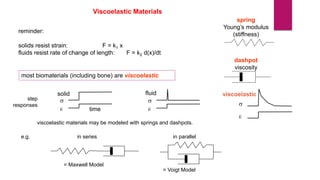
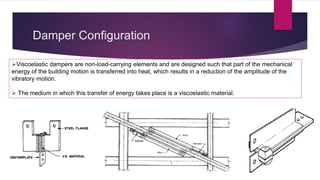
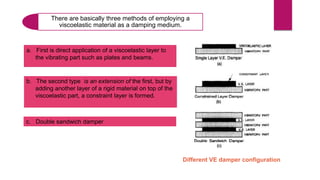
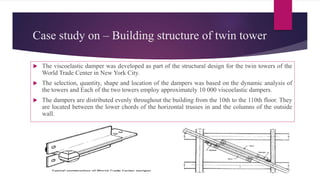
The document discusses the use of viscoelastic (VE) dampers in building structures to reduce vibrations from wind and earthquakes, highlighting their dual viscous and elastic properties. Case studies, including the Twin Towers of the World Trade Center, illustrate the effective implementation of VE dampers to enhance structural integrity and comfort. The text also covers the principles of vibration isolation, damper configurations, and various applications of viscoelastic materials in different fields.