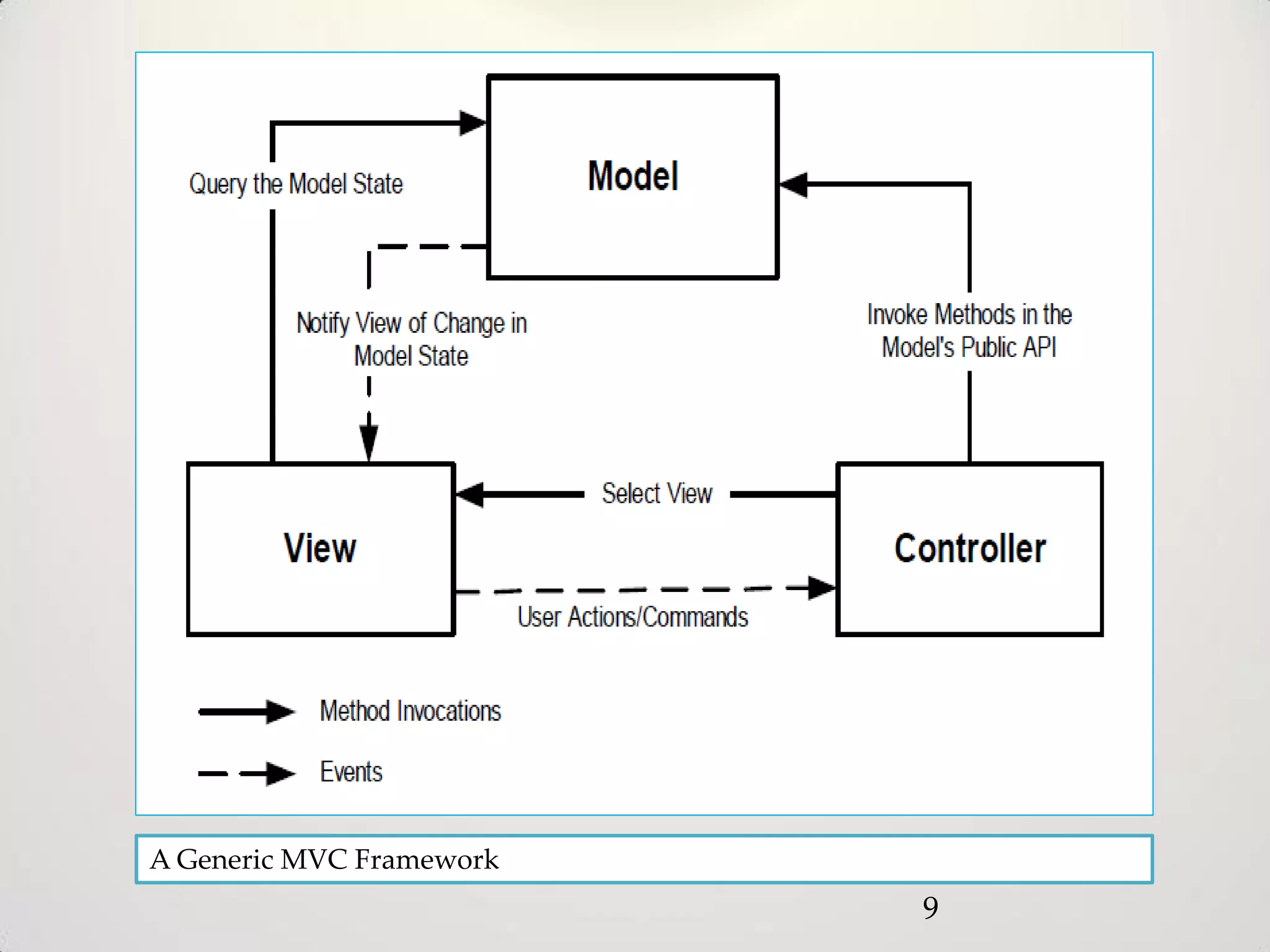
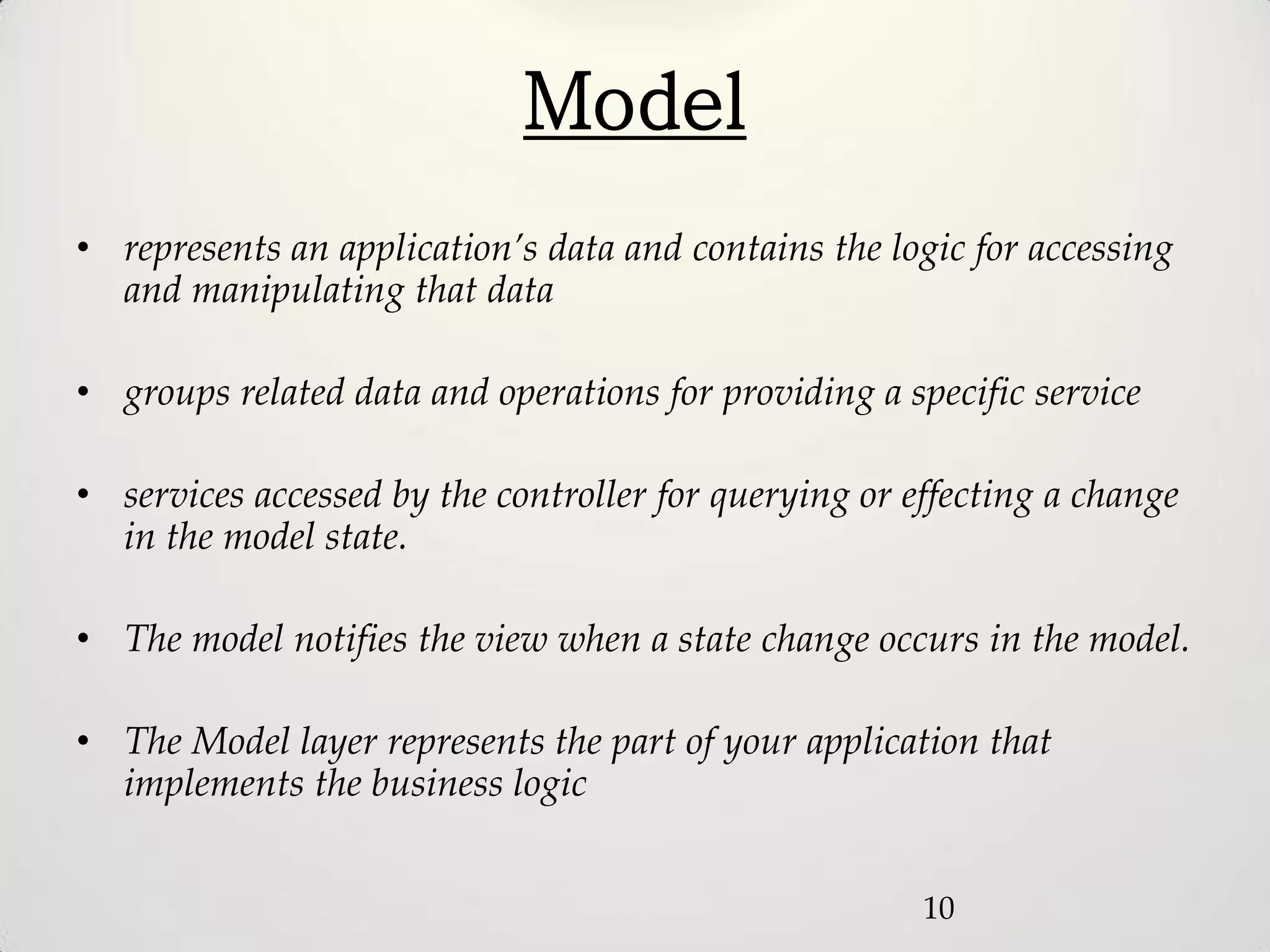
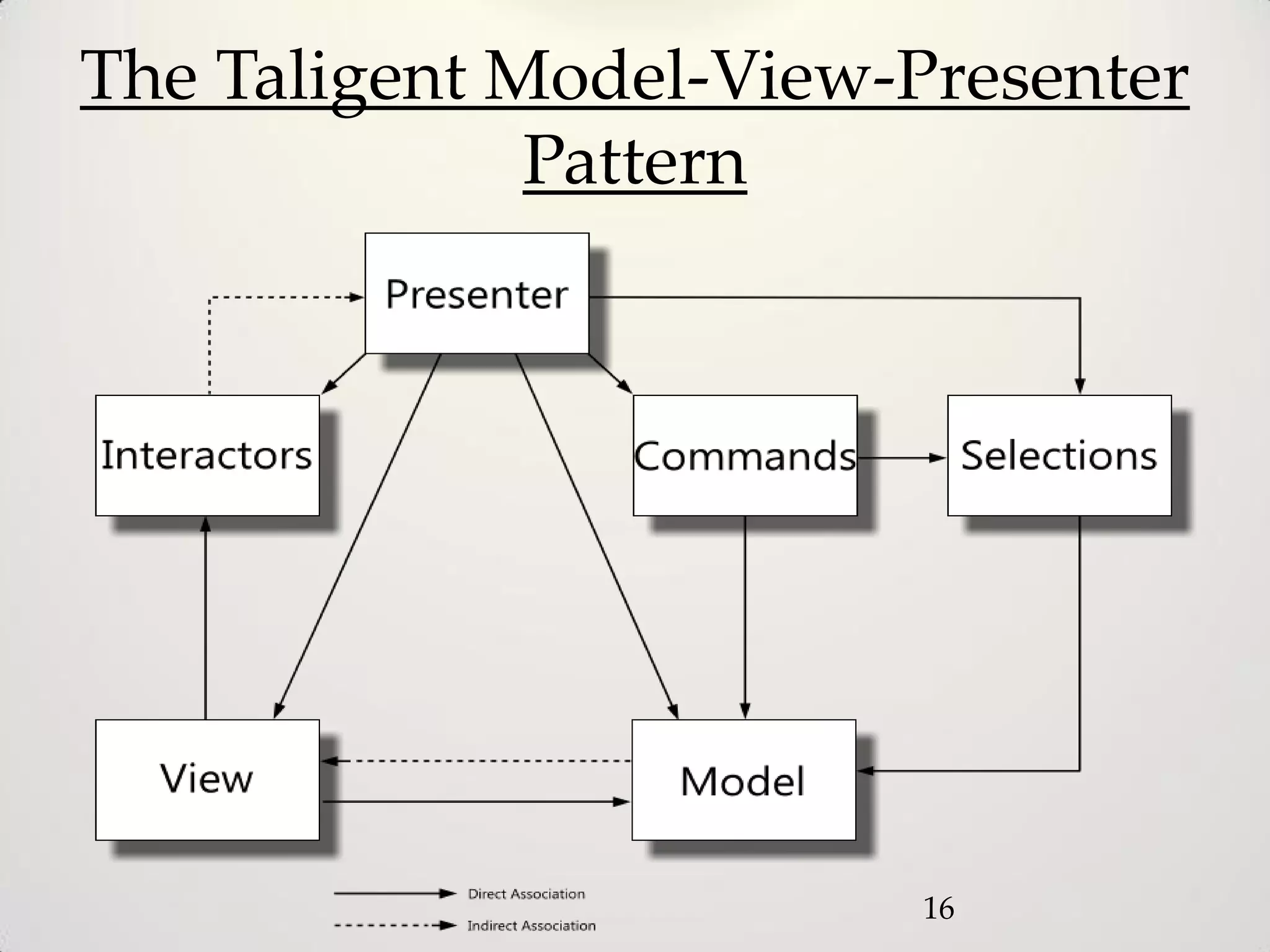
