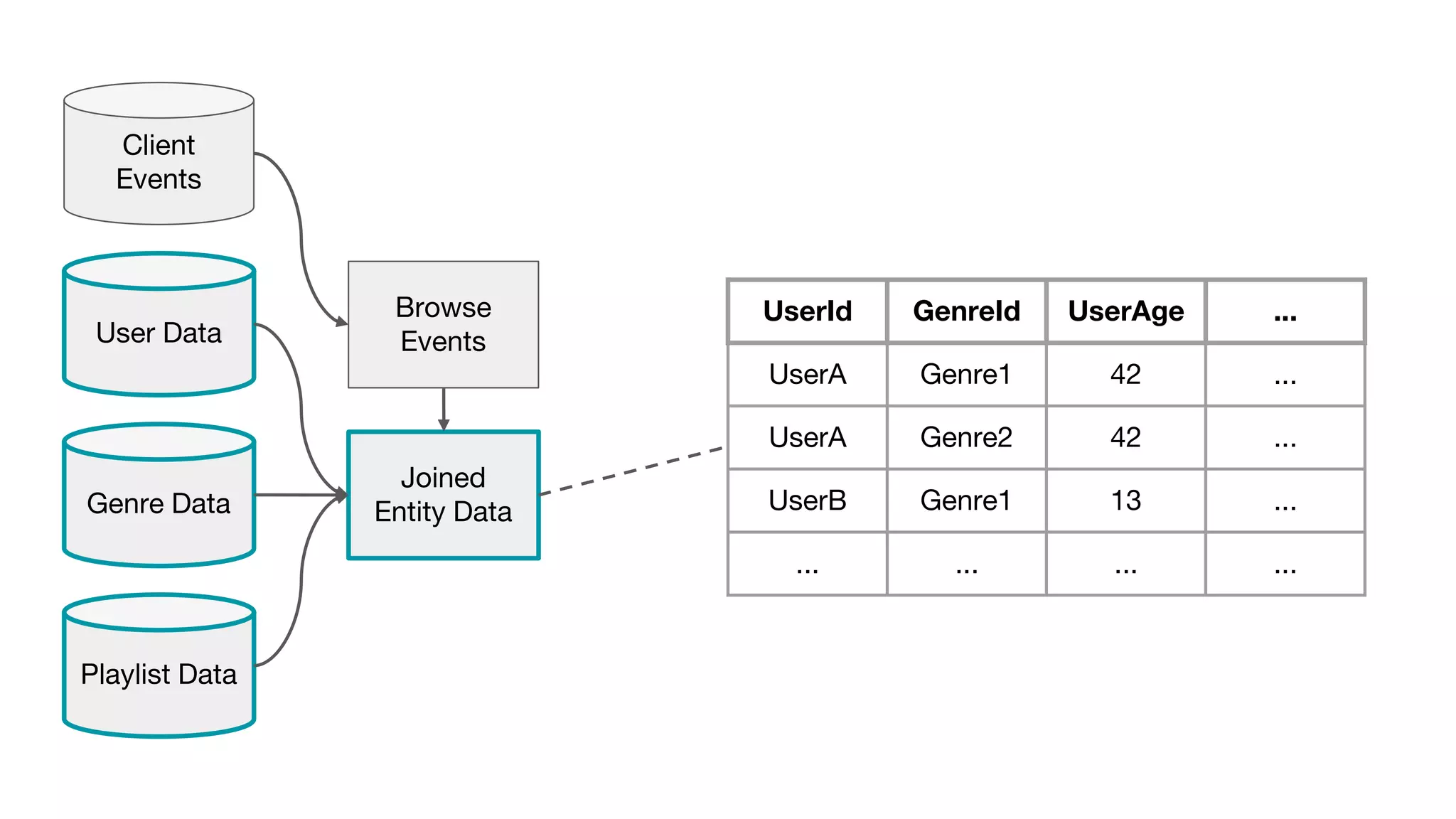
