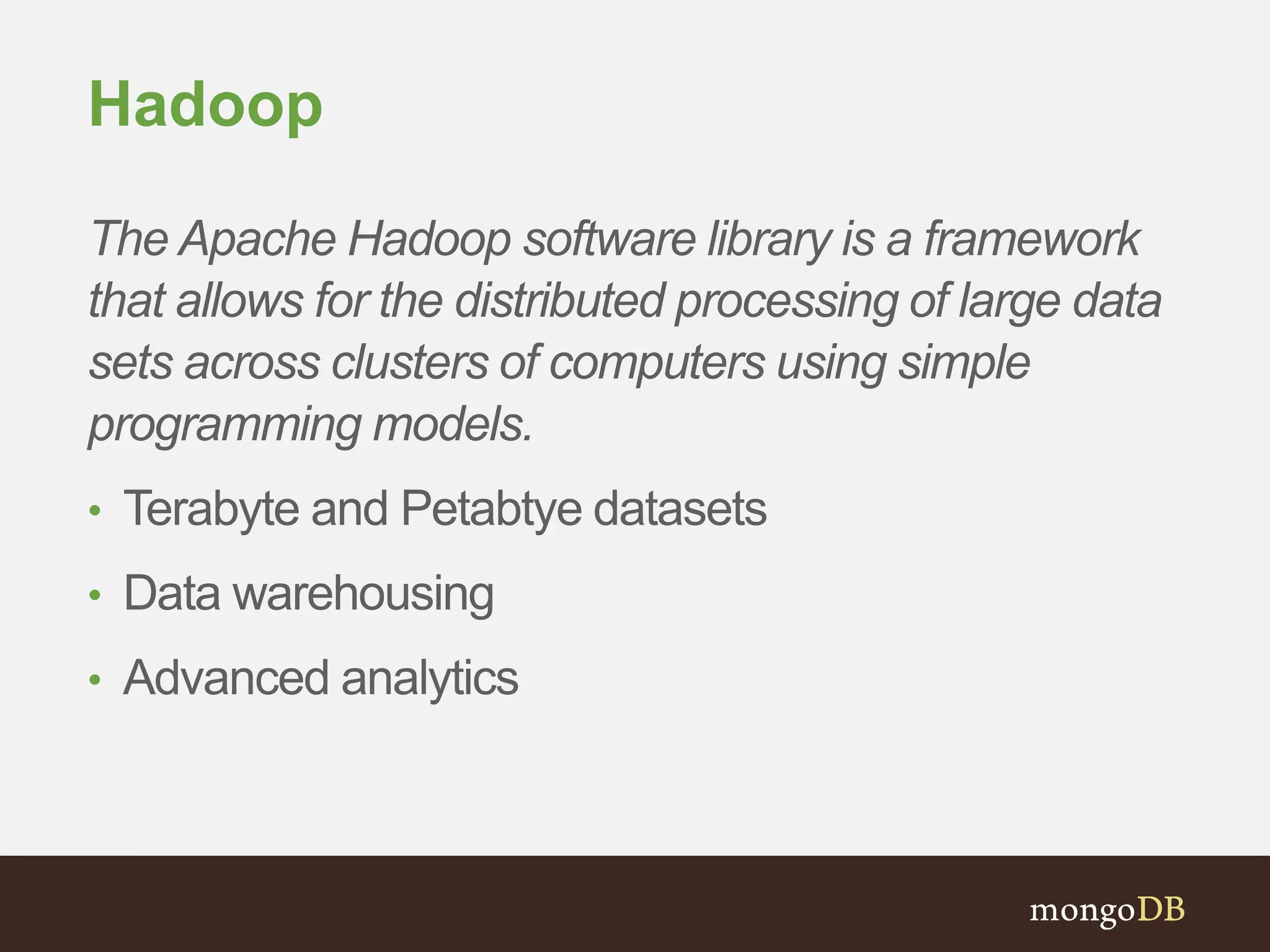
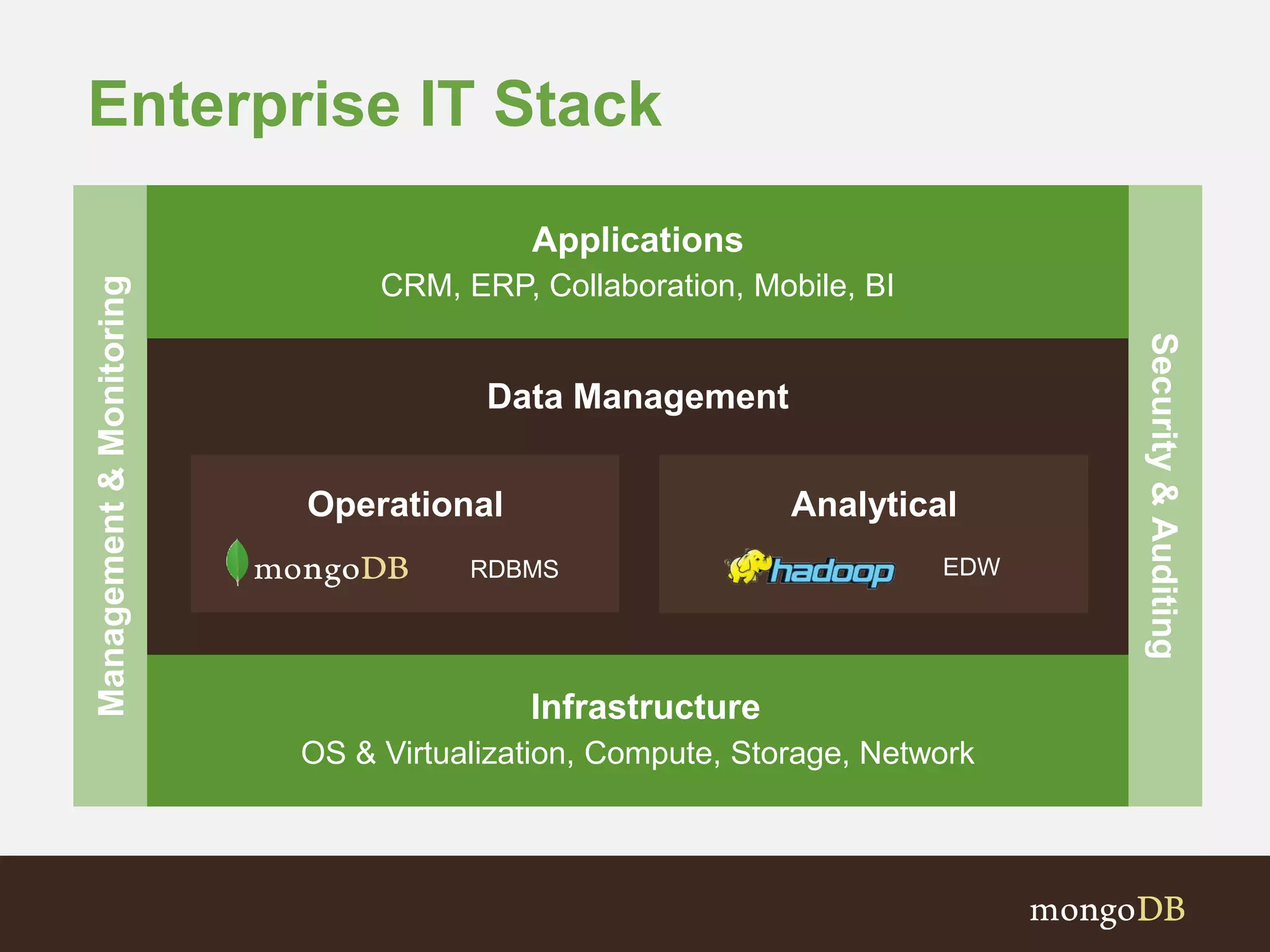
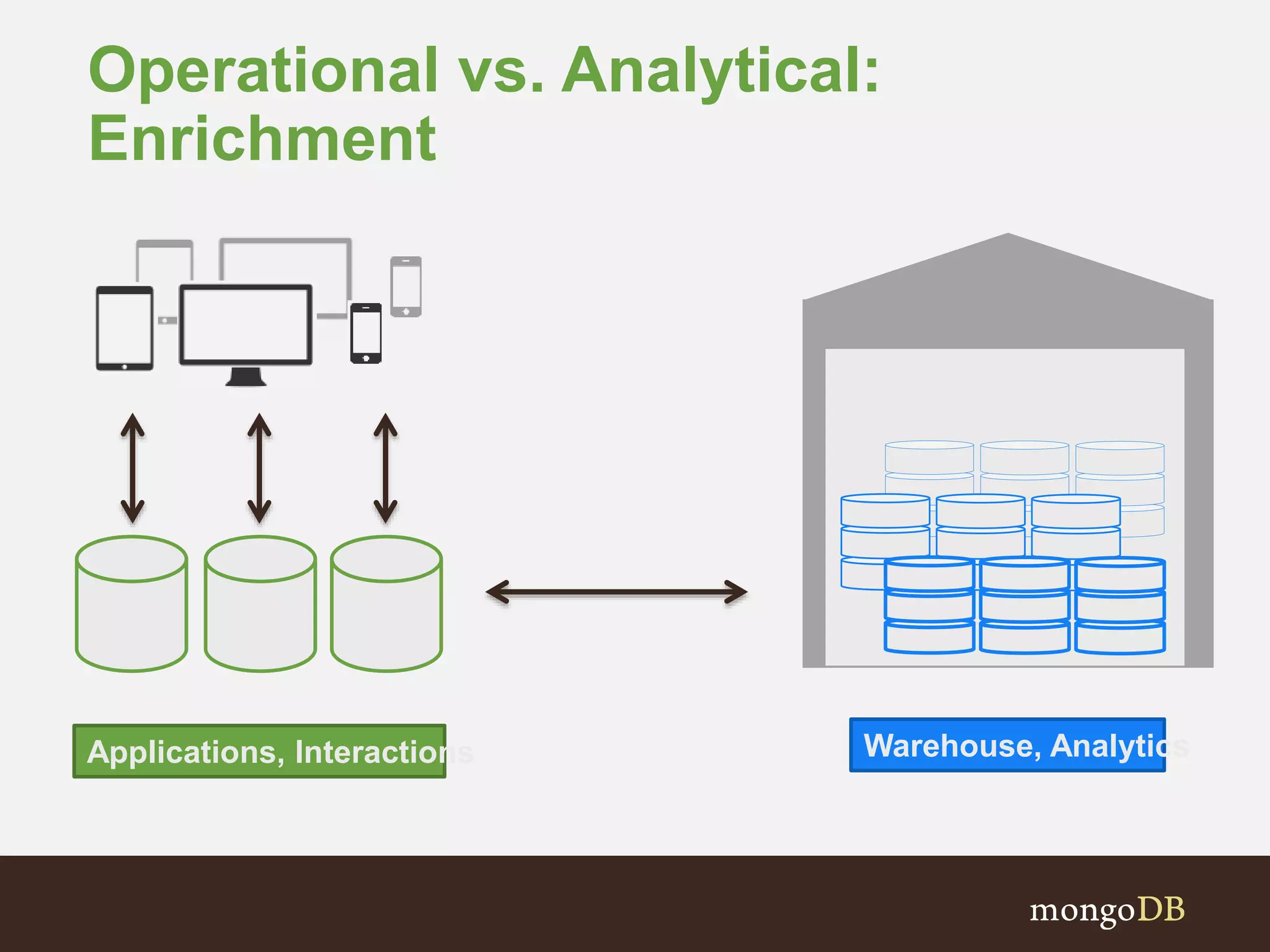
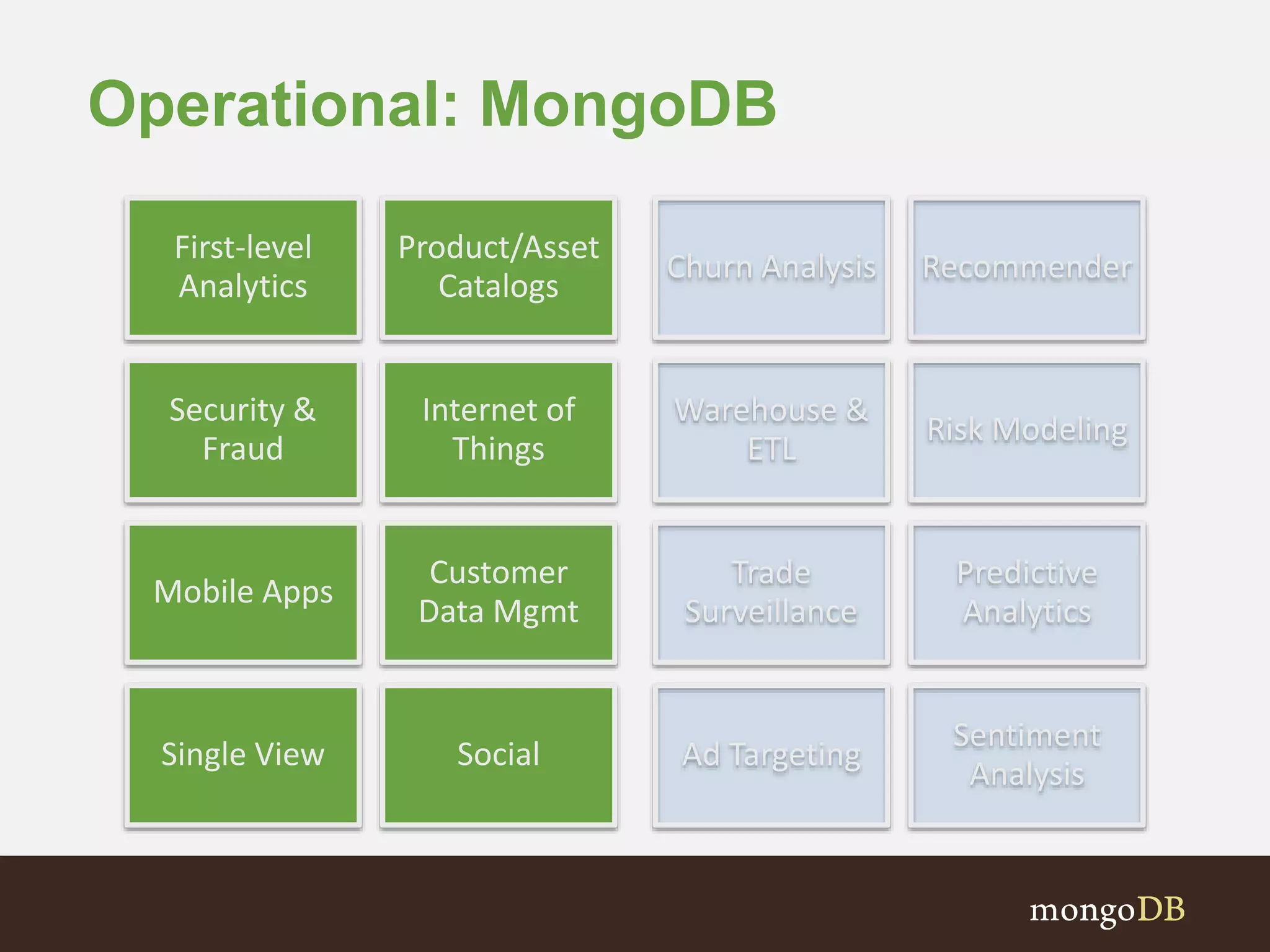