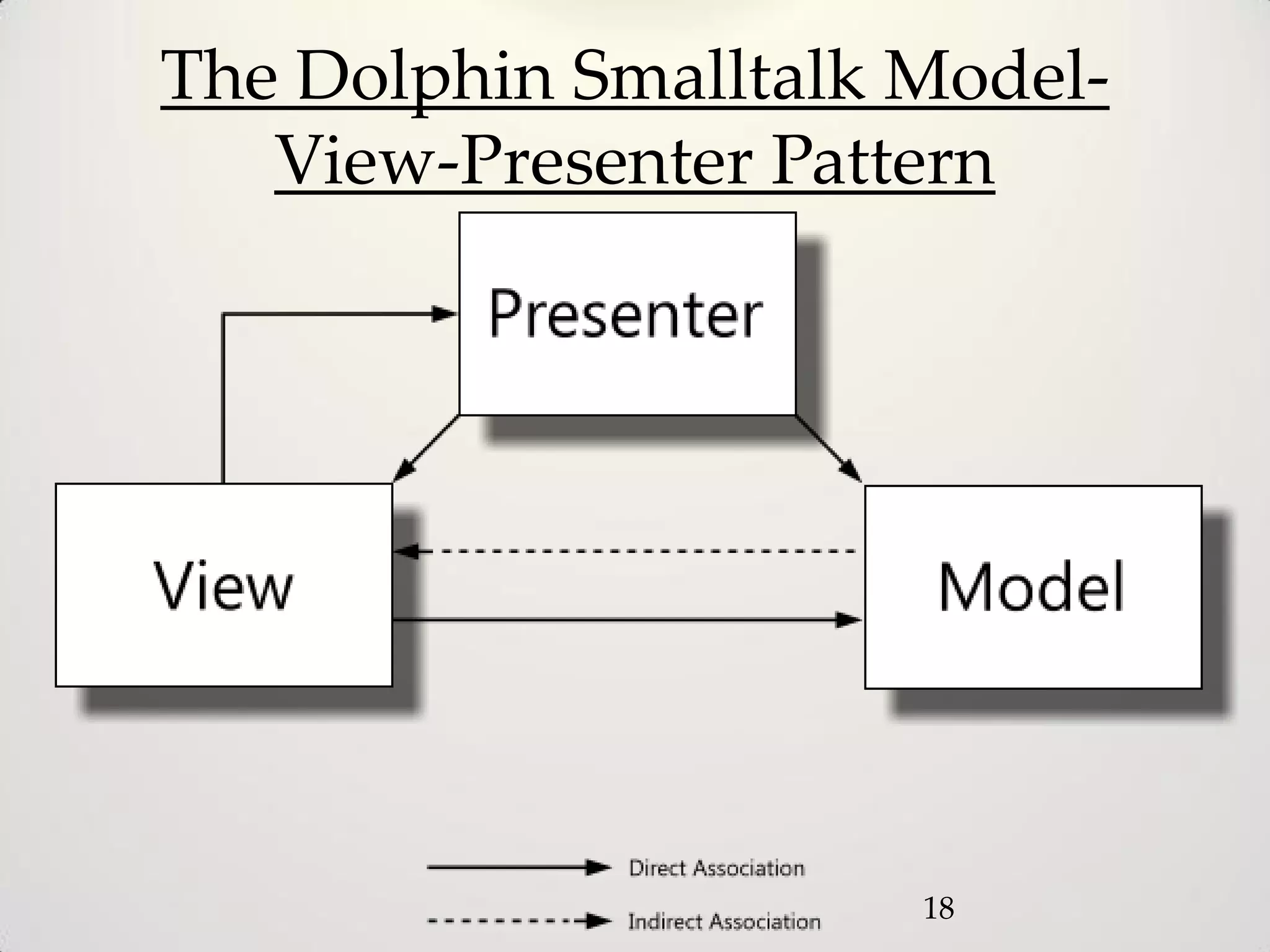
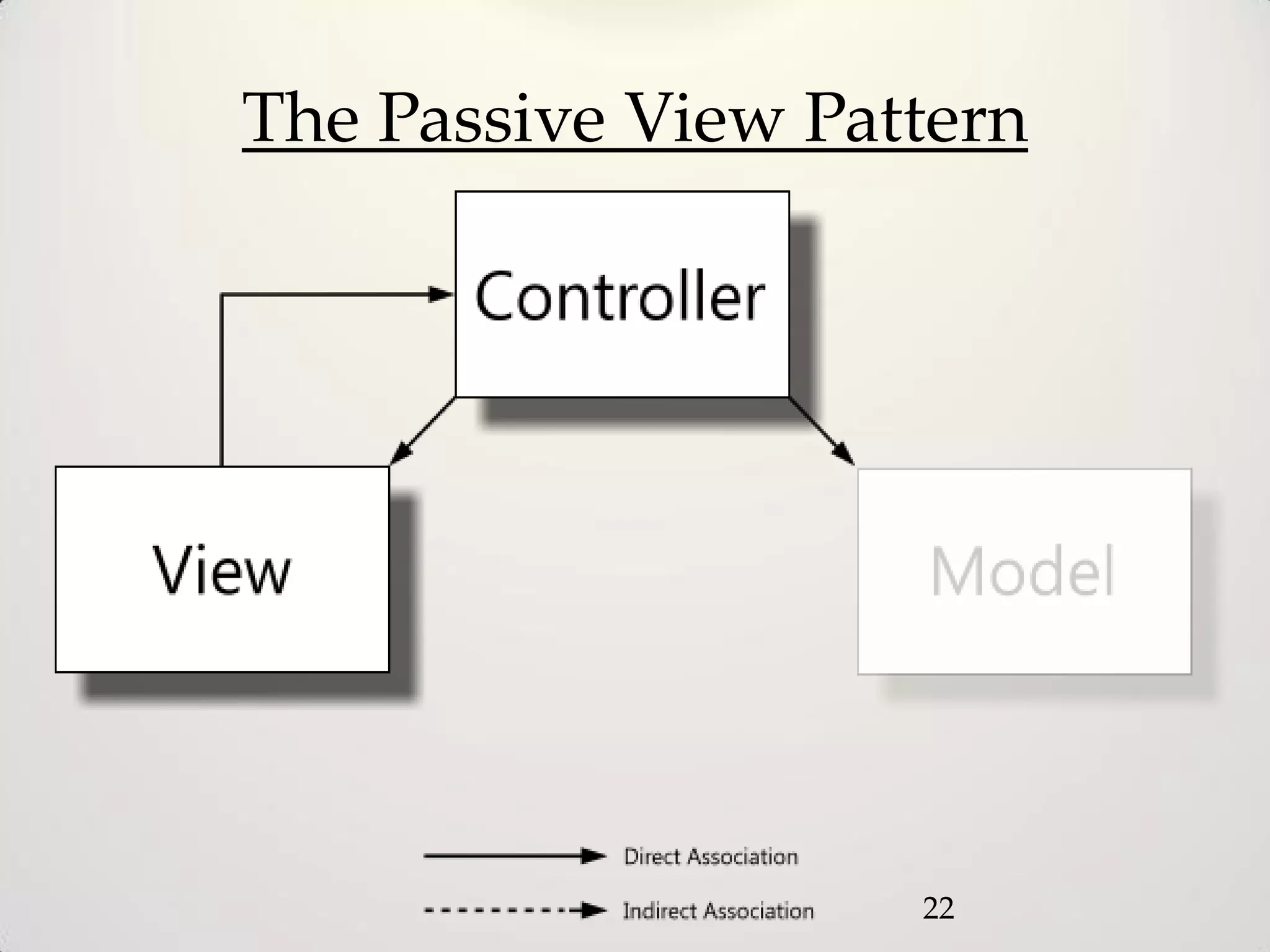
