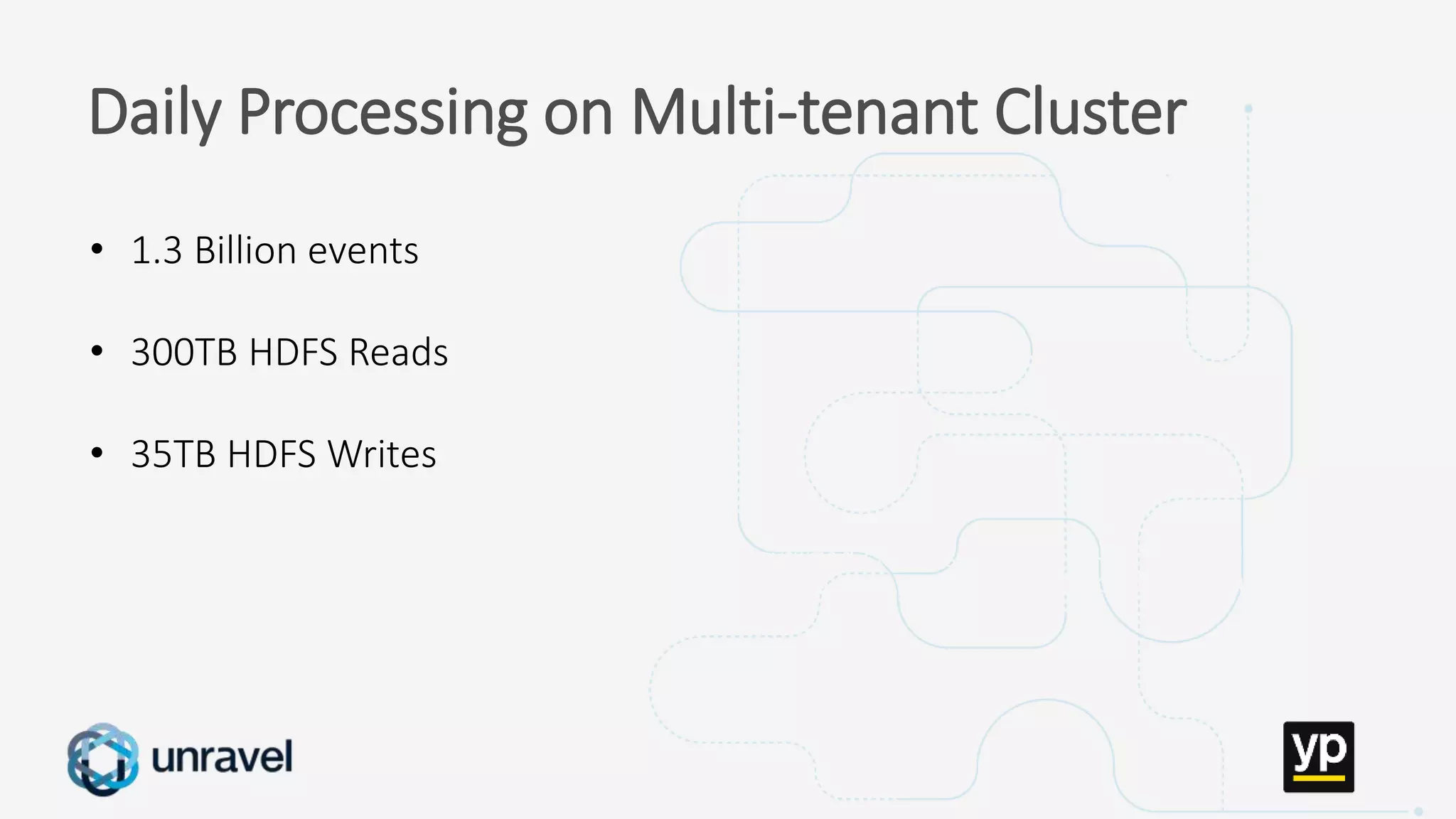
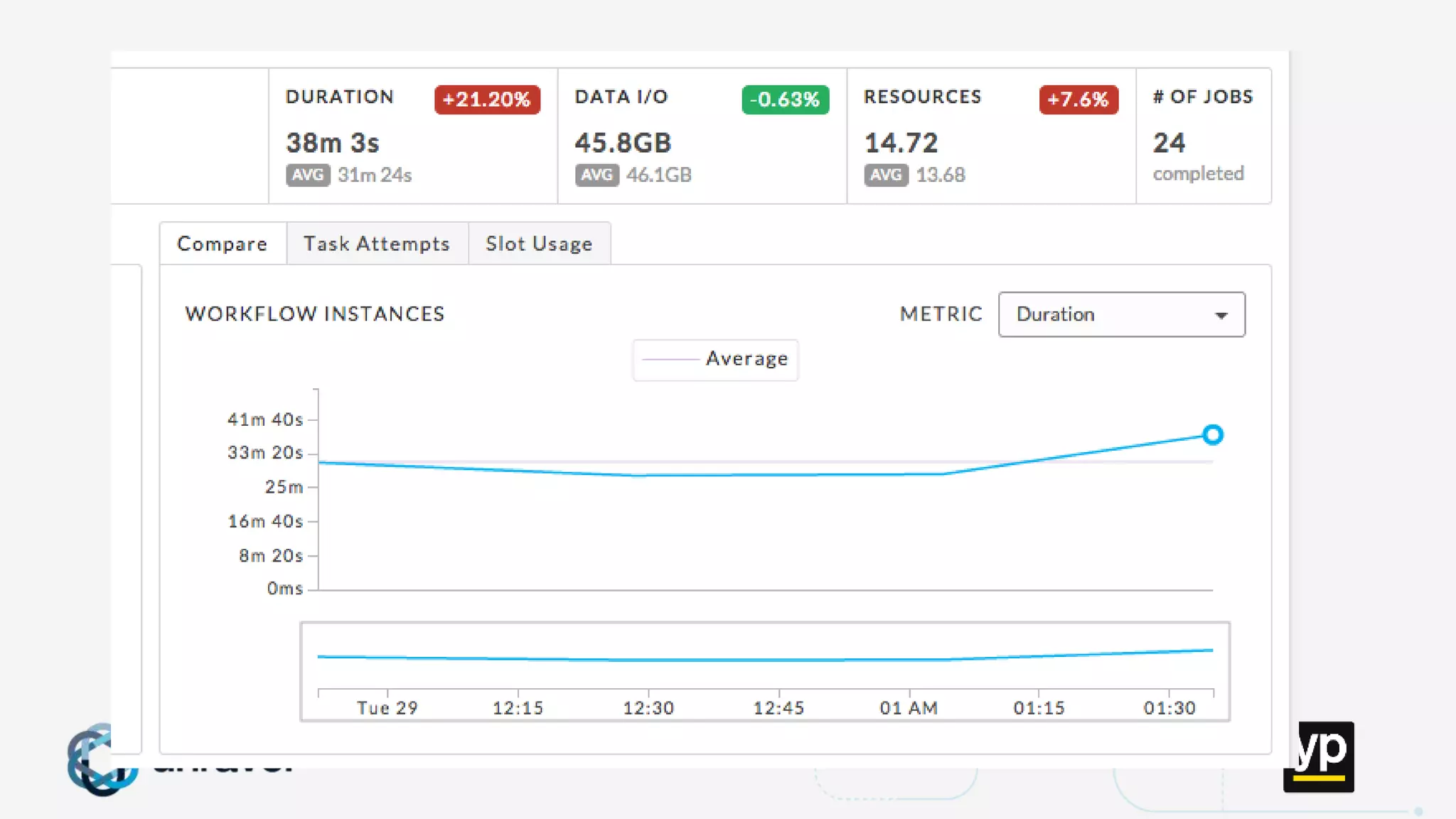
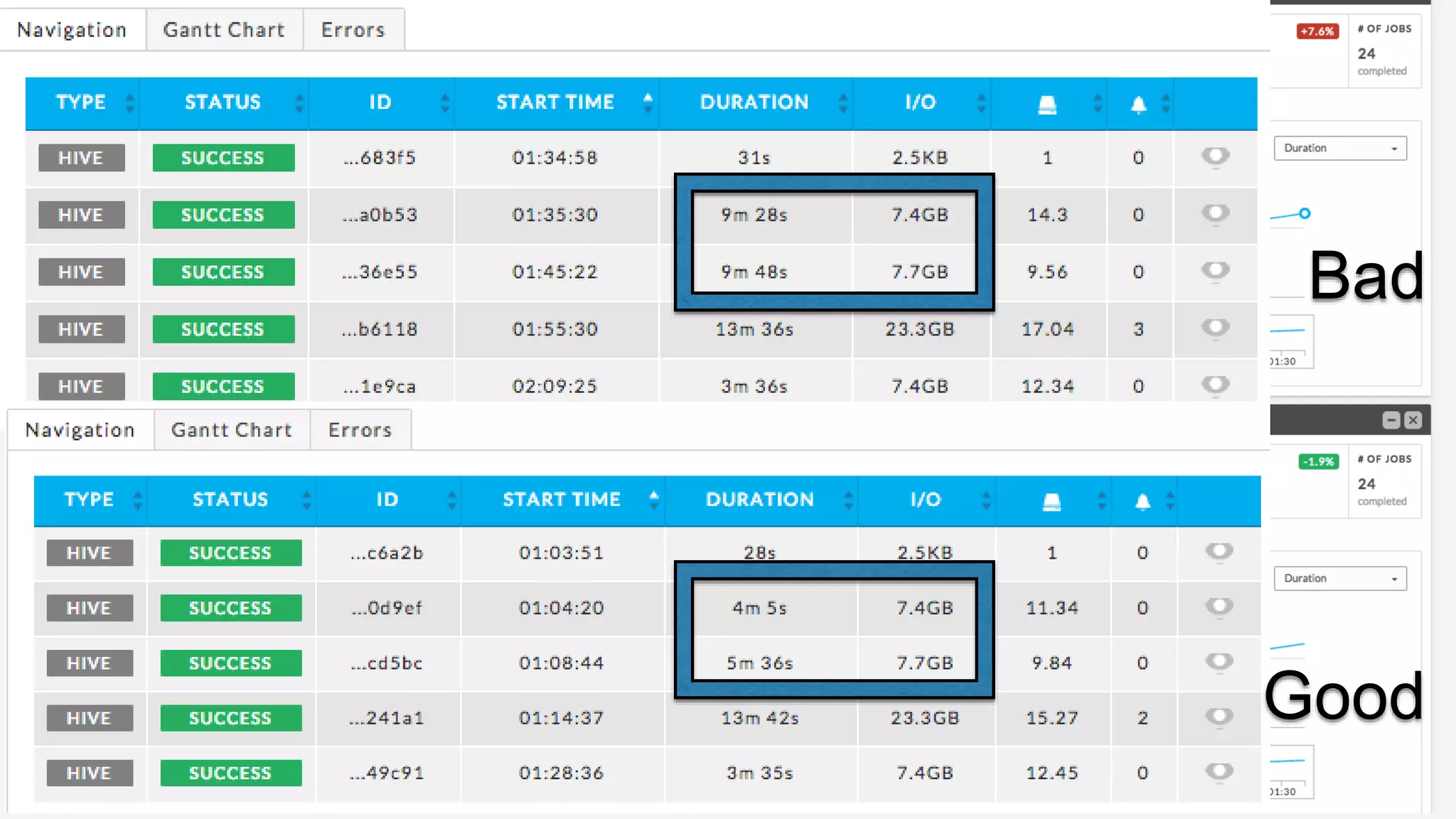
