This document discusses MongoDB and how it compares to relational databases. MongoDB is a non-relational database that stores data in JSON-like documents rather than tables. It supports horizontal scaling, data availability, and simple design. Common CRUD operations in MongoDB are similar to relational databases, but MongoDB uses methods and functions instead of a query language like SQL. The document provides examples of MongoDB queries and aggregation commands.








![Craeting a dummy data
for(i=0; i<1000;i++) { name = ["john", "smith",
"laura"]; for(j=0;j<3;j++){ db.student.insert
({"student_id": i, "stu_name":name[j], "score":
Math.round(Math.random()*100)}) } };](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hemant-150801011606-lva1-app6891/85/MongoDB-12-320.jpg)


![OR operator
db.student.find({$or: [{"score":90}, {"score" :
80}]});
This will fetch the data whose score is either 90
or 80.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hemant-150801011606-lva1-app6891/85/MongoDB-15-320.jpg)
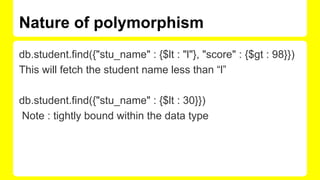
![Command [Regex , exists, type ]
db.student.find({"stu_name" : {$regex : "ih"}})
db.student.find({"stu_name" : {$exists : true}})
db.student.find({"stu_name" : {$type : 1}})
It will fetch the data of number type
db.student.find({"stu_name" : {$type : 2}})
It will fetch the data of string type](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hemant-150801011606-lva1-app6891/85/MongoDB-17-320.jpg)
![Seach in Array
db.student.insert({"stu_name" : 11, "subject" :["hindi", "english", "math"]})
db.student.insert({"stu_name" : 22, "subject" :["math", "german", "spanish"]})
db.student.insert({"stu_name" : 22, "subject" :["math", "german", 100]})
db.student.find({"subject" : "hindi"})
db.student.find({"subject" : 100})
(Another type of polymorphism)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hemant-150801011606-lva1-app6891/85/MongoDB-18-320.jpg)
![Continue...
db.student.find({"subject" : {$all : ["hindi", "english" ]}})
Fetch the data which contains both in subject array
db.student.find({"subject" : {$in : ["hindi", "math" ]}})
Return the data set which satisfy either of the value](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hemant-150801011606-lva1-app6891/85/MongoDB-19-320.jpg)
![Cursor
>cur = db.student.find({"subject" : {$in : ["hindi", "math" ]}}), null;
null
> cur.hasNext()
true
> cur.next()
{
"_id" : ObjectId("54421c362d3b0ea3d1c08eb2"),
"stu_name" : 11,
"subject" : [
"hindi",
"english",
"math"
]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hemant-150801011606-lva1-app6891/85/MongoDB-20-320.jpg)
![count the number of document
> cur = db.student.find({"subject" : {$in : ["hindi", "math" ]}});
{ "_id" : ObjectId("54421c362d3b0ea3d1c08eb2"), "stu_name" : 11, "subject" : [
"hindi", "english", "math" ] }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("54421c532d3b0ea3d1c08eb3"), "stu_name" : 22, "subject" : [
"math", "german", "spanish" ] }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("54421c982d3b0ea3d1c08eb4"), "stu_name" : 22, "subject" : [
"math", "german", 100 ] }
> cur = db.student.count({"subject" : {$in : ["hindi", "math" ]}});
3
>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hemant-150801011606-lva1-app6891/85/MongoDB-21-320.jpg)

![Command
Count
> db.student.aggregate([ {$group: { _id: "$stu_name", num_student: {$sum : 1}}}])
{
"result" : [
{
"_id" : 22,
"num_student" : 2
},
{
"_id" : 40,
"num_student" : 1
},
{
"_id" : 30,
"num_student" : 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hemant-150801011606-lva1-app6891/85/MongoDB-23-320.jpg)
![Sum with group
SUM on Score
> db.student.aggregate([ {$group: { _id: "$stu_name", num_student: {$sum : “$score”}}}])
Sort on score :
db.student.aggregate([ {$group: { _id: "$stu_name", num_student1: {$sum : "$score"}}}, {$sort :
{num_student1 : 1}}])
db.student.aggregate( {$match : {"stu_name" : "smith"}}, { $group: {_id : "$stu_name" , total : {$sum :
1}}} )
> db.student.aggregate([ {$group: { _id: "$stu_name", num_student: {$sum : “$score”}}}], {explain :](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hemant-150801011606-lva1-app6891/85/MongoDB-24-320.jpg)