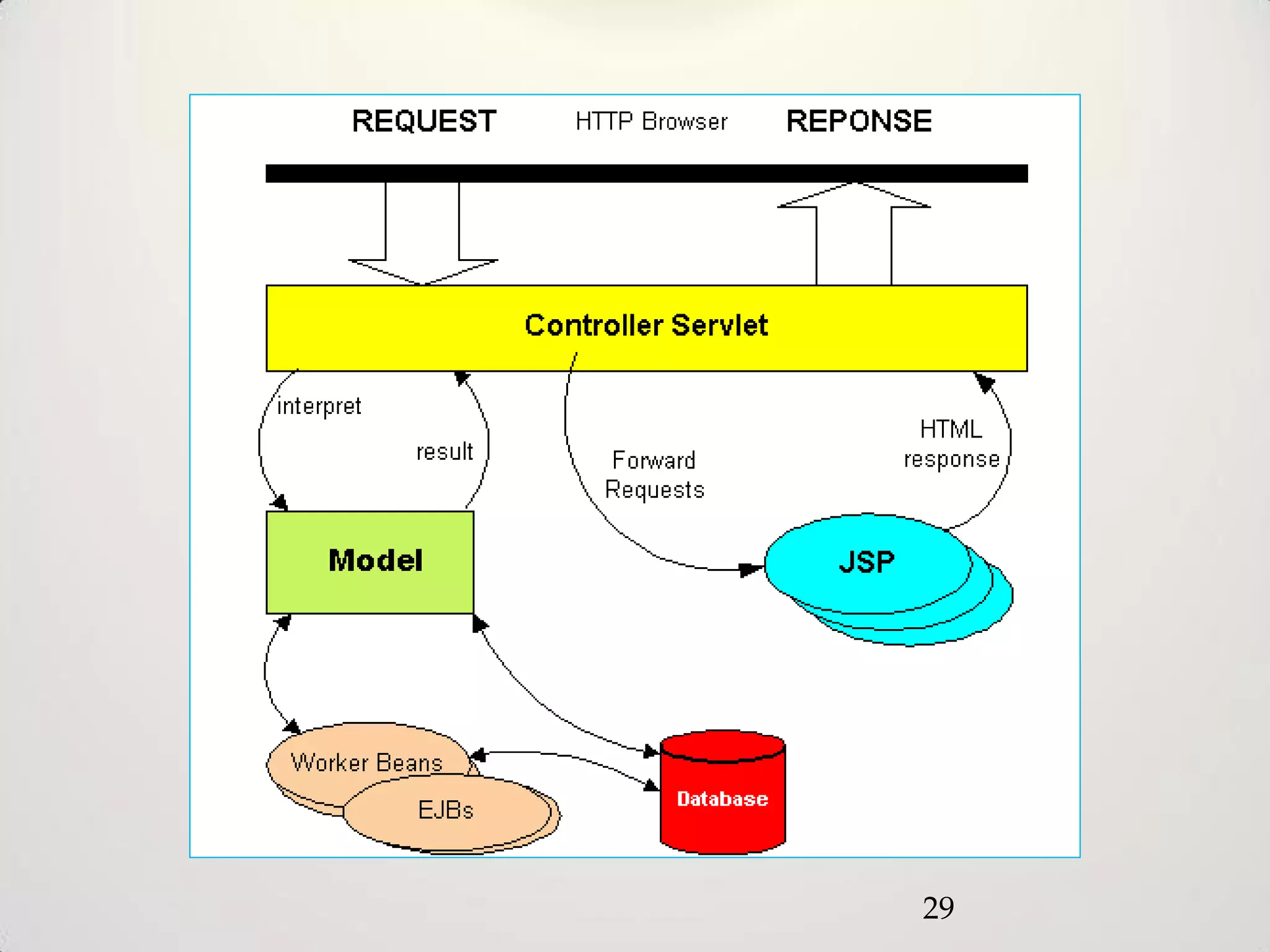
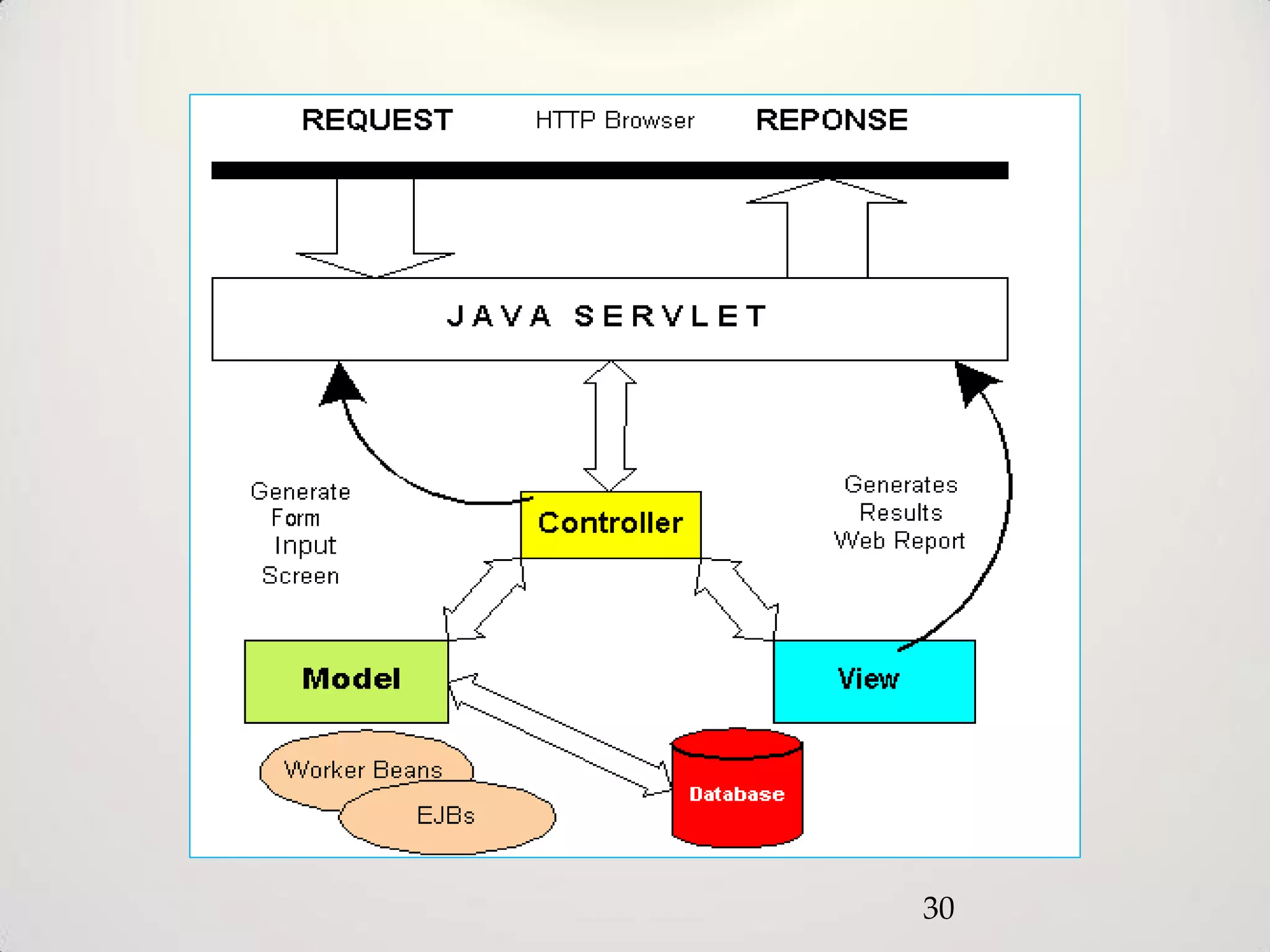
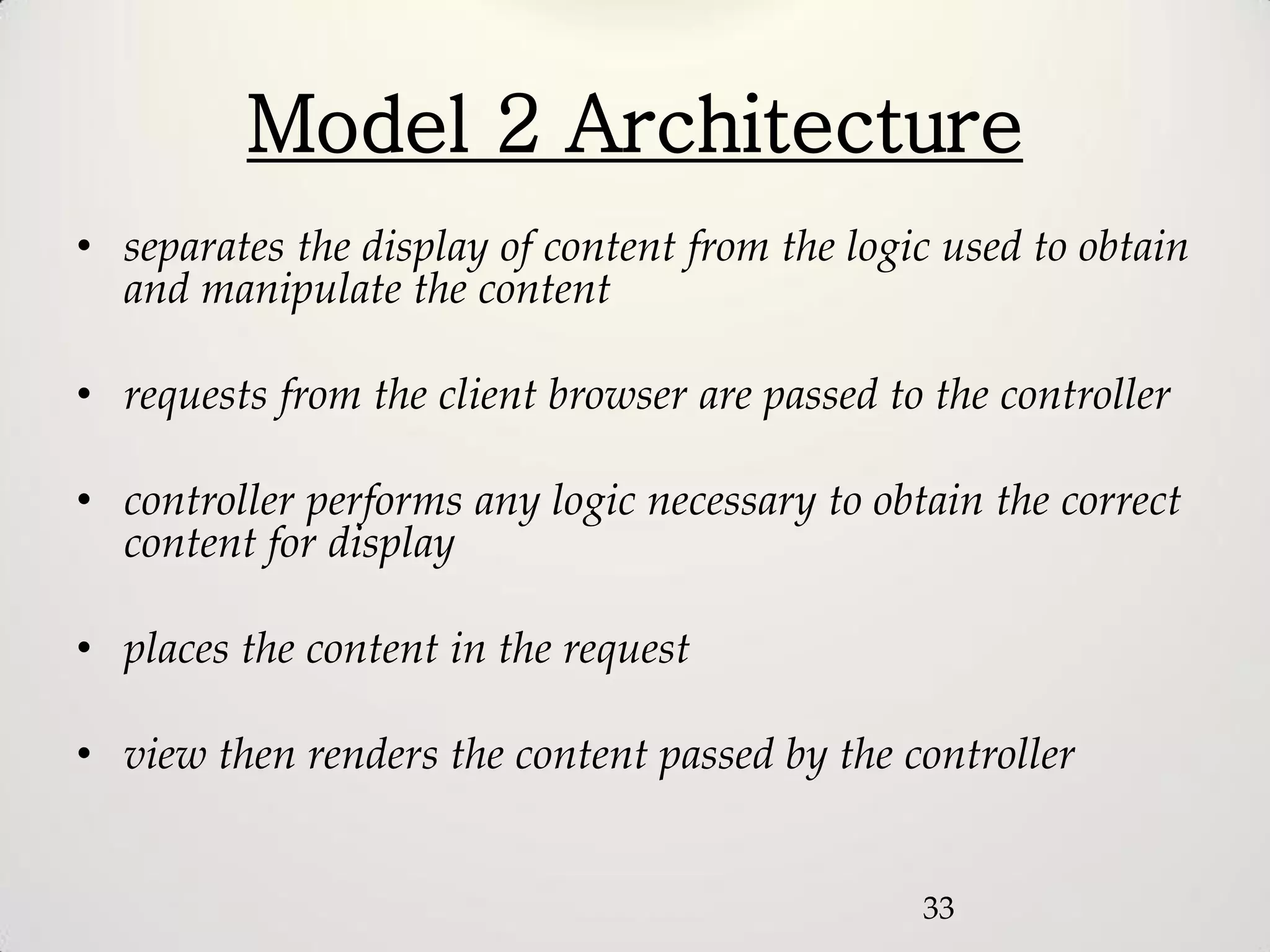
