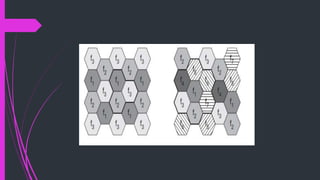
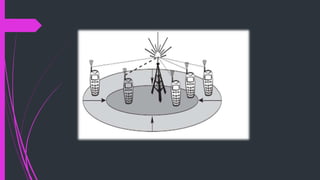
This document summarizes cellular systems and medium access control (MAC) for mobile computing. It defines cellular systems as using space division multiplexing with base stations transmitting within cell radii of varying distances. The advantages of cellular systems are higher capacity through frequency reuse, lower transmission power, and localized interference. Disadvantages include needing infrastructure and performing handovers between cells. The document then defines MAC as regulating user access to shared mediums and discusses motivations for specialized MAC protocols for mobile networks, including avoiding collisions.