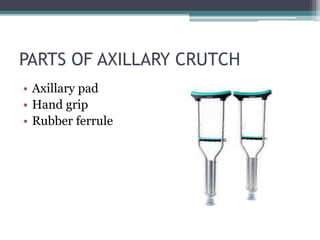
The document discusses various mobility aids designed to assist individuals with mobility and stability issues, detailing their functions, indications, and how they are selected based on patient needs. It covers types of aids like parallel bars, crutches, canes, walkers, and wheelchairs, including specific descriptions of each type, their components, and usage guidelines. Proper measurement and selection of these aids are critical to ensure patient safety and effectiveness in rehabilitation.