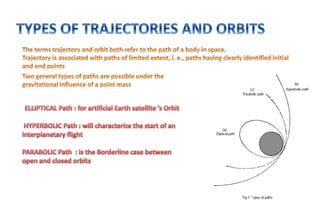
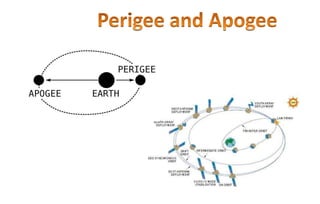
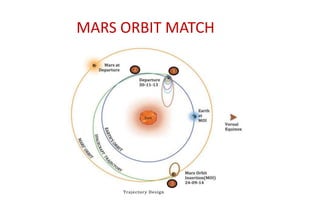
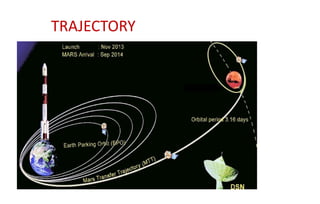
The Mars Orbiter Mission was launched by the Indian Space Research Organisation to demonstrate India's ability to design, plan, manage, and operate an interplanetary mission. The mission's orbiter was launched aboard a Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle and placed in an Earth orbit before engine firings raised its orbit and sent it on a trajectory to Mars. The orbiter's scientific payload included instruments to analyze Martian atmospheric composition and surface features. It successfully entered orbit around Mars in 2014 to study the planet.