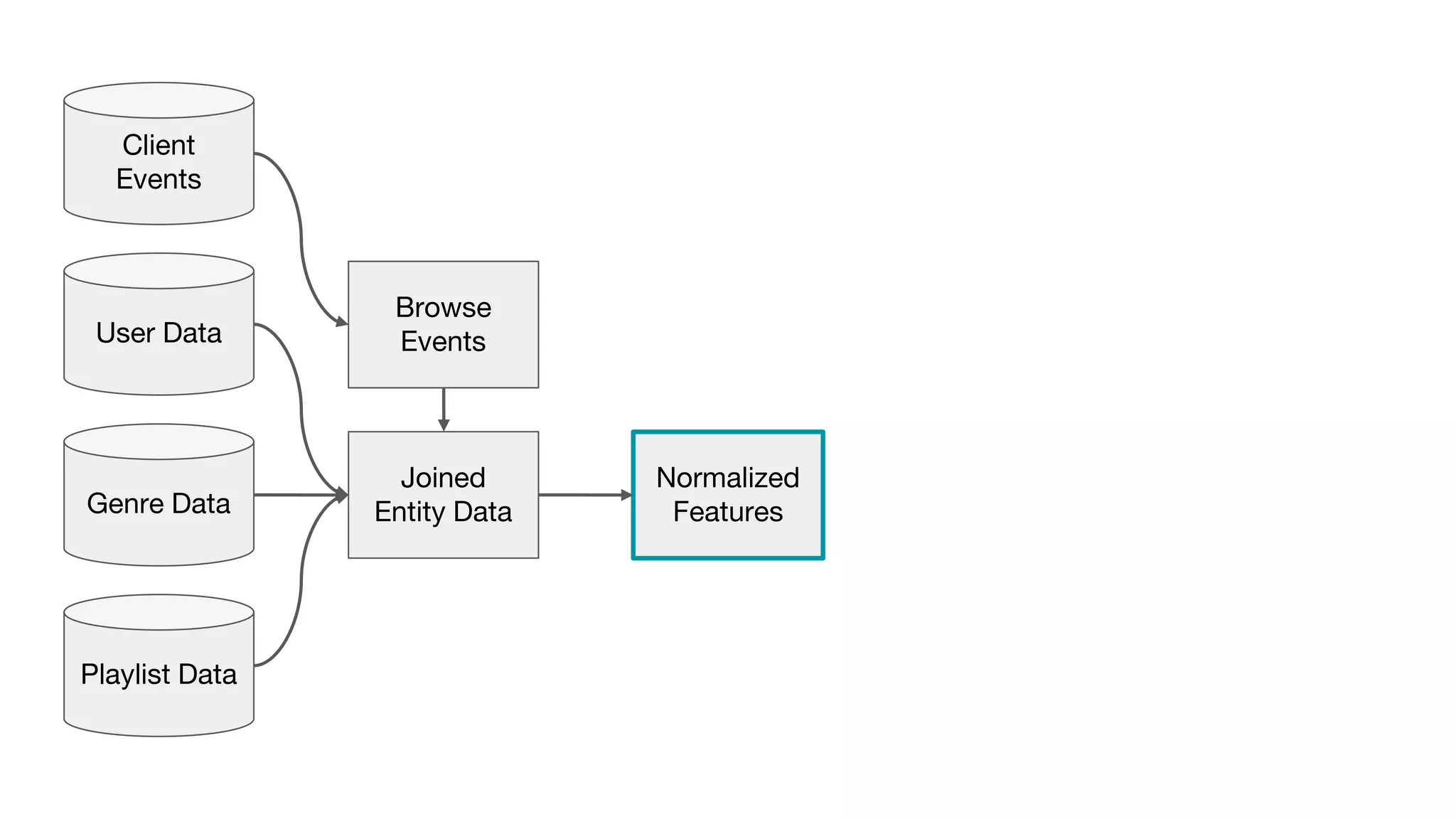
