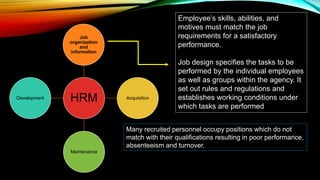
This document discusses the functions of human resource management (HRM) in organizations. It outlines several key functions of HRM including job organization and information, acquisition, maintenance, and development of employees. For each function, it provides details on related processes like job analysis, recruitment and selection, performance evaluation, training and development. It also discusses how the size of an organization's HRM department depends on the number of employees and resources. In small agencies, HR functions may be combined with other roles, while in large agencies there are often separate and specialized HR units.