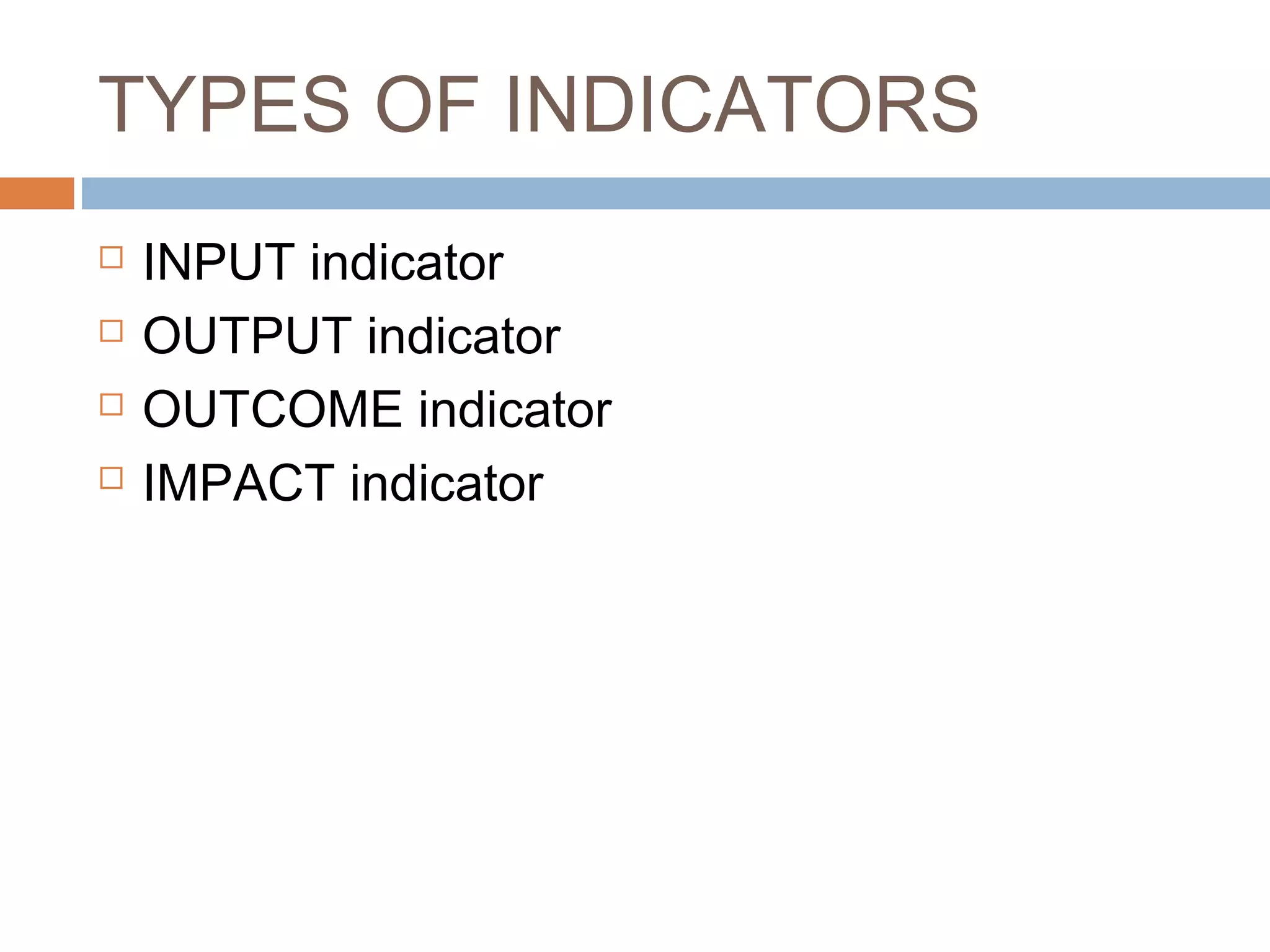
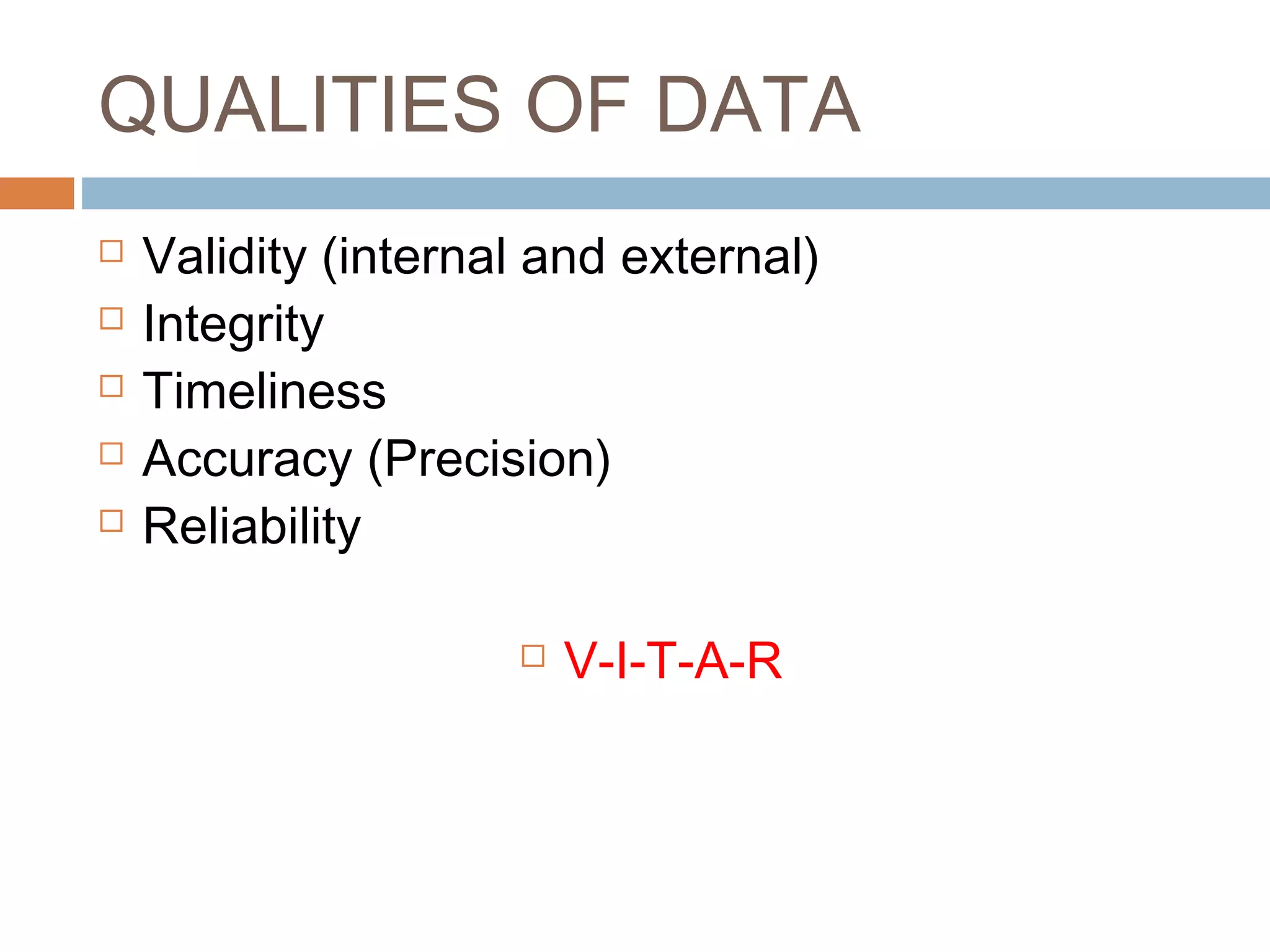
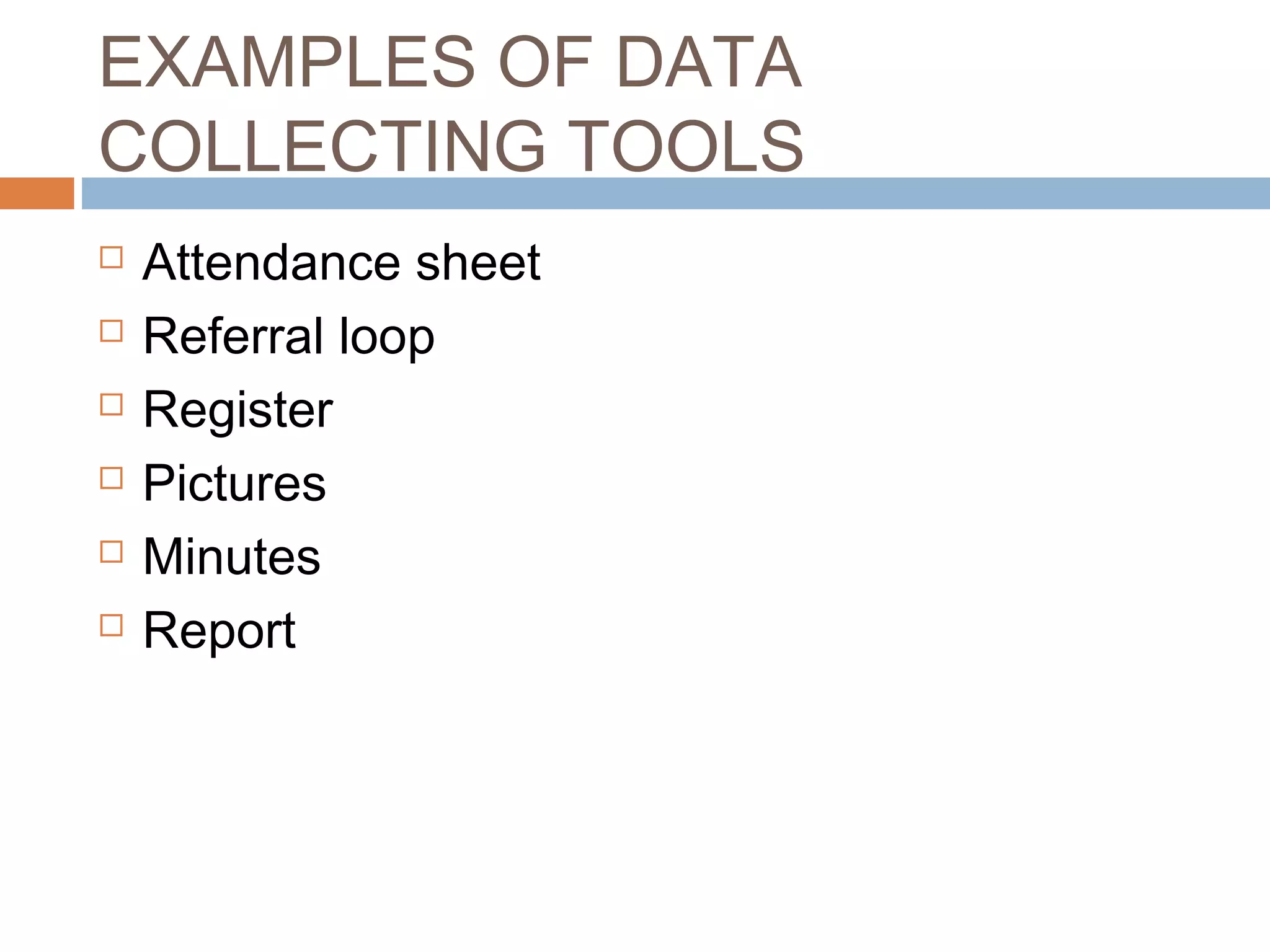
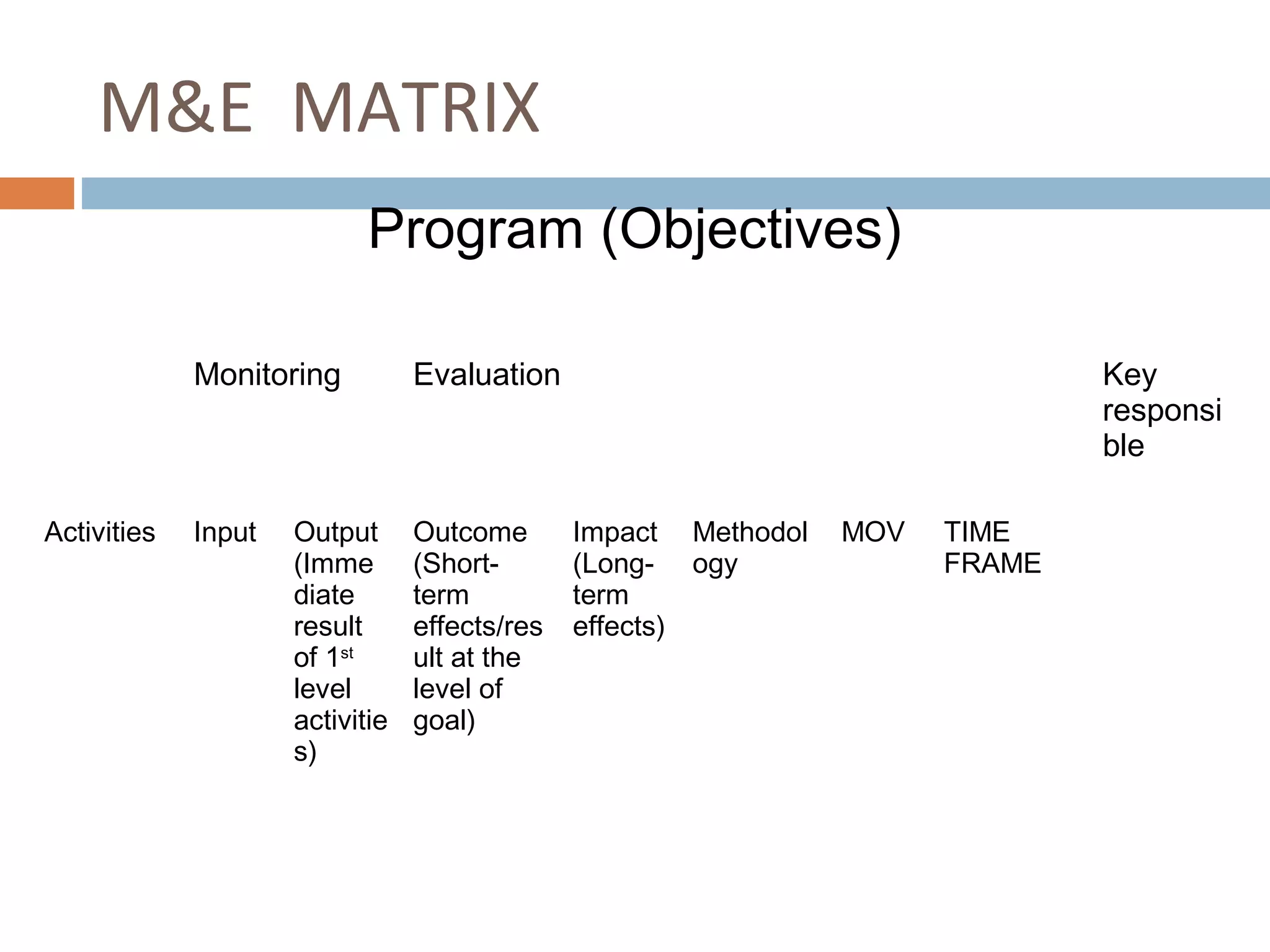
Monitoring and evaluation (M&E) involves collecting data on a regular basis to measure progress towards objectives. Evaluation determines the value of a program by measuring whether planned outcomes and impacts are achieved. The key difference between monitoring and evaluation is that monitoring is a regular, routine collection of input, process and output data, while evaluation is a periodic assessment of outcome and impact that can involve external evaluators. Developing a strong M&E plan is important to make informed decisions, ensure efficient use of resources, and determine if a program's objectives are being met.