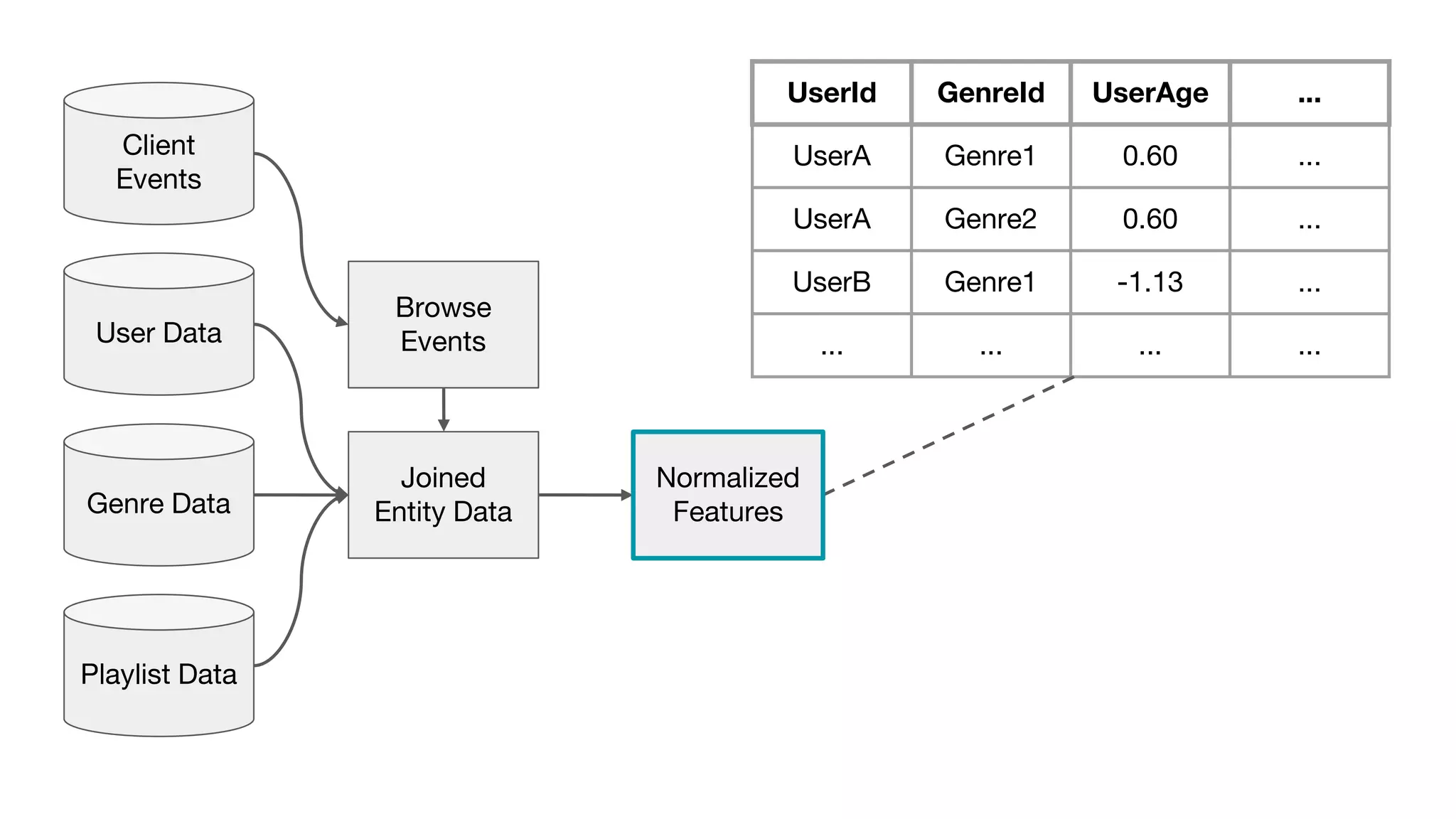