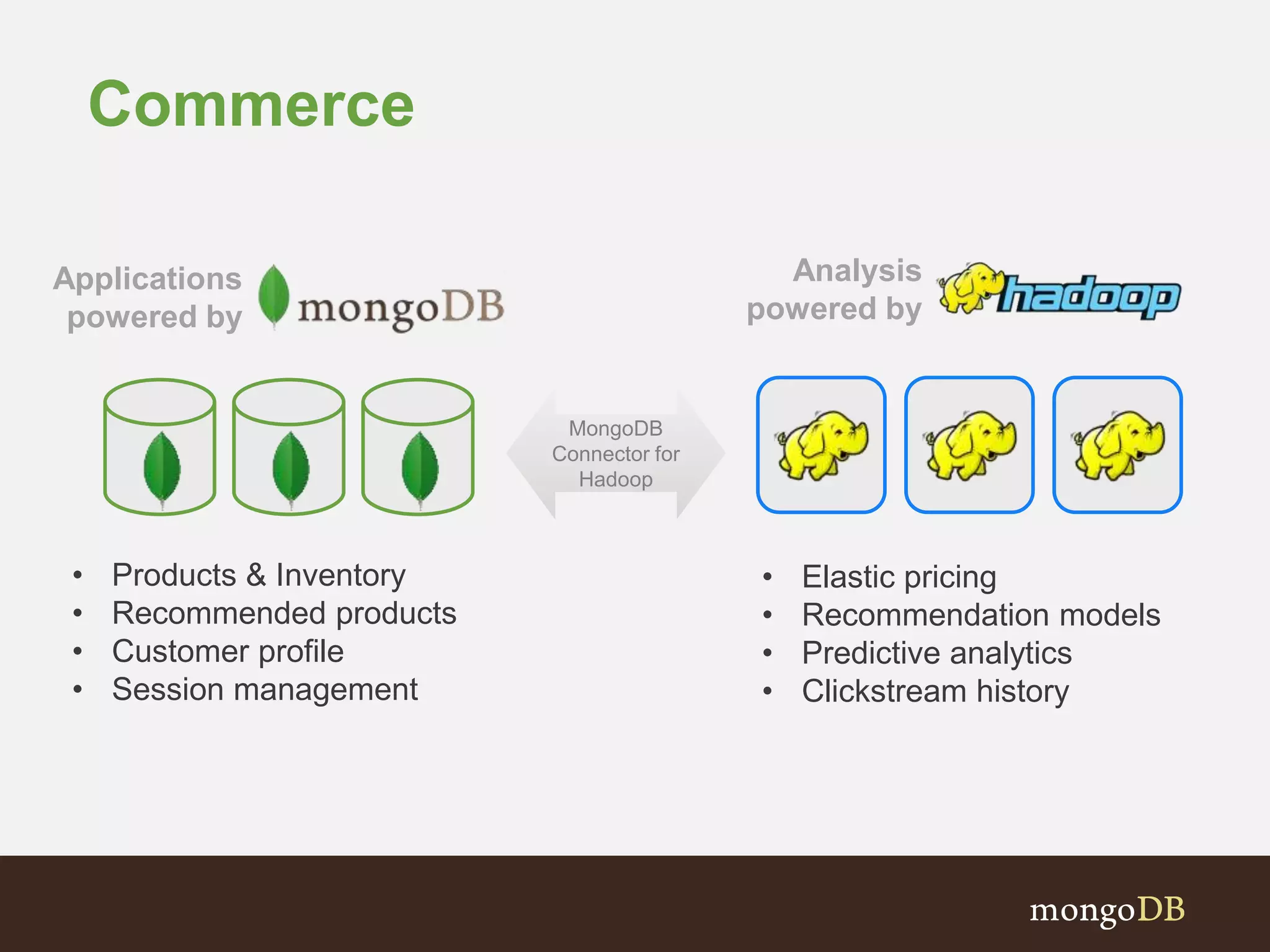
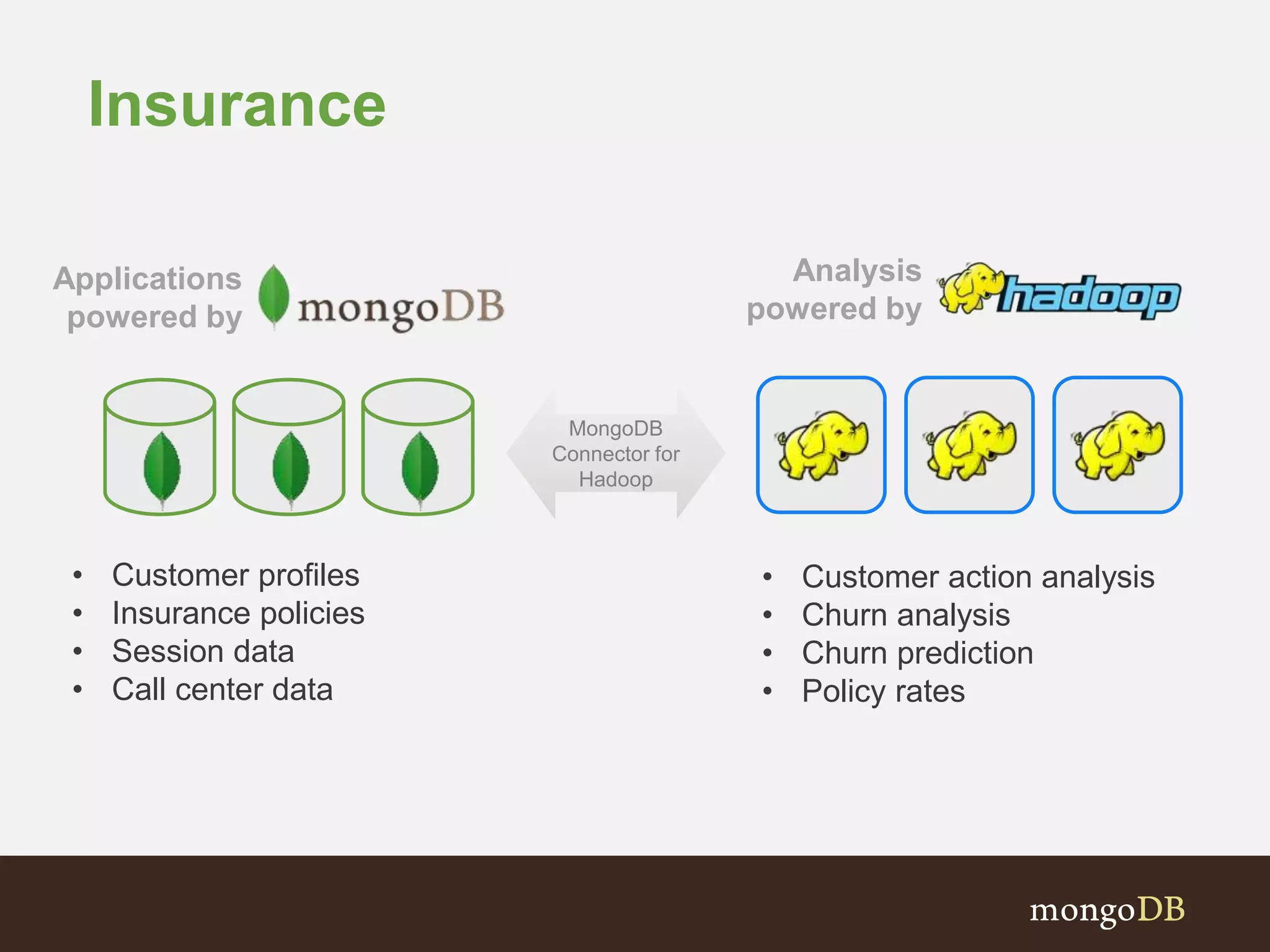
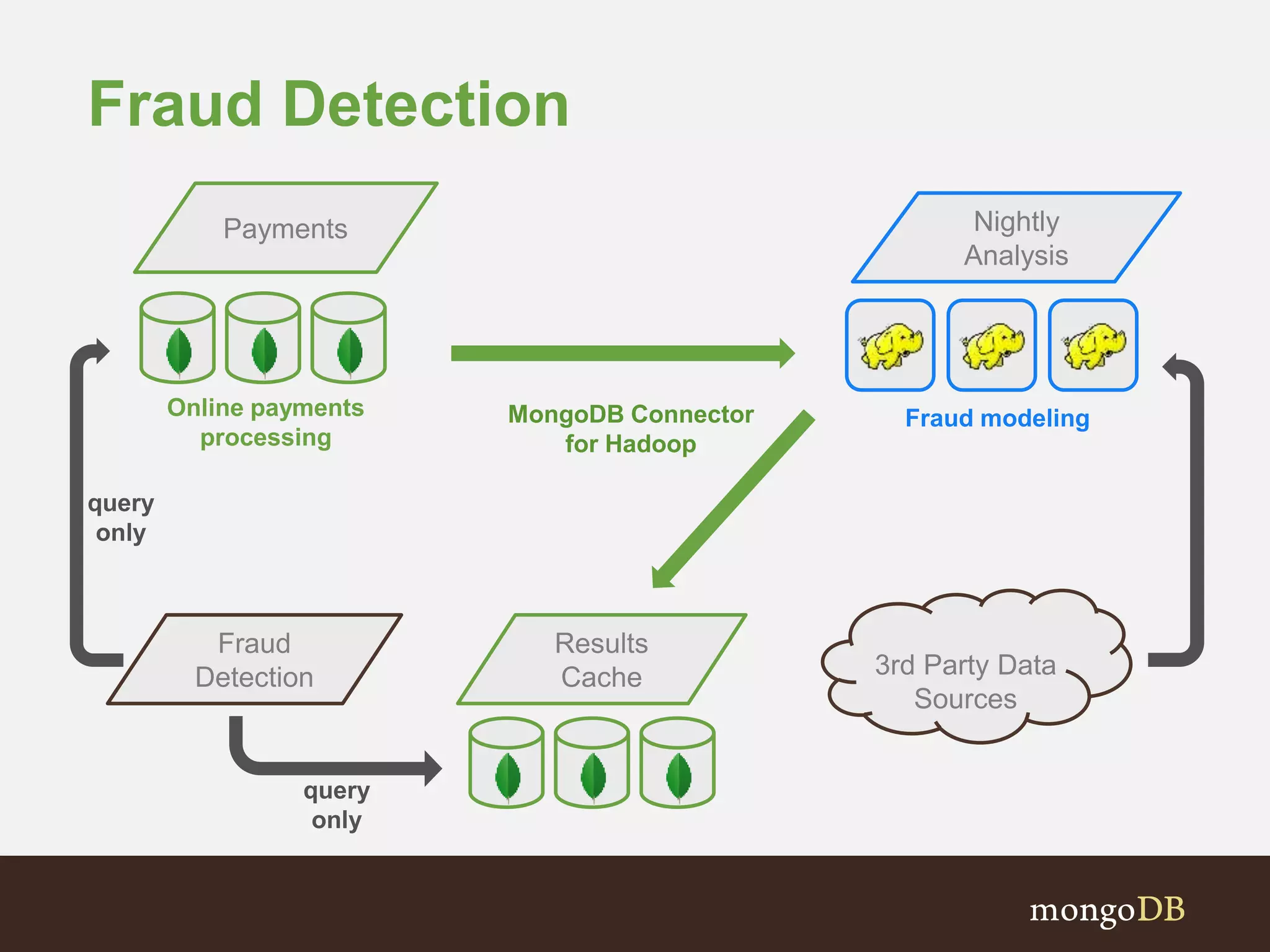
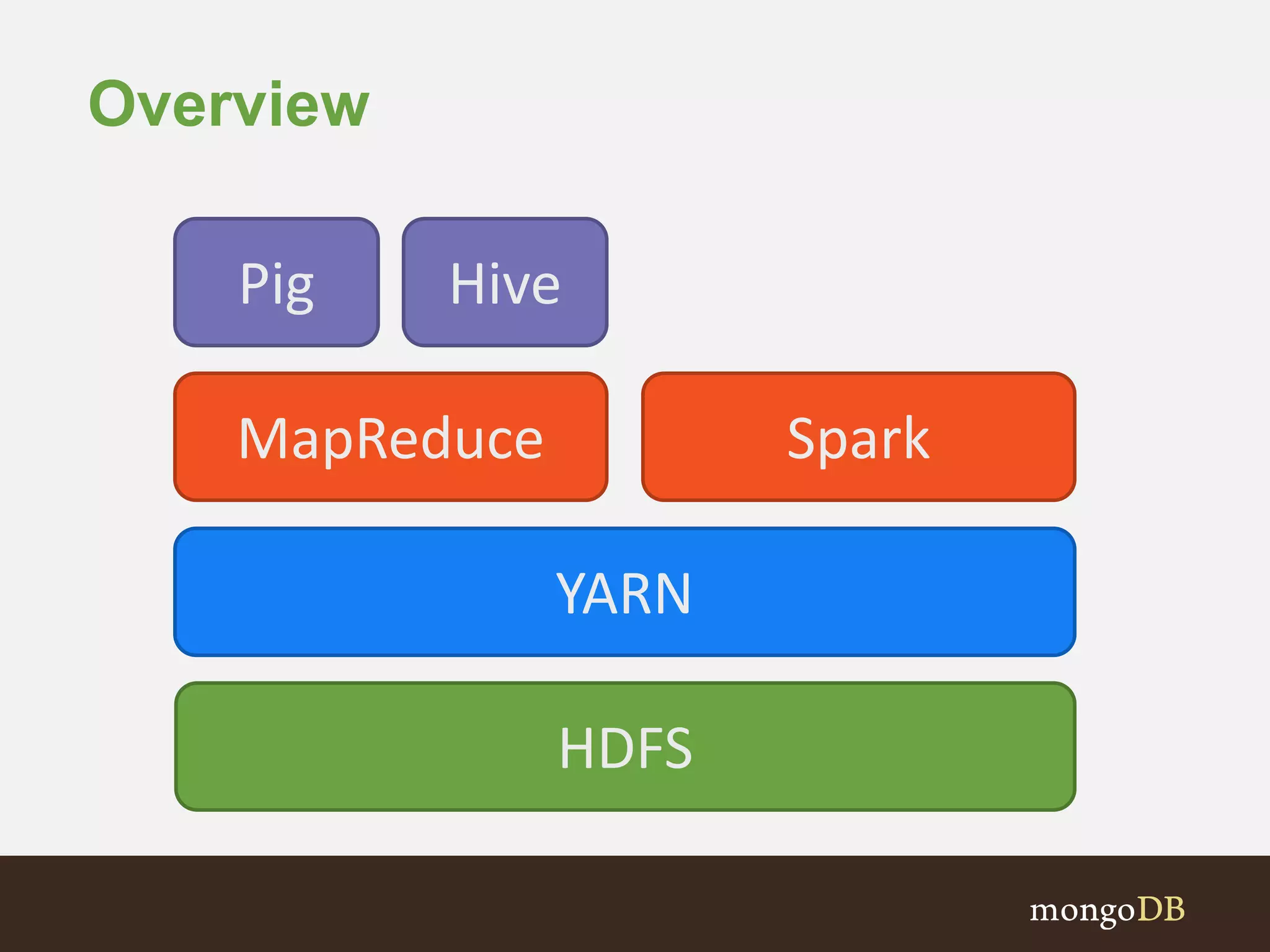
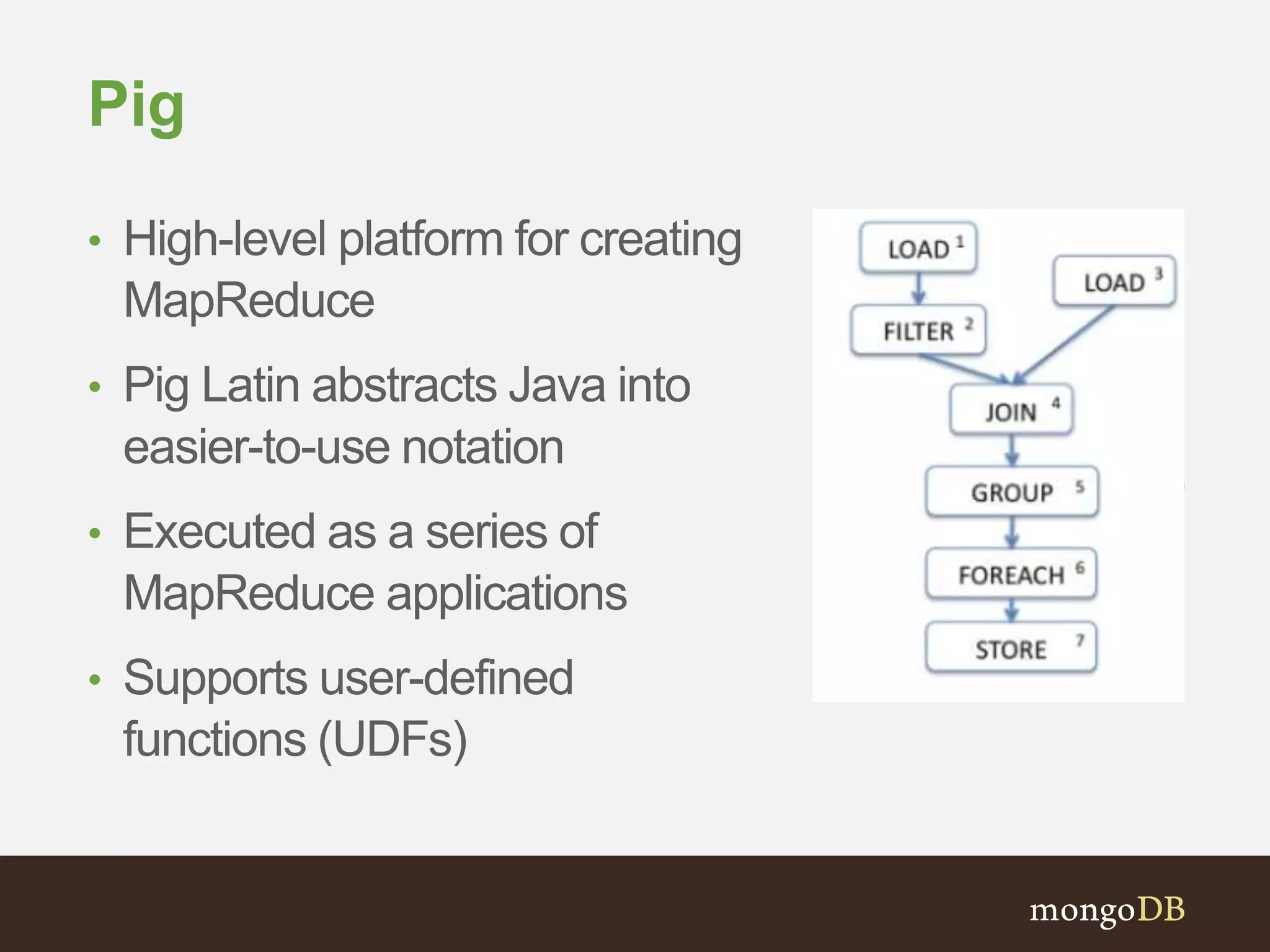
