This document provides information about the Power Electronics module offered at Caledonian College of Engineering in Oman for the 2019-2020 academic year. The module is worth 20 credits and intended for third year undergraduate students in Electrical Power Engineering. It will be taught over one semester with 6 contact hours per week, including lectures and tutorials. The module aims to teach students about power electronic devices, circuits, systems and their applications. Key topics covered include rectifiers, inverters, choppers, cycloconverters, thermal protection and applications. Assessment will be based on a mid-term test, coursework in the form of a mini project, and a final examination.


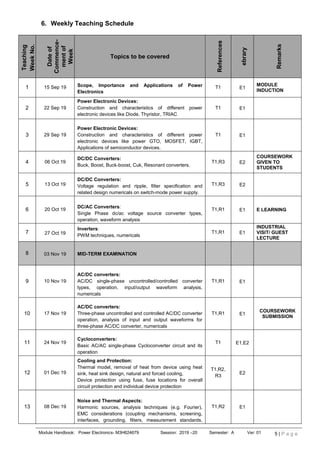
![Module Handbook: Power Electronics- M3H624679 Session: 2019 –20 Semester: A Ver: 01 6 | P a g e
age 1
circuit layout)
14 15 Dec 19
Applications: Electric motor drives, HV DC link, static
VAR compensator, UPS, lighting and heating controls.
Power systems (FACTS).
T1,R2
E1,E2
22 Dec 19 Discussions / Doubt clearing sessions
Text Book
T1
Lander, C.W., 2013. Power Electronics. 3rd edition. McGraw-Hill. ISBN 13:
9780077077143.
References
R1
Rashid, M.H., 2013. Power Electronics Handbook Devices, Circuits and
Applications.3rd
Edition. USA: Butterworth-Heinemann-ISBN-13: 978-0133125900
R2 Ned Mohan, 2012. Power Electronics: First course.1st
Edition. USA: John Wiley&
Sons, ISBN-13: 978-1118074800
R3
Bimbhra, P.S., 2012. Power Electronics. Khanna Publishers. ISBN-13: 978-
8174092793.
Ebrary
E1
Bose, Bimal K.. Power Electronics and Motor Drives : Advances and Trends.
Burlington, MA, USA: Academic Press, 2006. ProQuest ebrary.
http://site.ebrary.com/lib/caledonian/detail.action?adv.x=1&docID=10138178&f00
=subject&p00=POWER+ELECTRONICS . [30th
June 2019].
E2
Rashid., M. Power Electronics Handbook : Devices, Circuits, and Applications
2006, Elsevier Science & Technology, Burlington. Available from: ProQuest
Ebook Central https://ebookcentral.proquest.com/lib/caledonian-
ebooks/reader.action?docID=283963&query=%2522Ned%2BMohan%2522. [30th
June 2019].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulehandbook-200914054307/85/Module-hand-book-6-320.jpg)