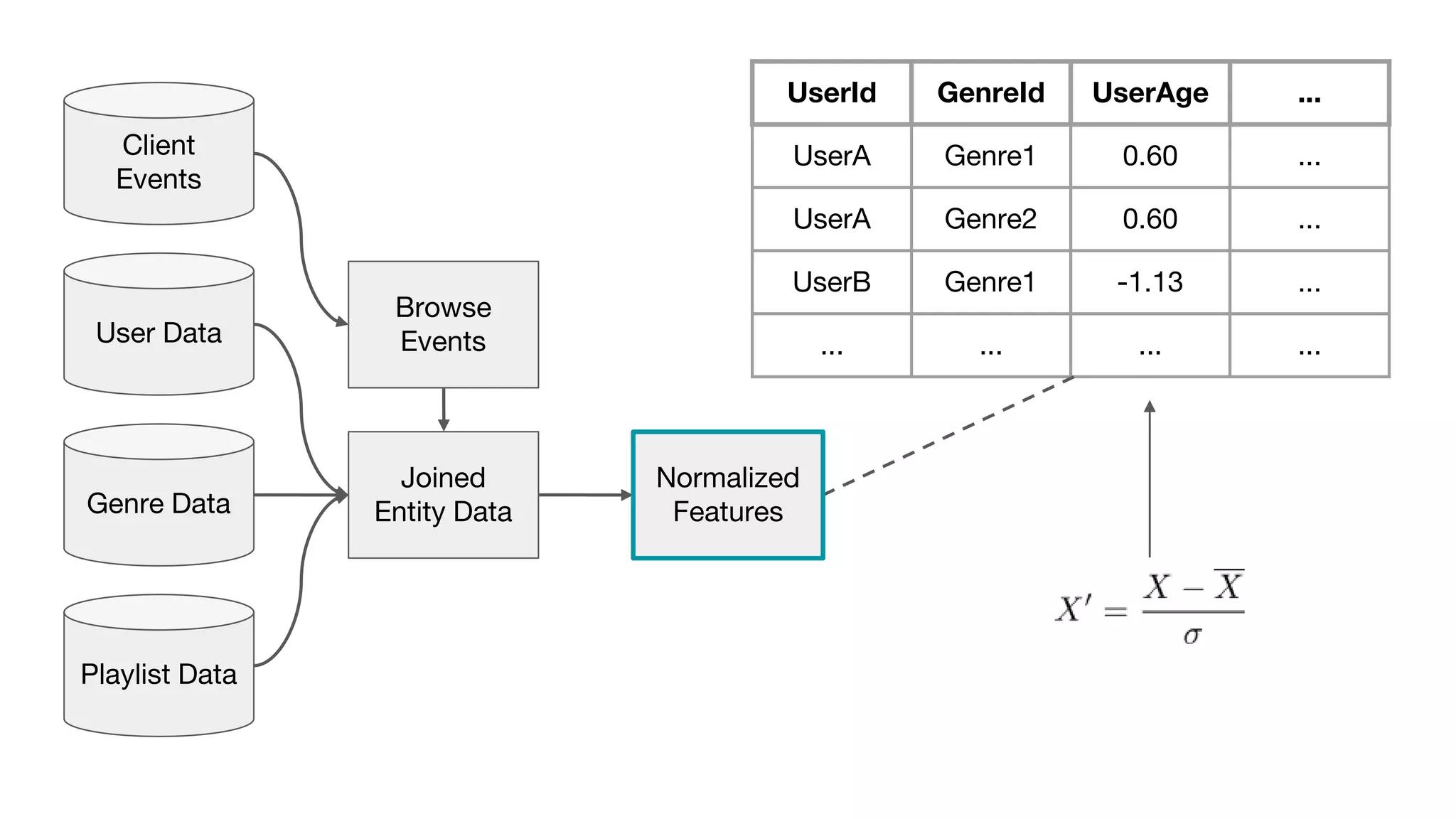
