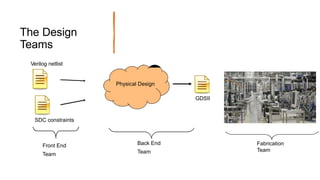
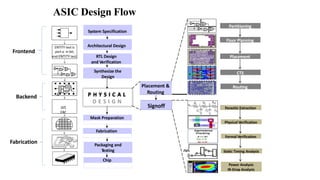
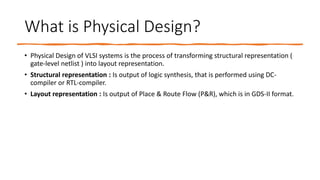
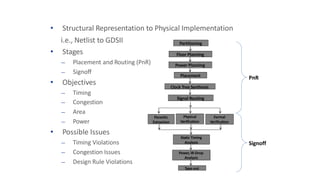
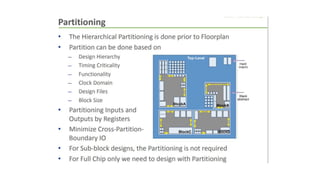
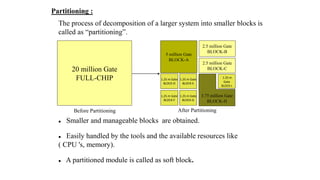
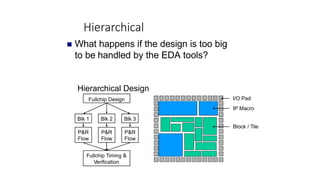
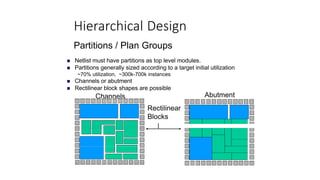
This document provides an overview of the physical design flow for an ASIC chip. It discusses the key stages of physical design including partitioning, floorplanning, placement and routing (PnR), signoff, and parallel verification steps. The goals of physical design are to meet timing constraints while managing congestion, area, and power. Challenges include avoiding timing violations, congestion issues, and design rule violations. Hierarchical design is also covered as a way to partition very large designs for improved runtime and turnaround time.