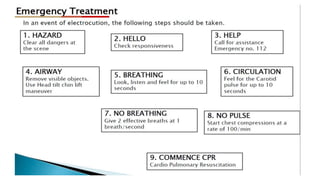
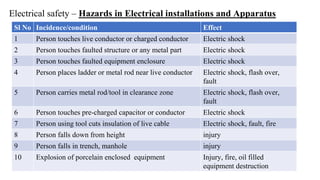
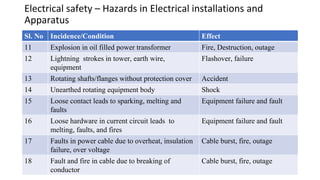
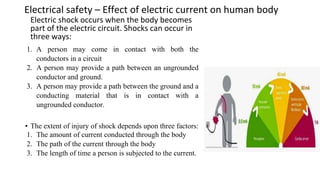
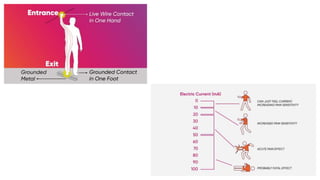
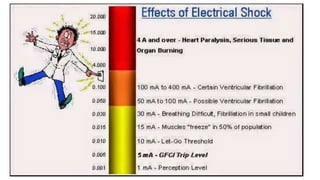
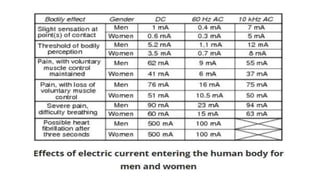
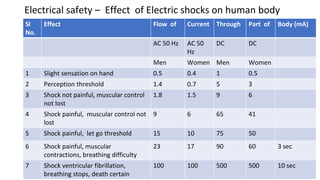
This document discusses electrical safety and provisions according to Indian Electricity Rules 1956 and OSHA standards. It outlines key hazards of electricity including electric shocks, fires, explosions and injuries. The rules cover safety requirements for electrical equipment, installations, clearances, earthing and working on live lines. OSHA standards mandate de-energizing and locking out equipment before work. Objectives of safety measures are to prevent accidents through education, control of hazards and emergency response. Common electrical hazards include shocks from direct and indirect contact, falls, fires and release of toxic gases.