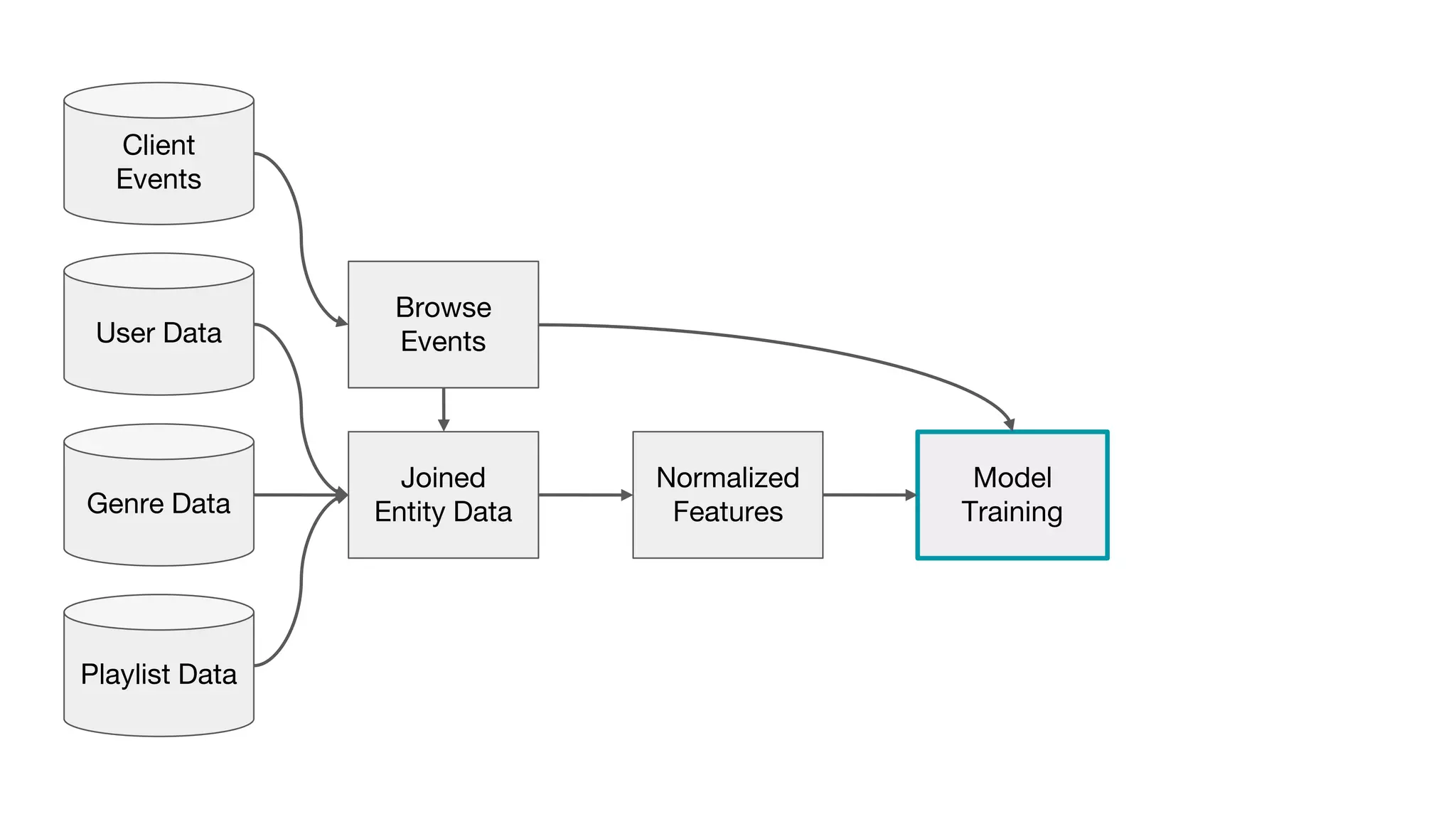
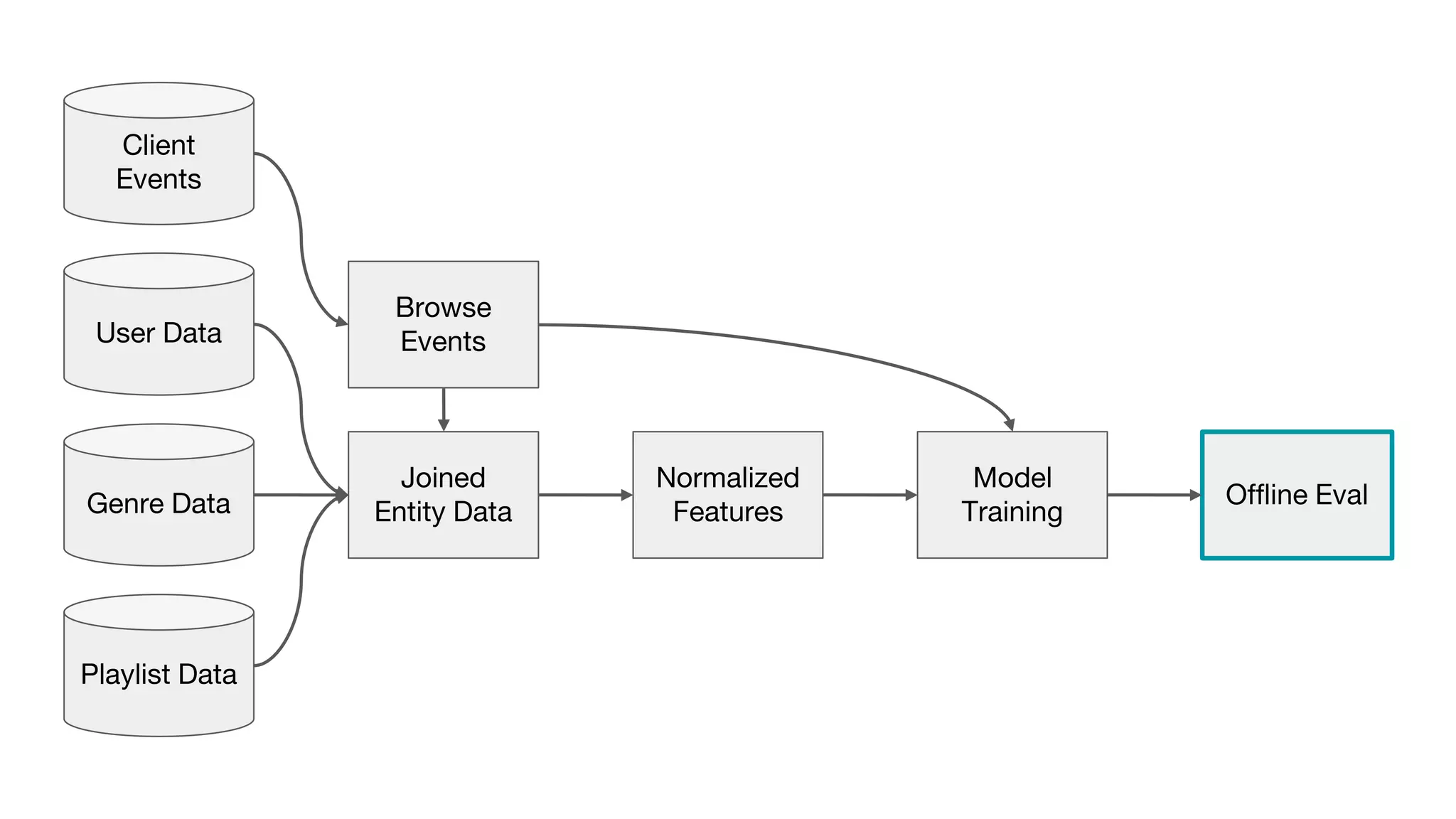