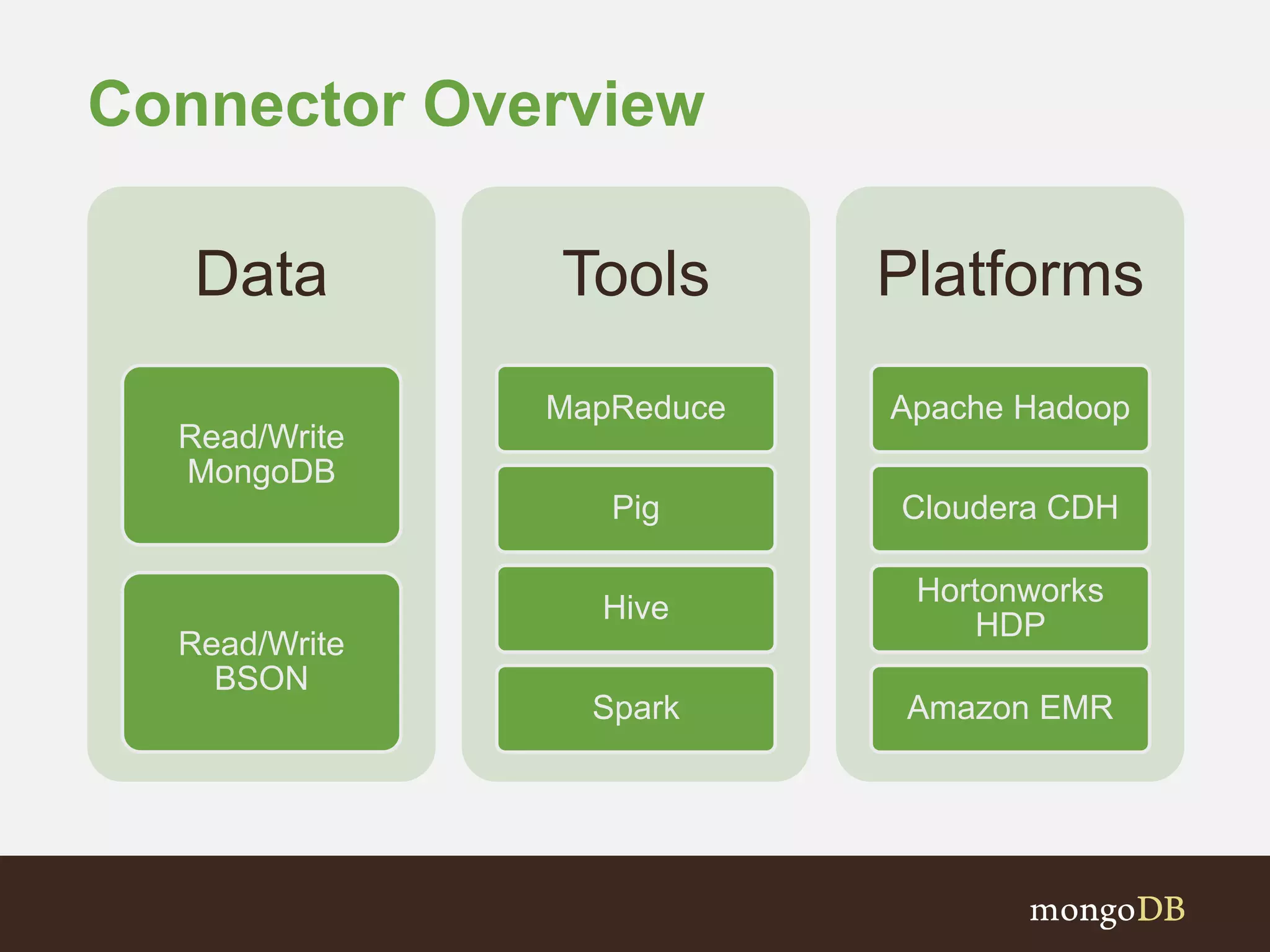
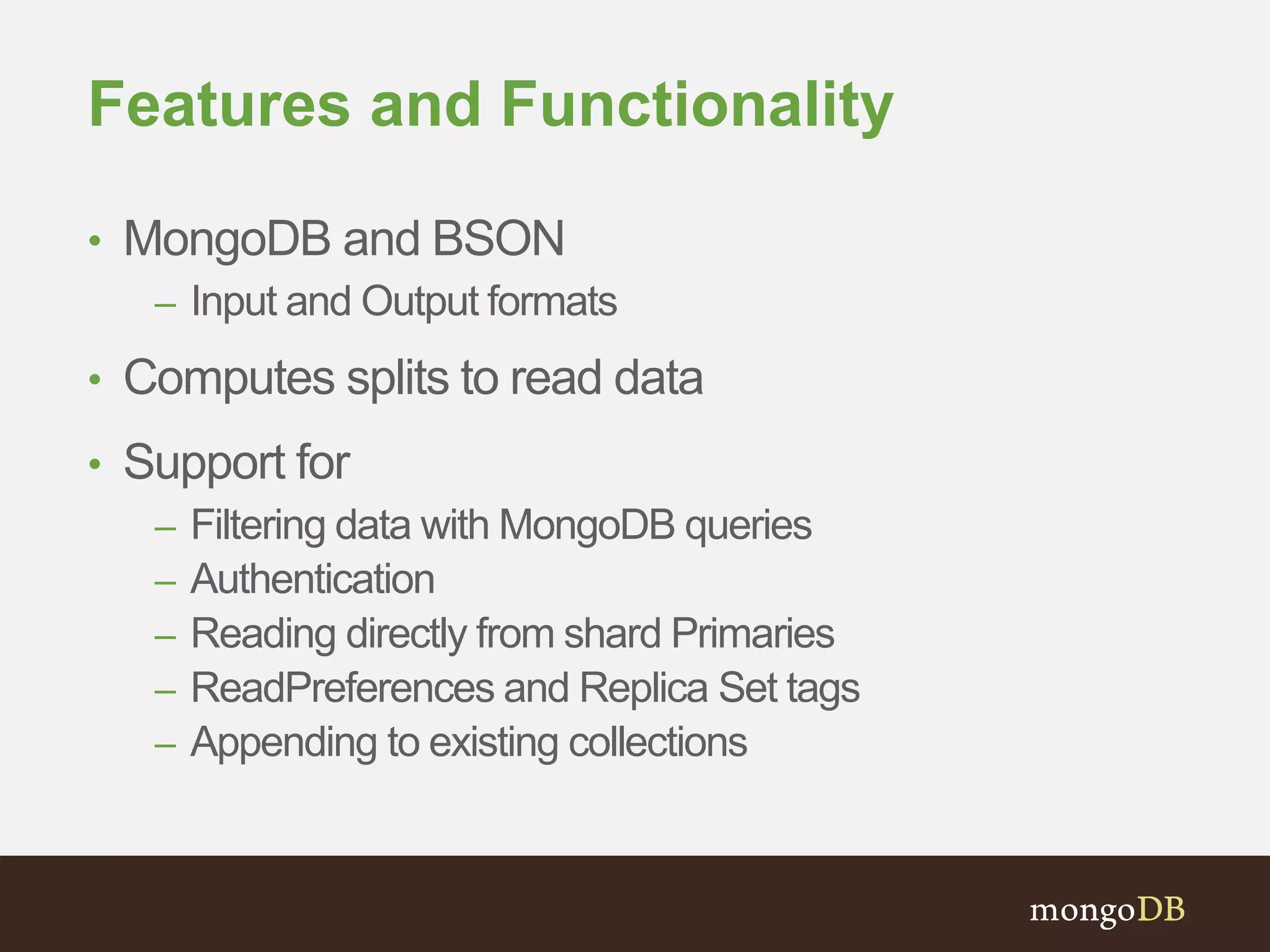
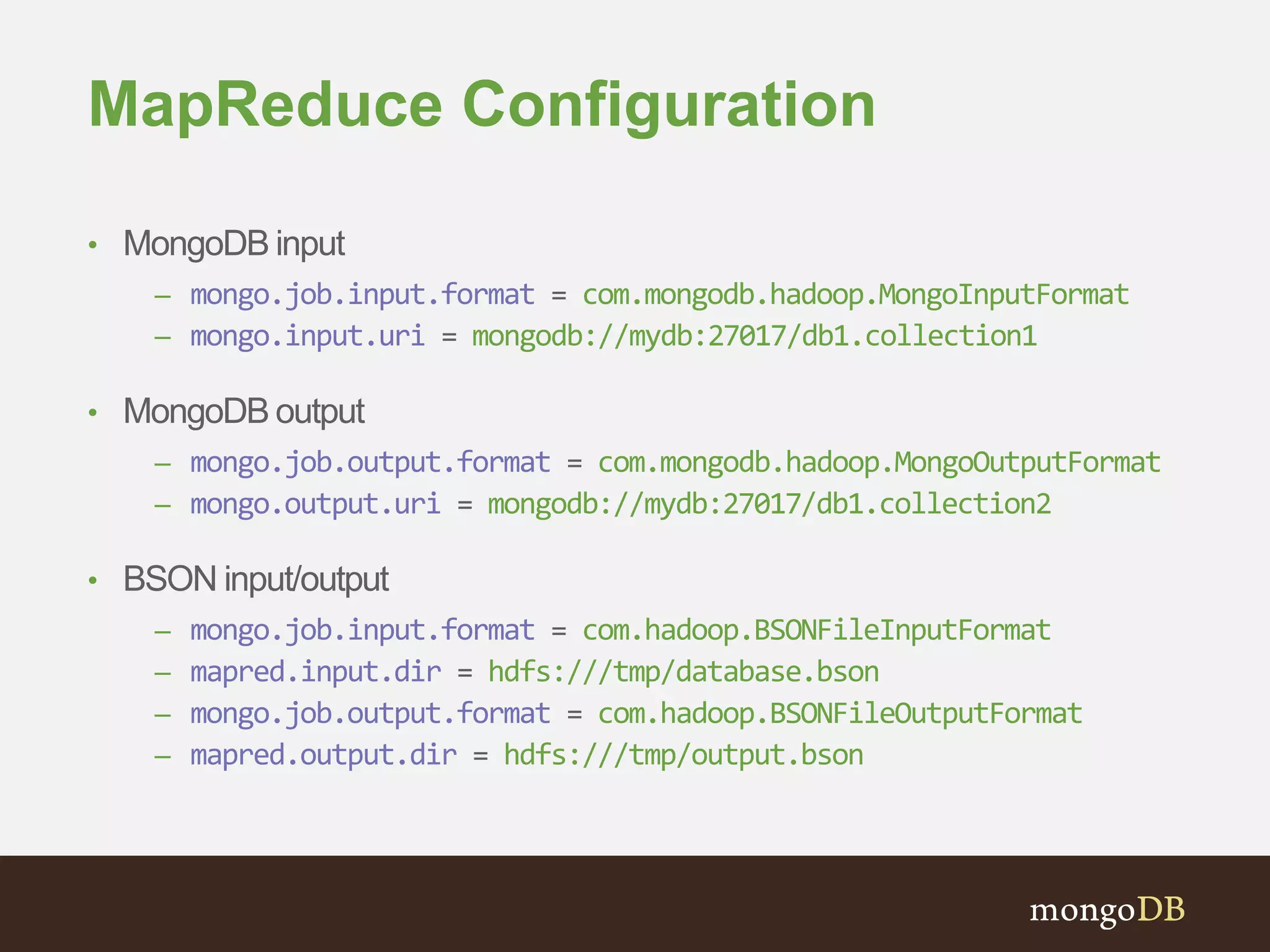
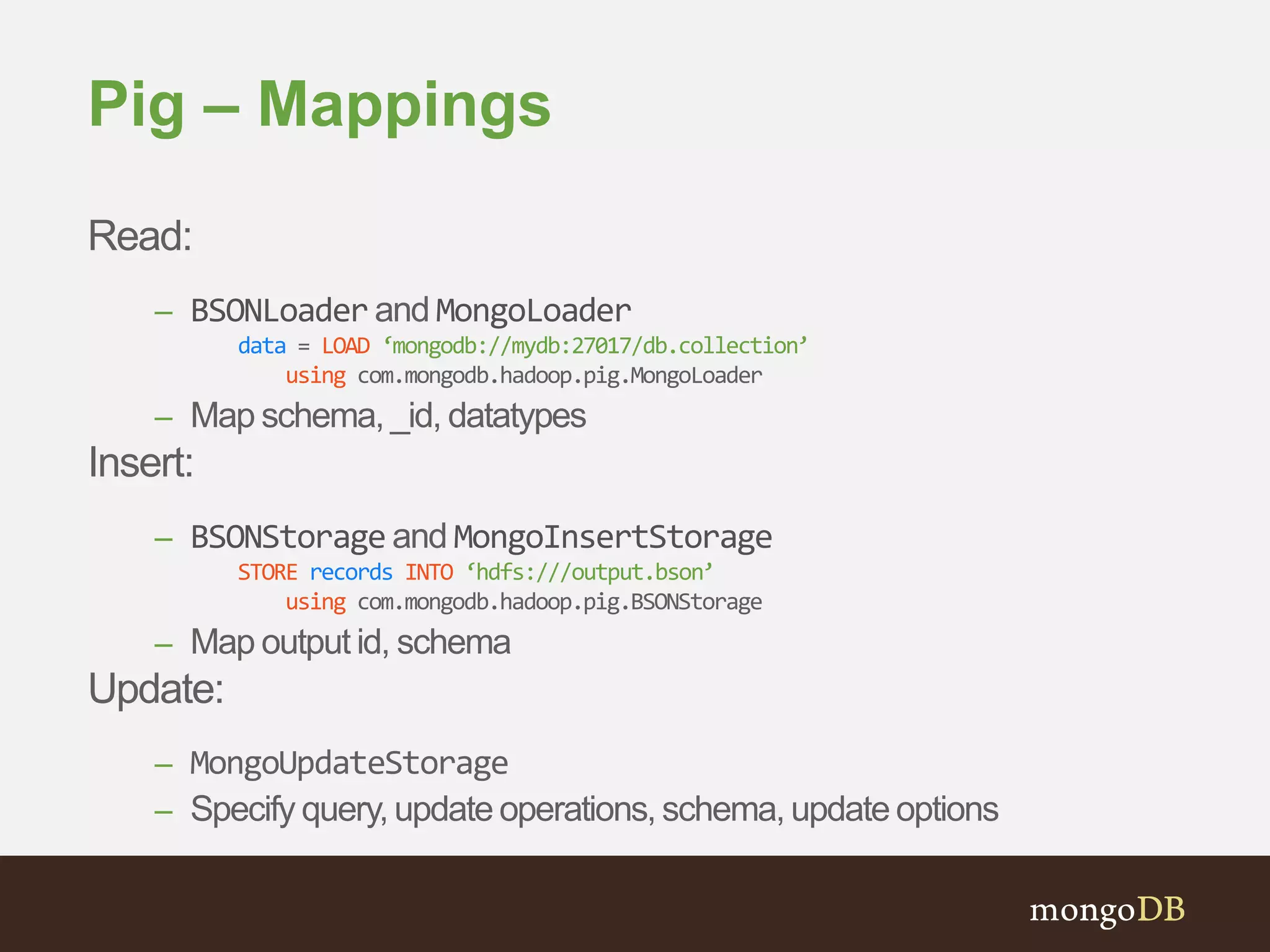