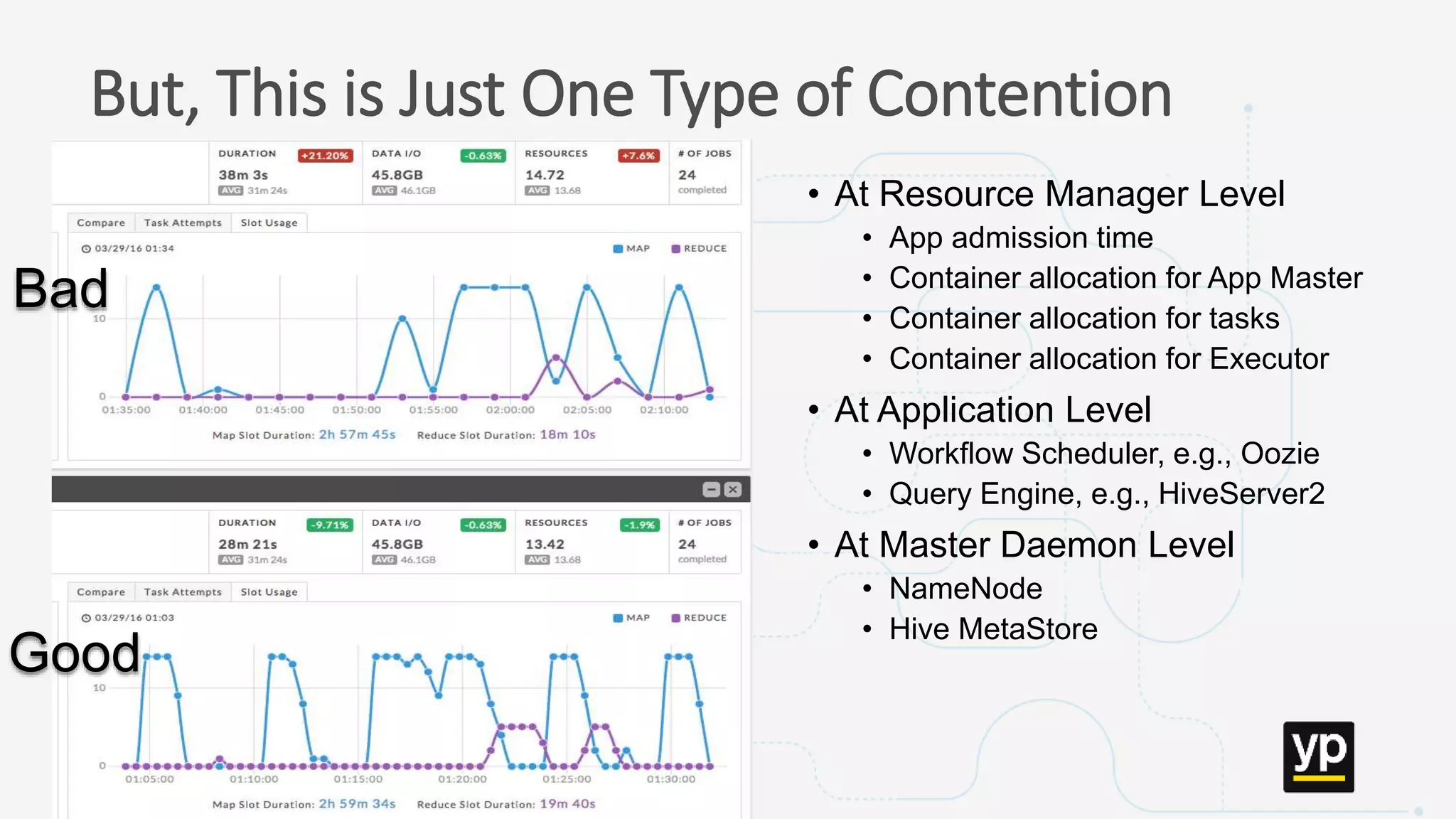
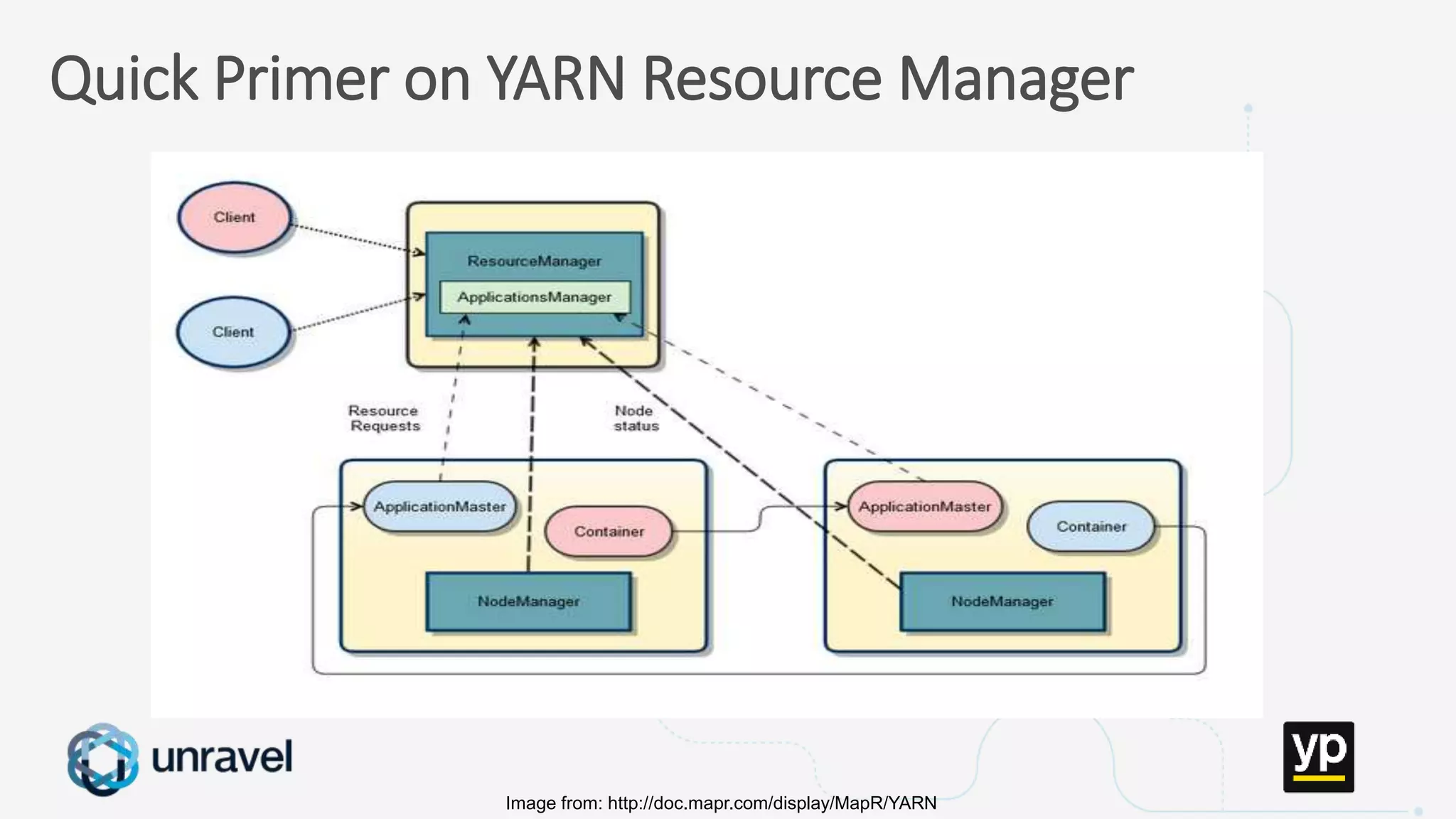
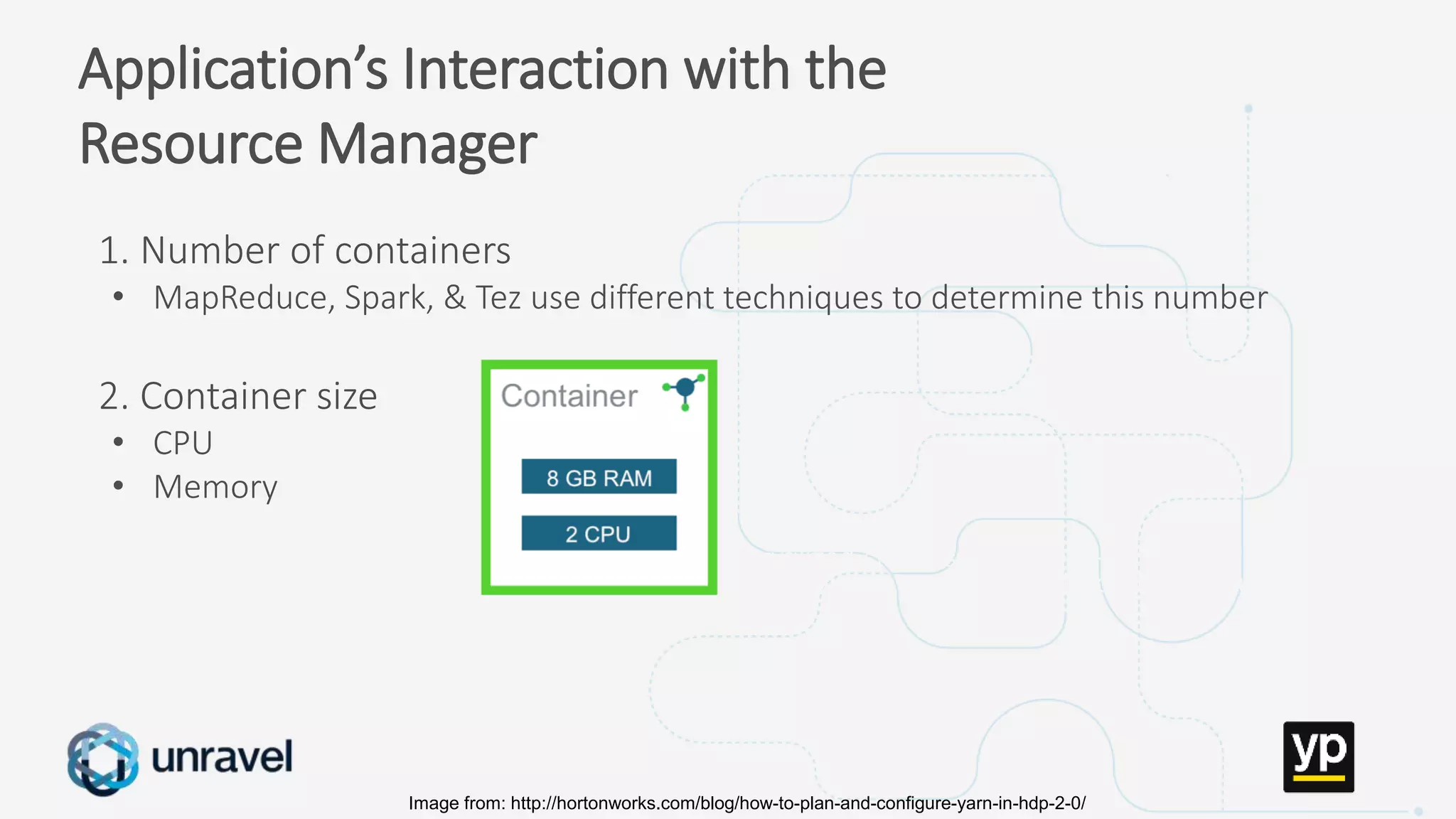