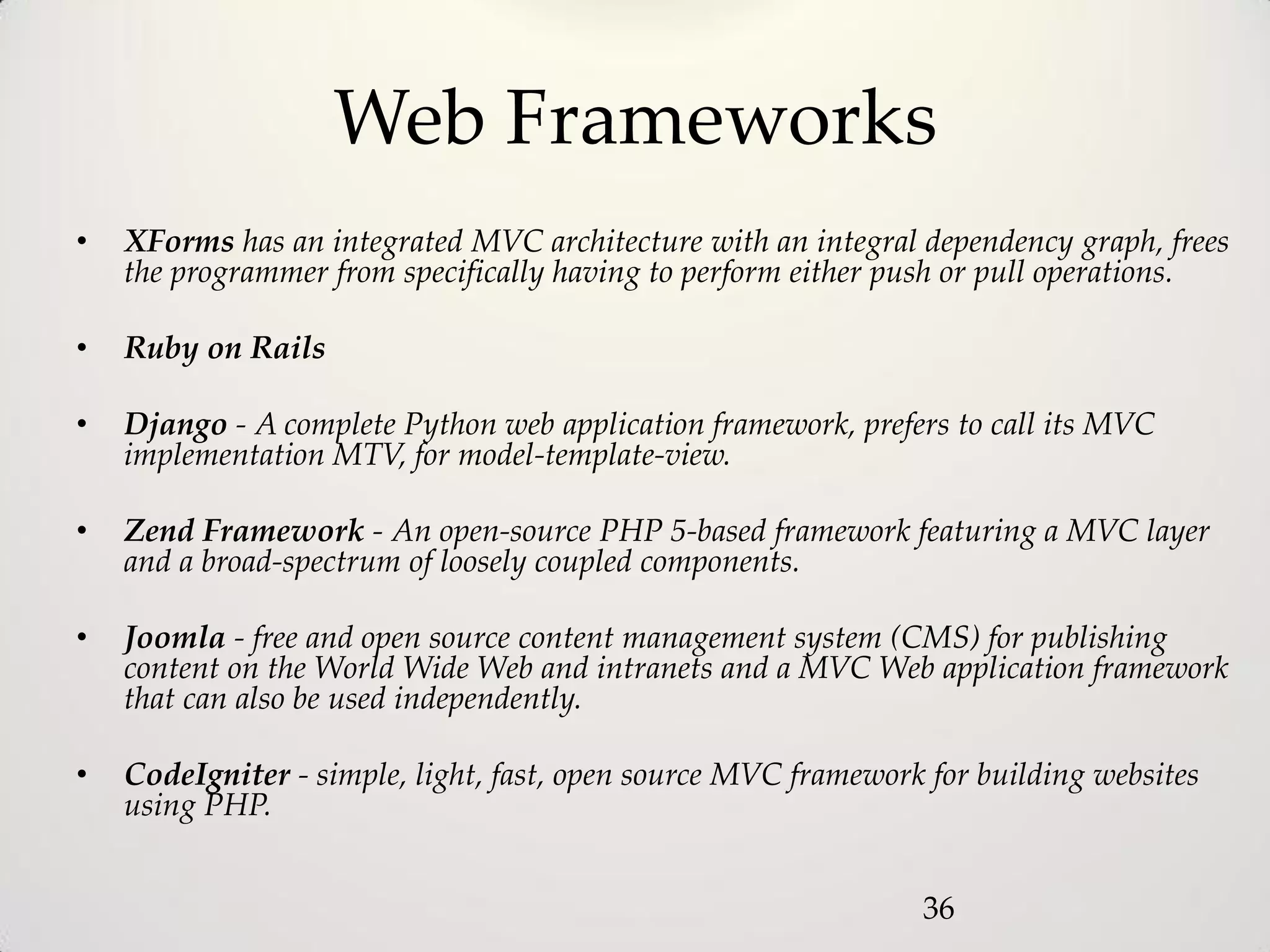
The document provides an overview of the Model-View-Controller (MVC) design pattern, explaining its components (model, view, controller) and their roles in application architecture. It discusses the benefits of using MVC, such as improved productivity through separation of concerns, and highlights alternatives like the Model-View-Presenter (MVP) pattern. Additionally, it covers various MVC implementation frameworks and their associated advantages and disadvantages.