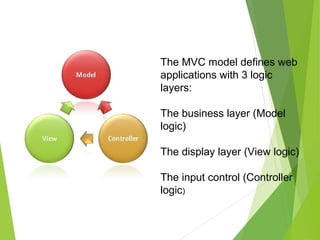
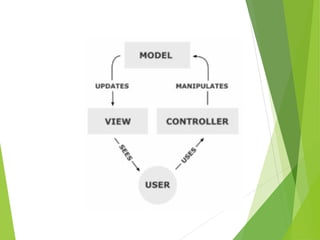
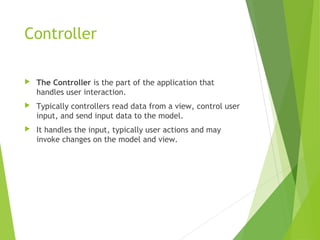
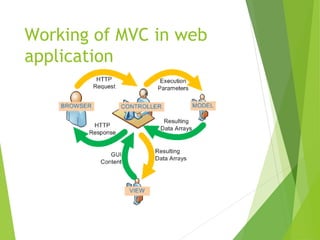
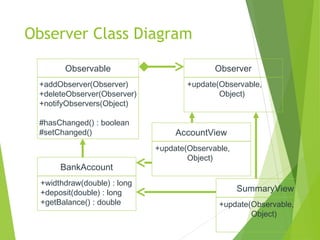
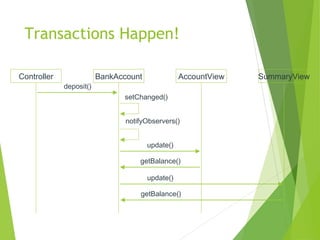
The document discusses the Model-View-Controller (MVC) design pattern for developing web applications. It describes MVC as separating the representation of information from user interaction with it. The key parts of MVC are the model, which manages application data; the view, which displays data; and the controller, which handles user input. The model notifies the view of changes, which then updates the visual elements. This allows changes in one part of the app to propagate throughout, keeping components separated and independent.