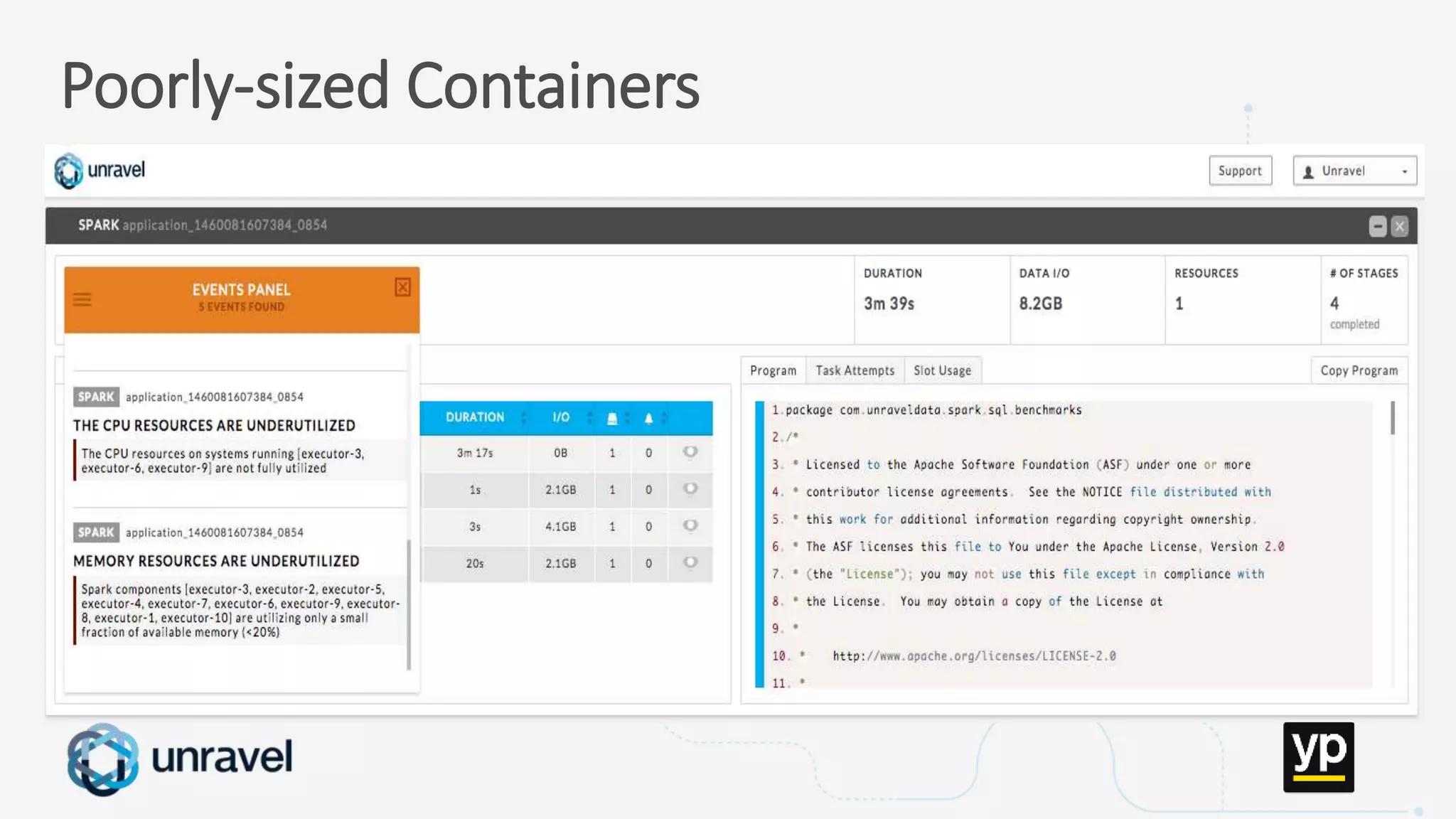
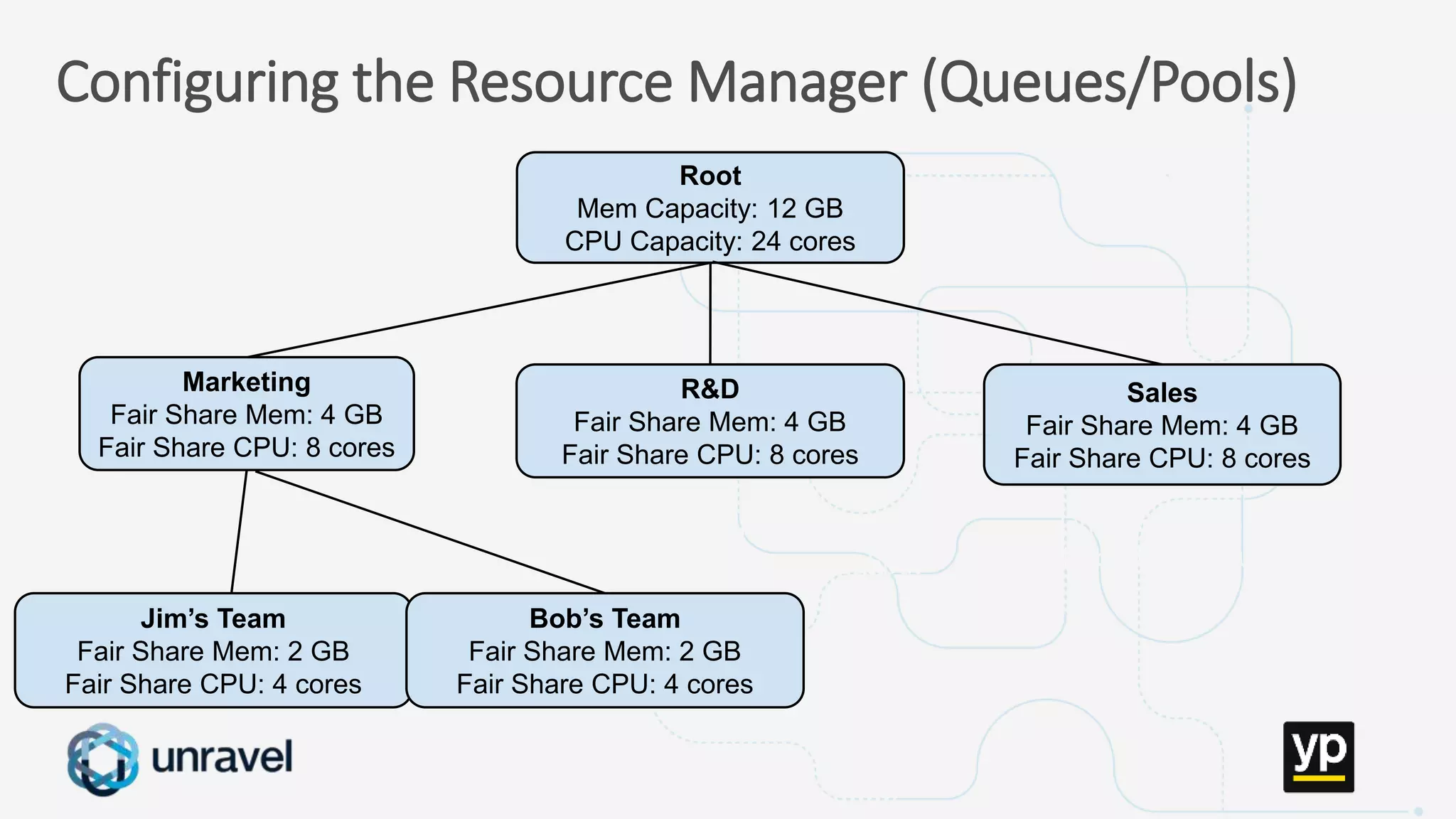
The document discusses the challenges of managing a multi-tenant Hadoop cluster over time as the cluster grows and diversifies. As the cluster scales up in size and number of users, it faces performance problems such as missed SLAs, poor application performance, underutilized resources, and low throughput. Managing such a complex cluster manually is difficult. The document proposes automating resource management and using a new interface that allows administrators to specify performance goals and ask "what-if" questions to optimize configuration settings and improve performance.