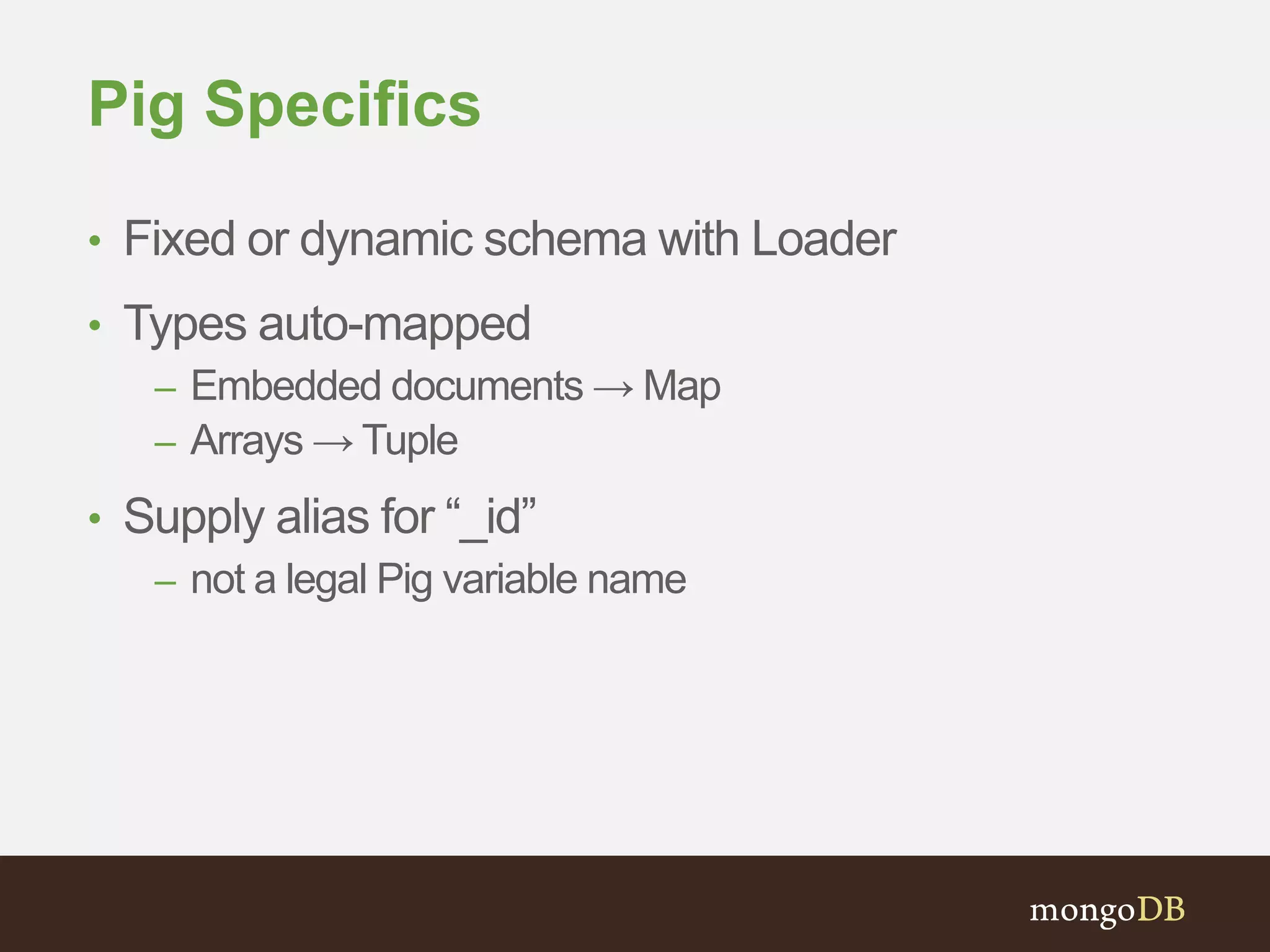
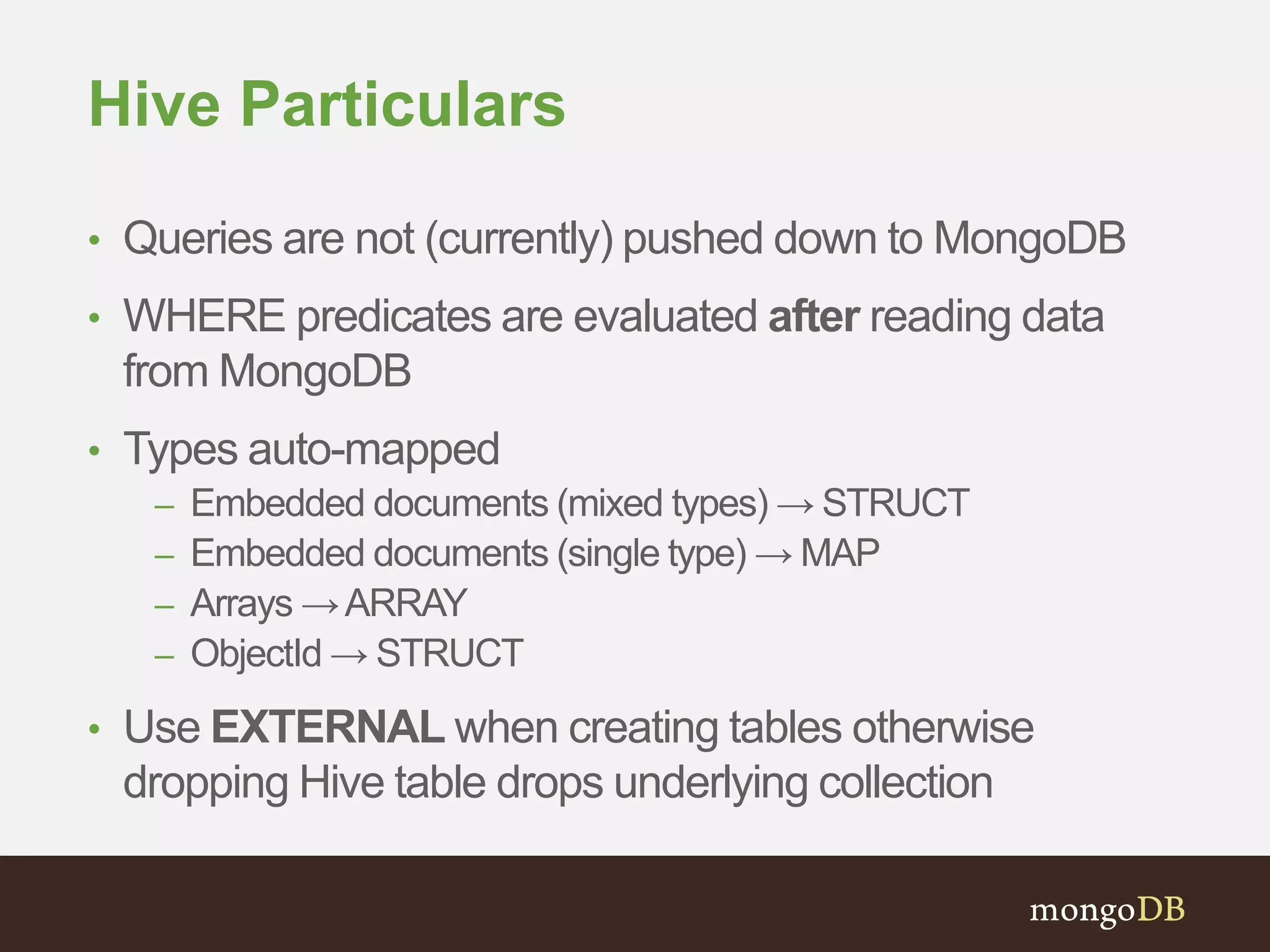
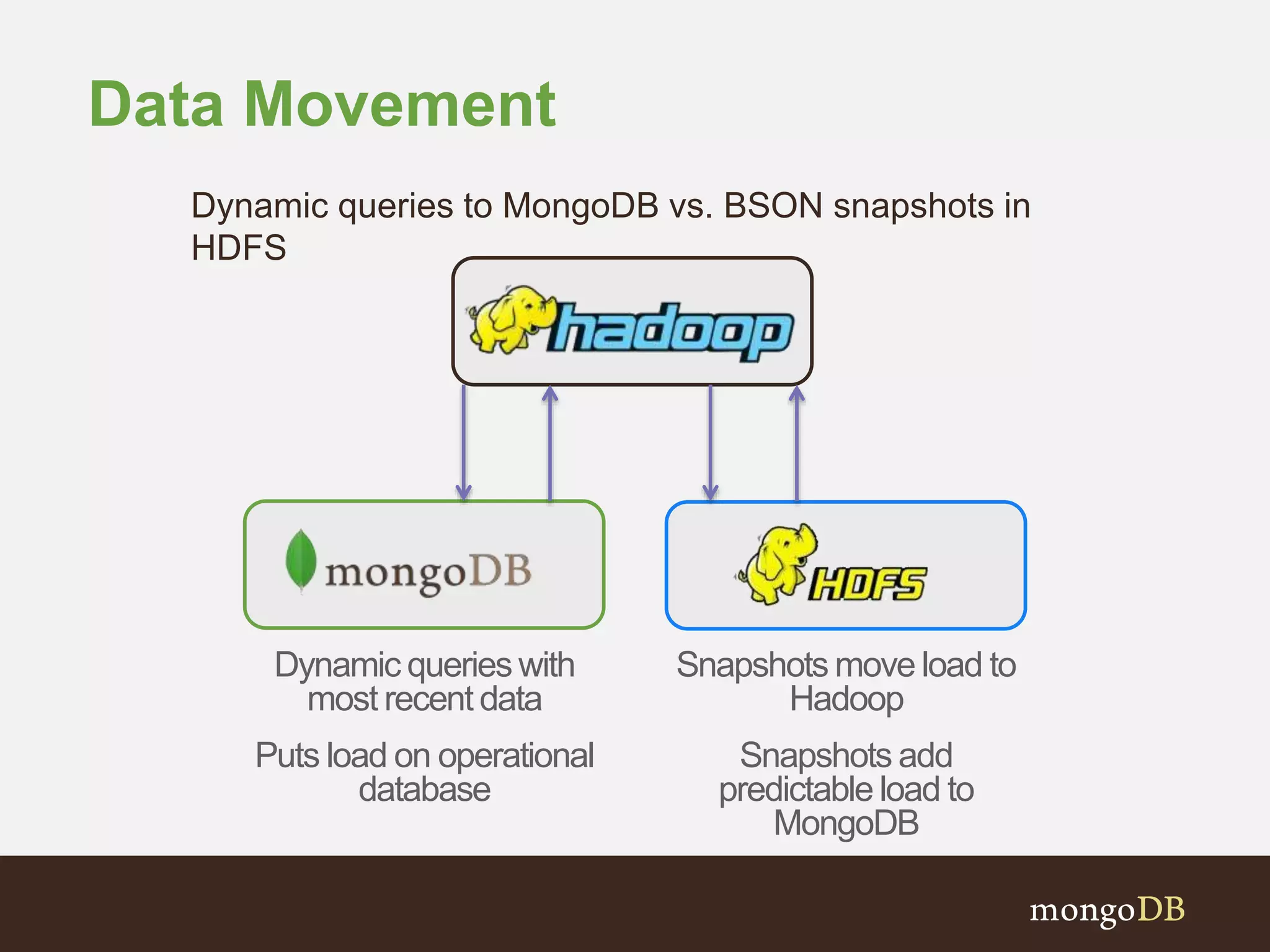
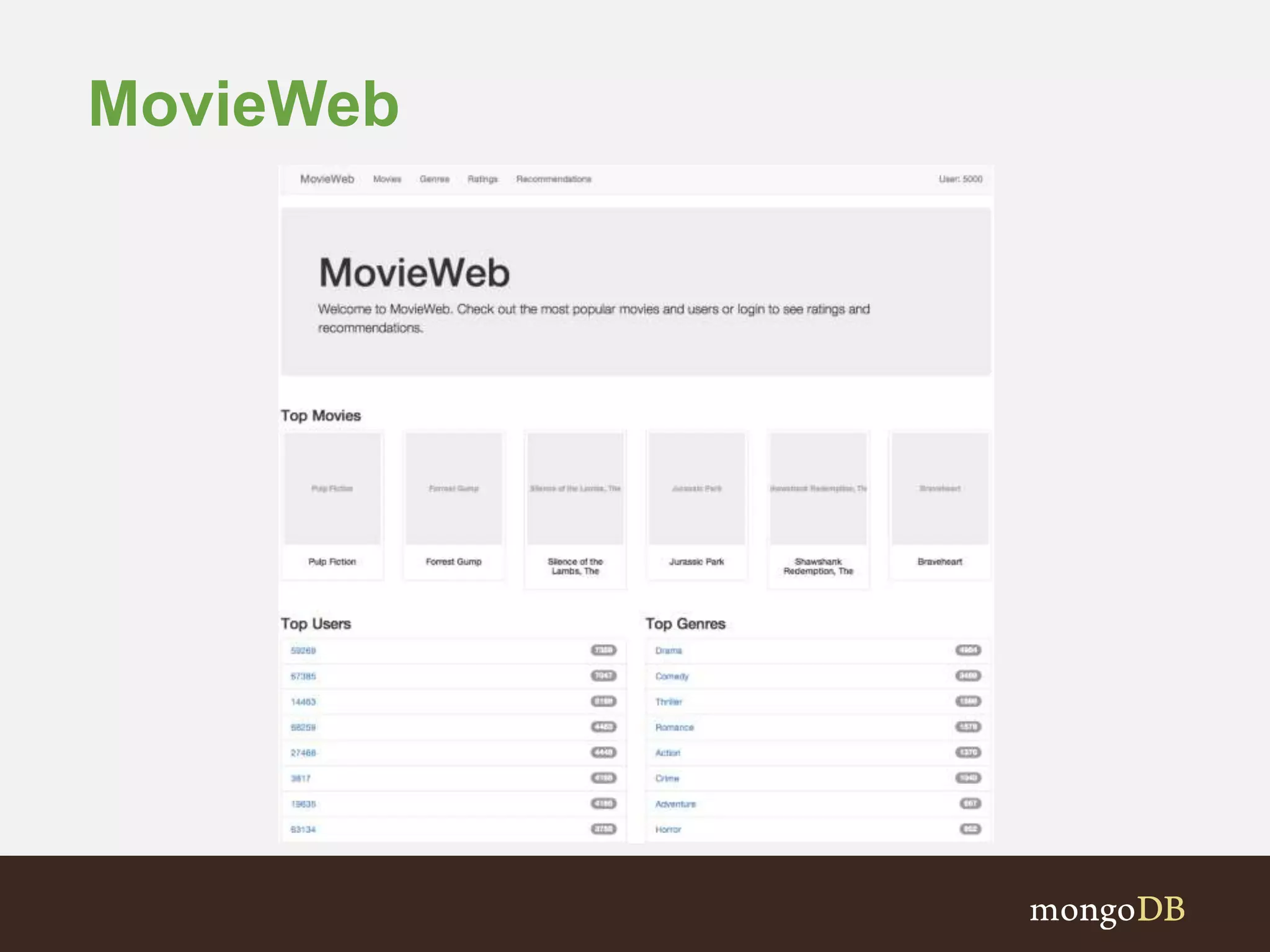
