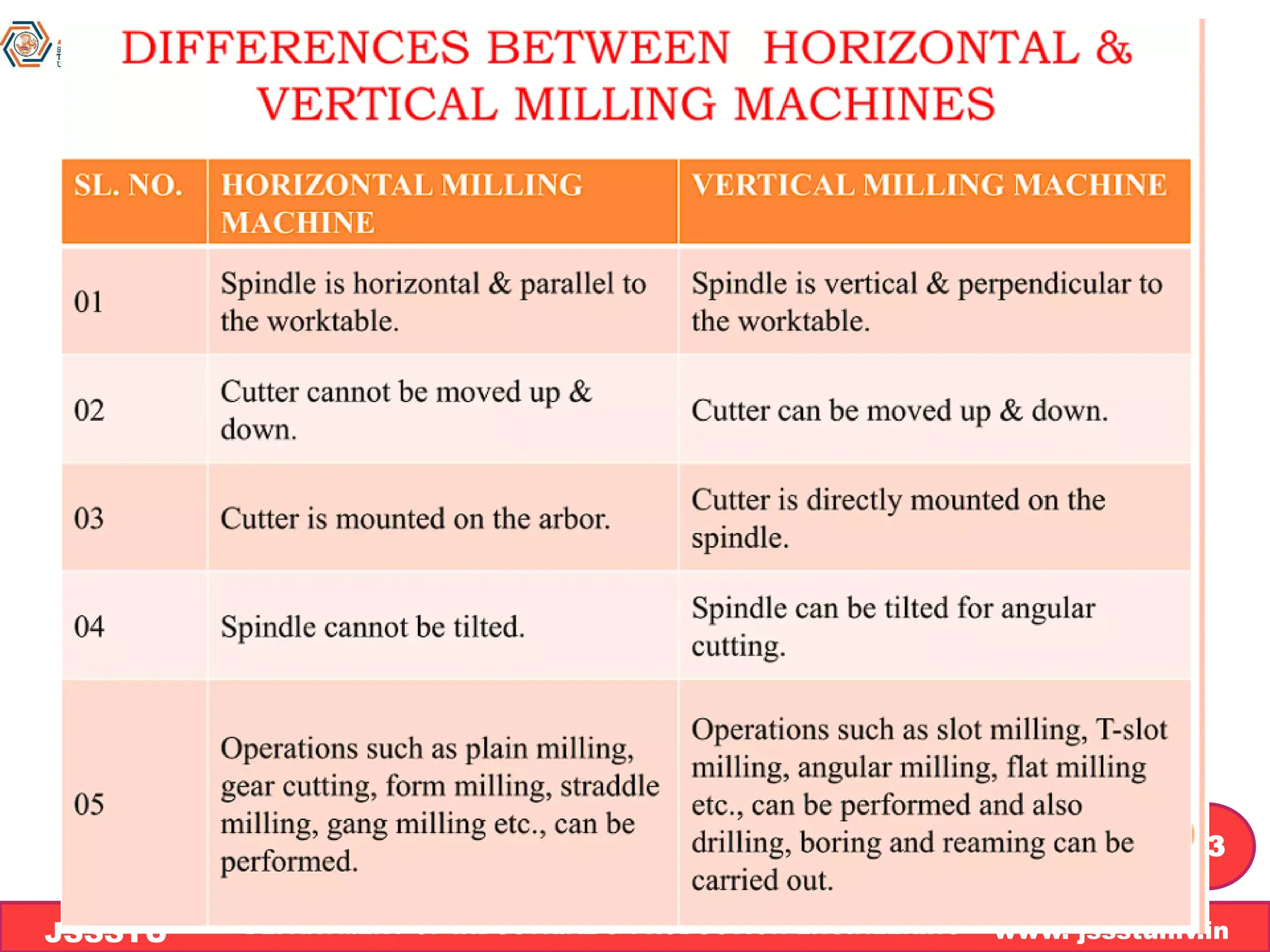
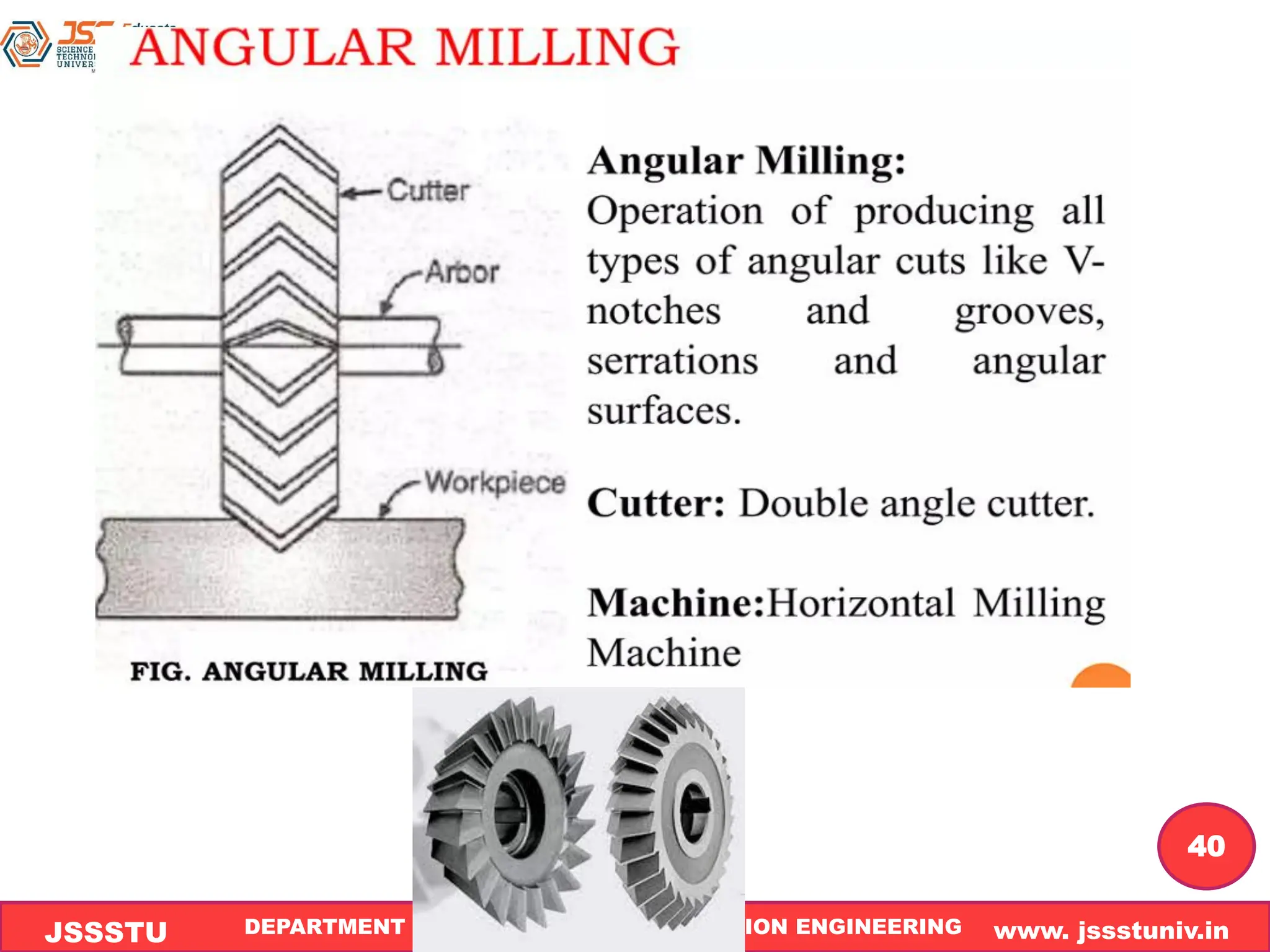
The document outlines the syllabus and details related to shaping and milling machines, including their construction, operation, and types of milling methods. It explains the principles of milling, distinctions between up-milling and down-milling, classifications of milling machines, and various milling operations. Additionally, it covers types of milling cutters and important questions pertaining to milling concepts.