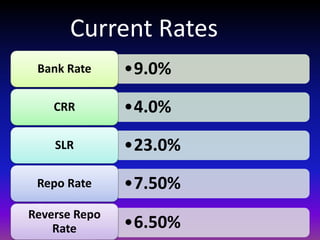
The document discusses monetary policy, defining it as actions by authorities to influence money supply, interest rates, and money availability to achieve objectives. It outlines the elements of monetary policy as regulating money supply, banking systems, and interest rates. The objectives are listed as regulating money supply, price stability, economic growth, and others. Types of monetary policy controls discussed include quantitative tools like bank rates, cash reserve ratios, and qualitative tools like moral persuasion and credit monitoring. Limitations and ways to improve monetary policy are also presented.