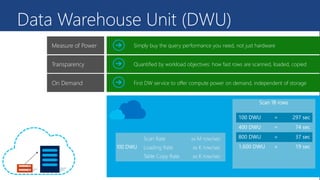
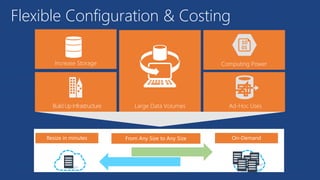
This document provides an overview of Azure Data Warehouse, a cloud data warehousing service from Microsoft Azure. It discusses how Azure Data Warehouse allows users to setup data warehouse environments rapidly and scale compute power on demand to meet peak demands in a cost effective manner compared to on-premise data warehousing. Key features highlighted include enterprise-grade reliability, SQL compatibility, flexible pricing based on query performance needed via Data Warehouse Units, and the ability to handle large datasets and queries efficiently through its columnar data store technology.