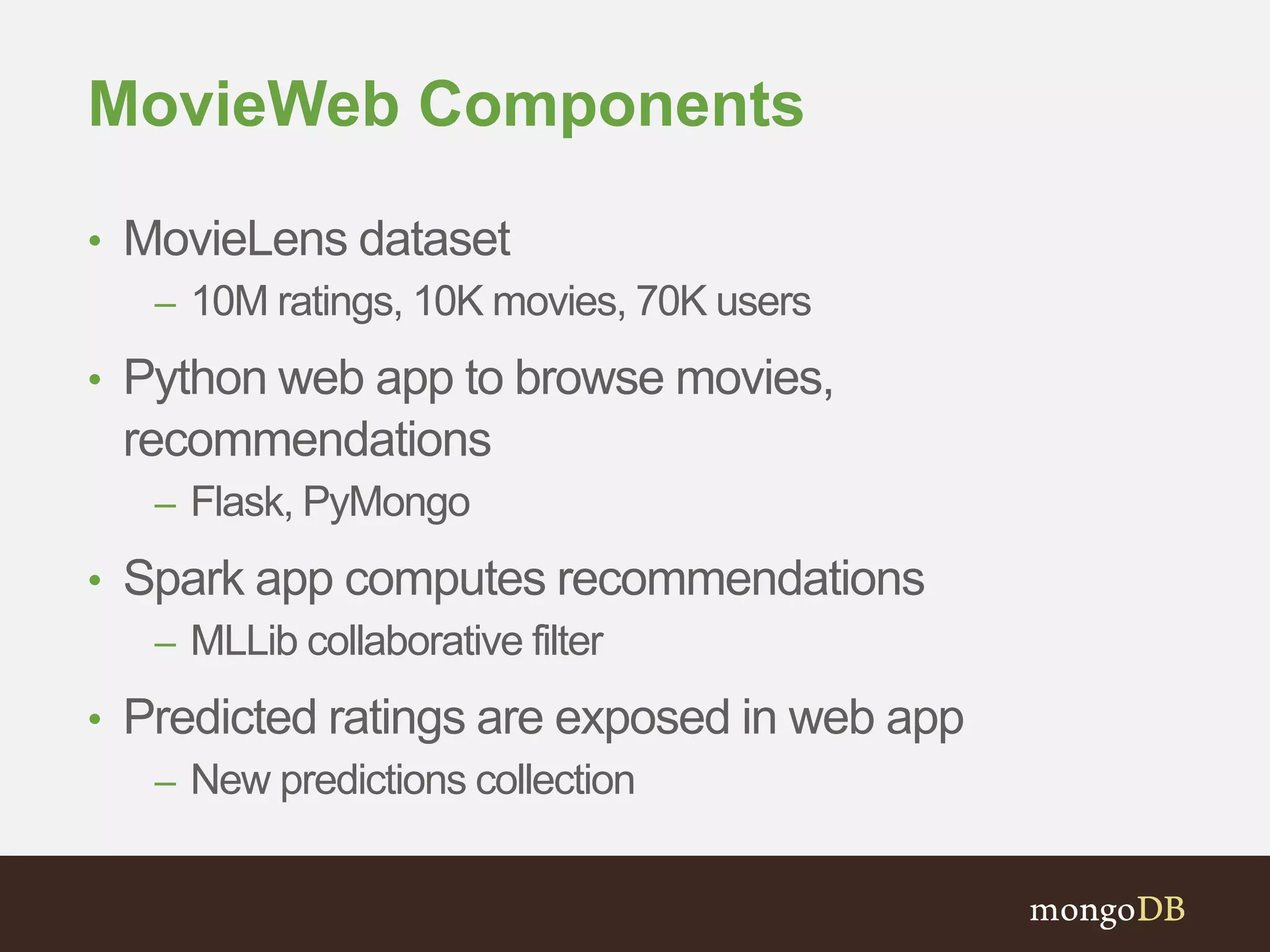
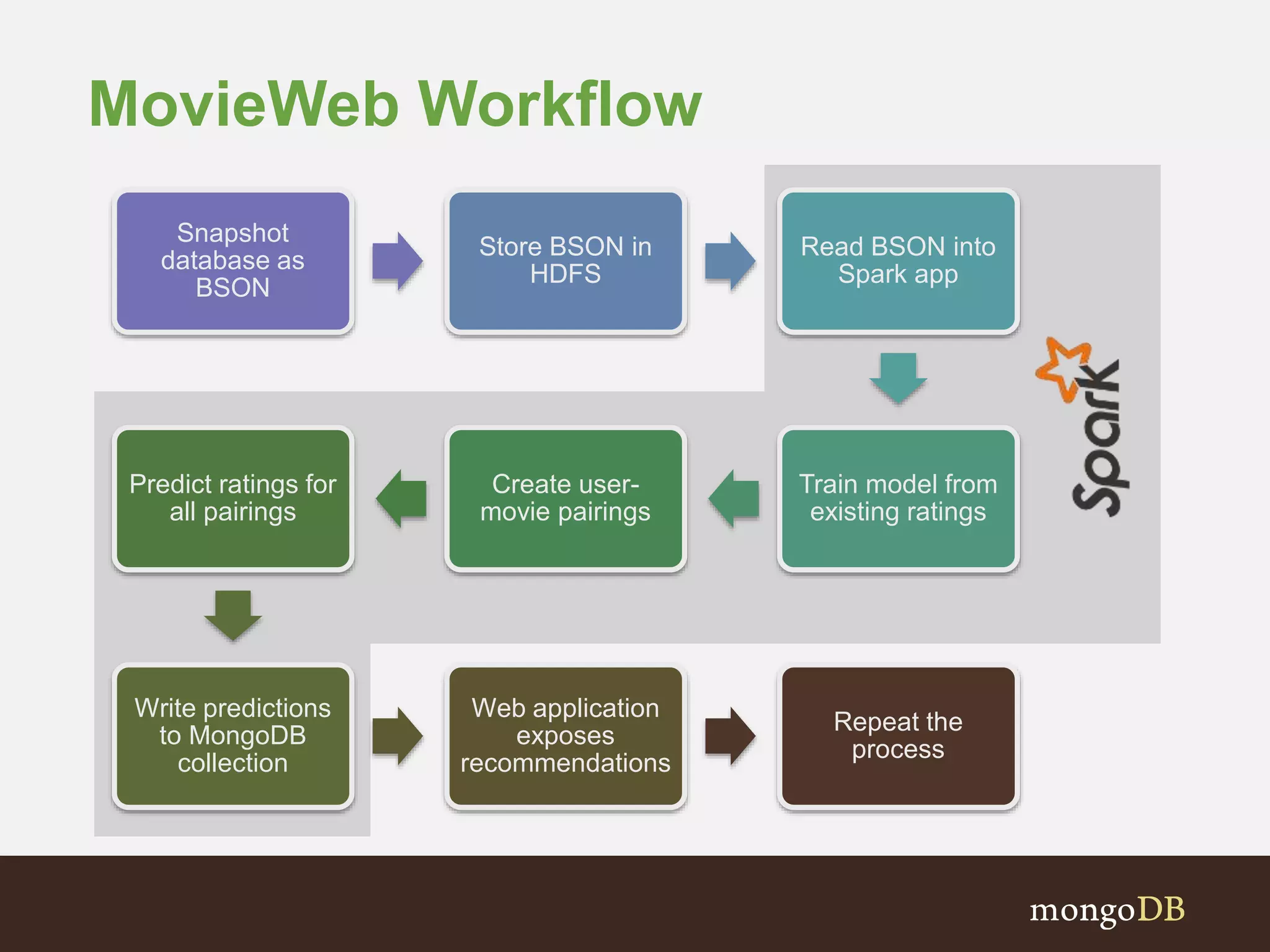
The document presents an overview of the integration between MongoDB and Hadoop, highlighting their capabilities in handling large datasets and providing business insights. It discusses various use cases across different industries, details on Hadoop components, and implementation strategies, including the MongoDB connector for Hadoop. Additionally, it features a demonstration of a web application leveraging both technologies for movie recommendations.