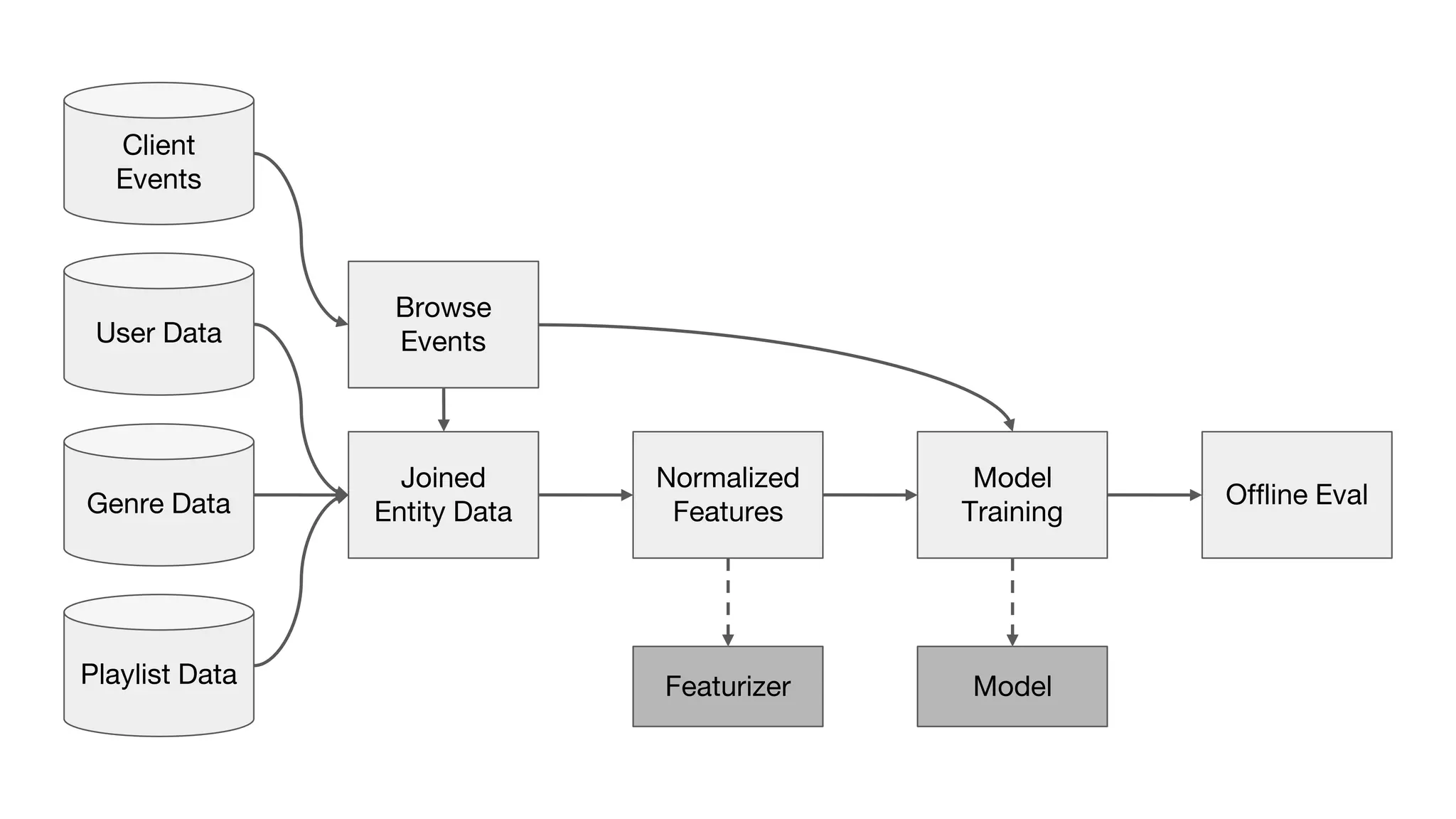
