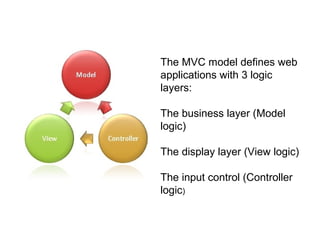
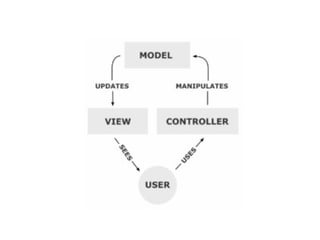
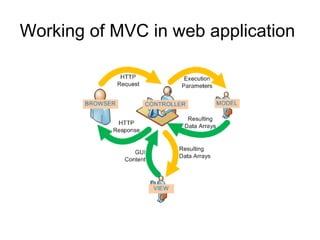
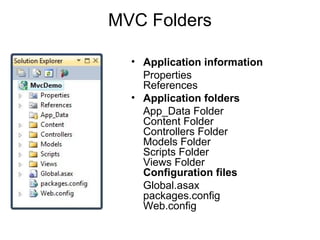
The document discusses the Model View Controller (MVC) web application architecture. MVC separates an application into three main components: the model, the view, and the controller. The model manages the core data and logic of the application. The view displays the model's data to the user. The controller interprets user input, often updating the model in response. Together these components allow for separation of concerns in building dynamic web applications.