![Mapper Example
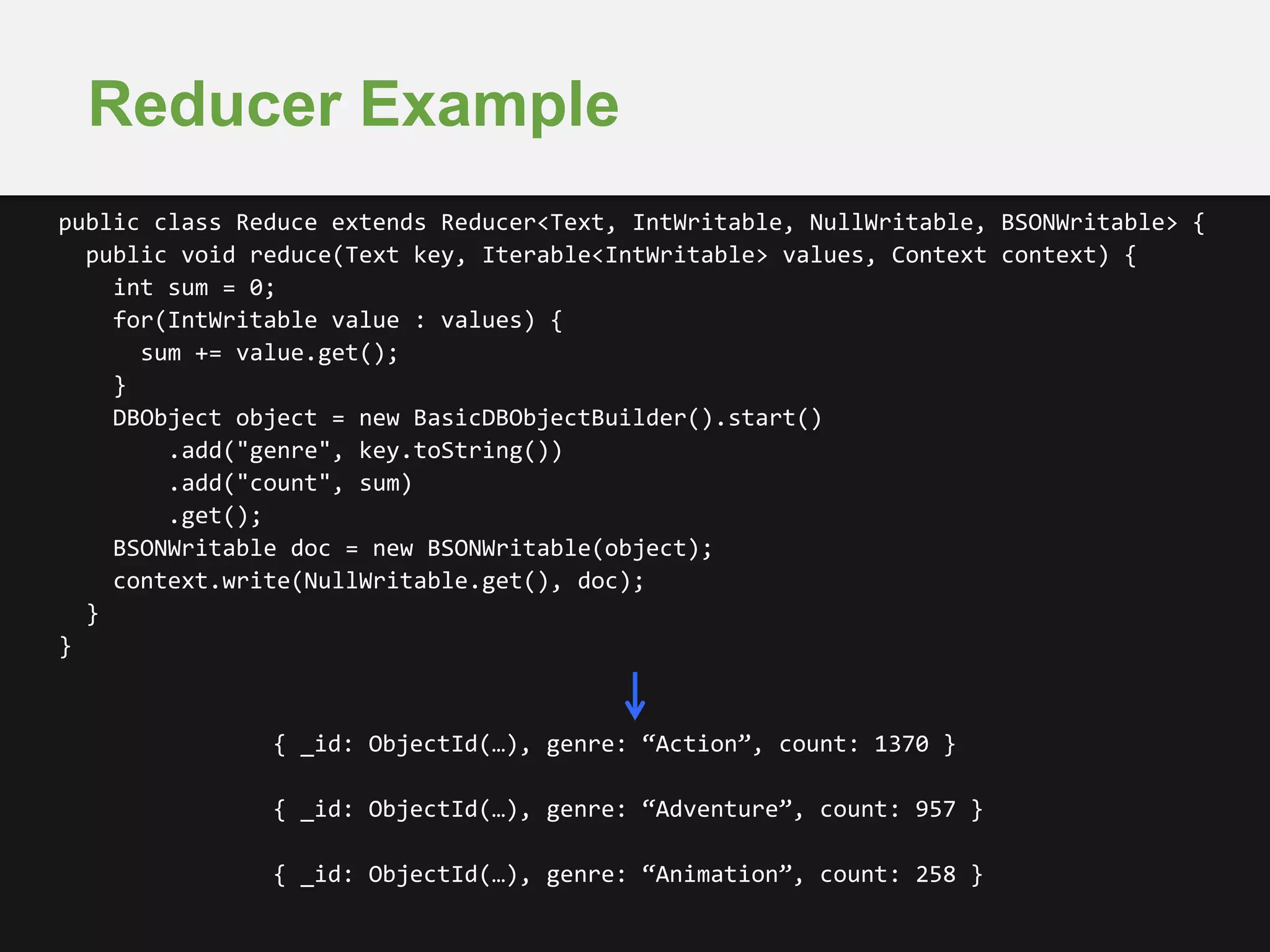
public class Map extends Mapper<Object, BSONObject, Text, IntWritable> {
public void map(Object key, BSONObject doc, Context context) {
List<String> genres = (List<String>)doc.get("genres");
for(String genre : genres) {
context.write(new Text(genre), new IntWritable(1));
}
}
}
{ _id: ObjectId(…), title: “Toy Story”,
genres: [“Animation”, “Children”] }
{ _id: ObjectId(…), title: “Goldeneye”,
genres: [“Action”, “Crime”, “Thriller”] }
{ _id: ObjectId(…), title: “Jumanji”,
genres: [“Adventure”, “Children”, “Fantasy”] }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbseattle-mongodbandhadoop2014-09-16-140924165735-phpapp01/75/MongoDB-and-Hadoop-Driving-Business-Insights-25-2048.jpg)




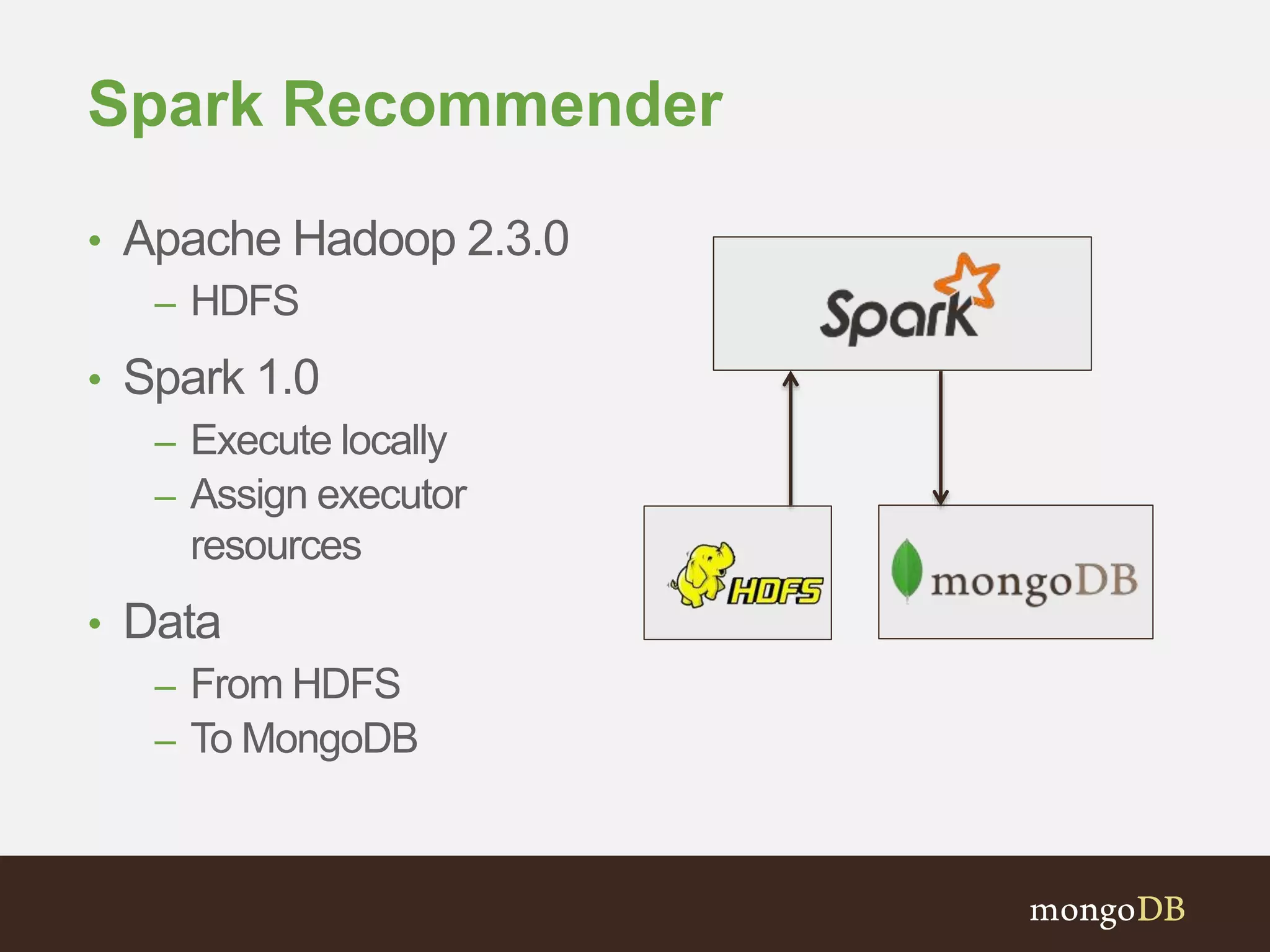
![Execution
$ bin/spark-submit
--master local
--class com.mongodb.hadoop.demo.Recommender demo-1.0.jar
--jars mongo-java-2.12.3.jar,mongo-hadoop-core-1.3.0.jar
--driver-memory 2G
--executor-memory 1G
[insert job args here]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbseattle-mongodbandhadoop2014-09-16-140924165735-phpapp01/75/MongoDB-and-Hadoop-Driving-Business-Insights-40-2048.jpg)