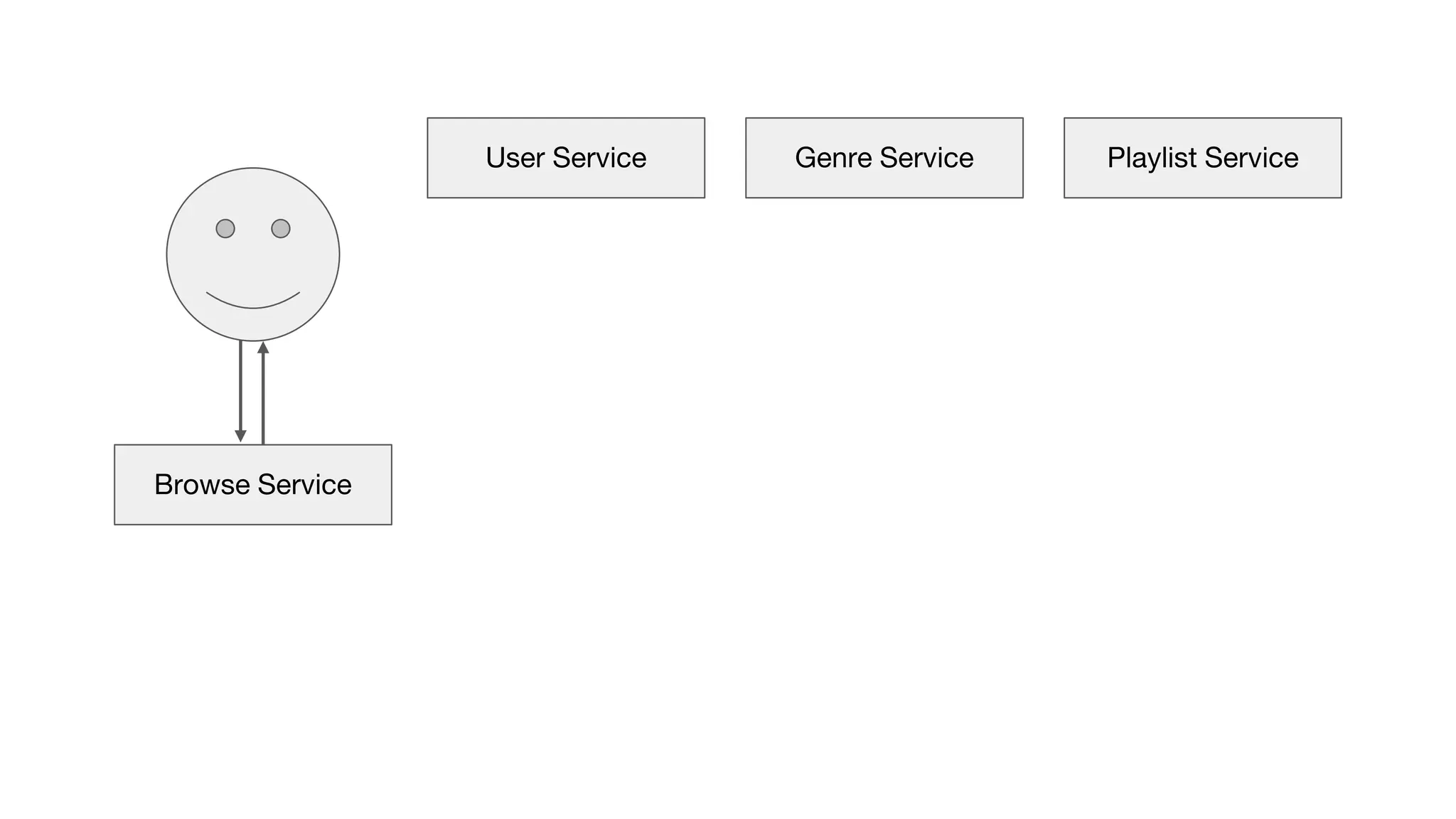
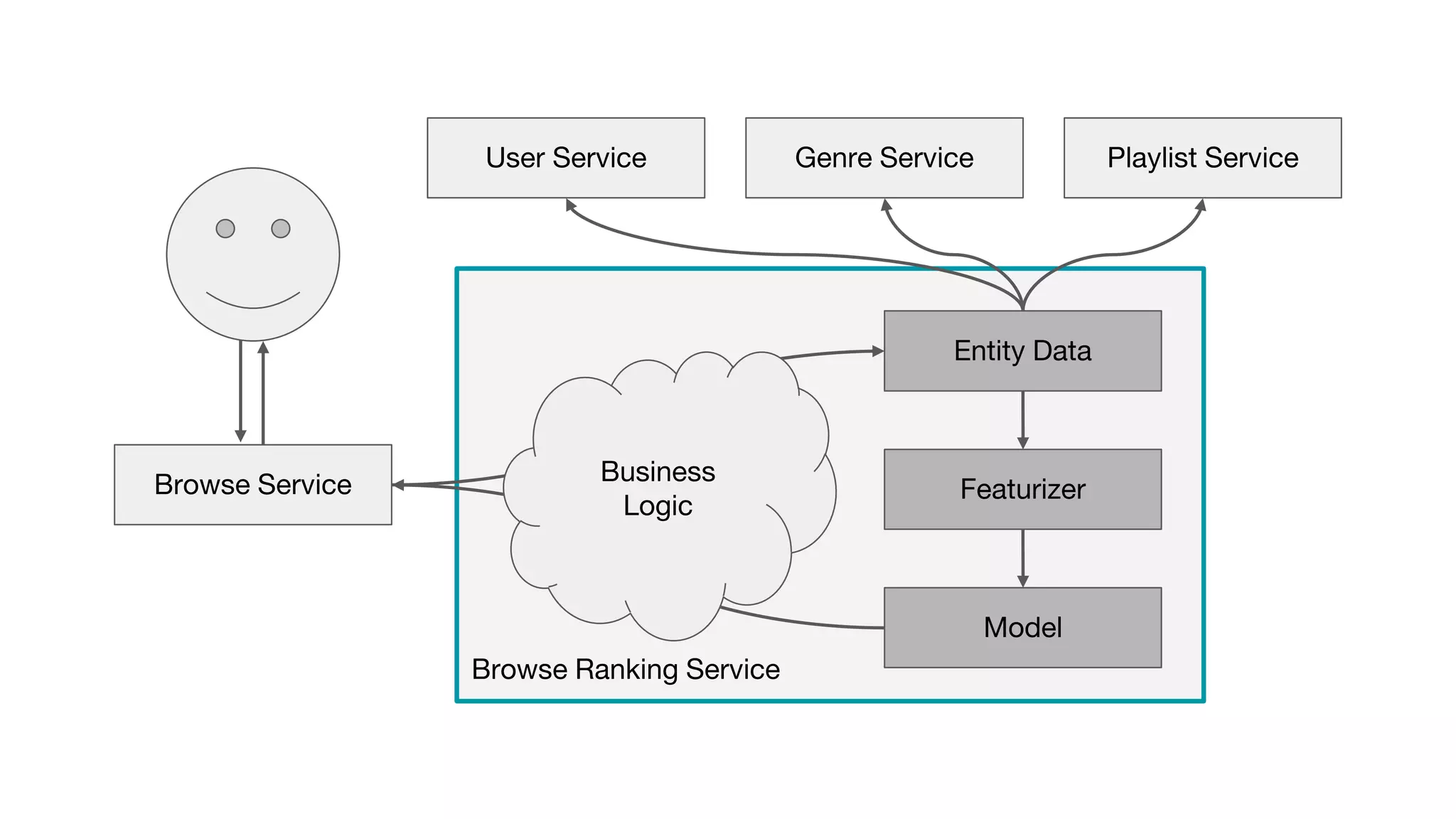
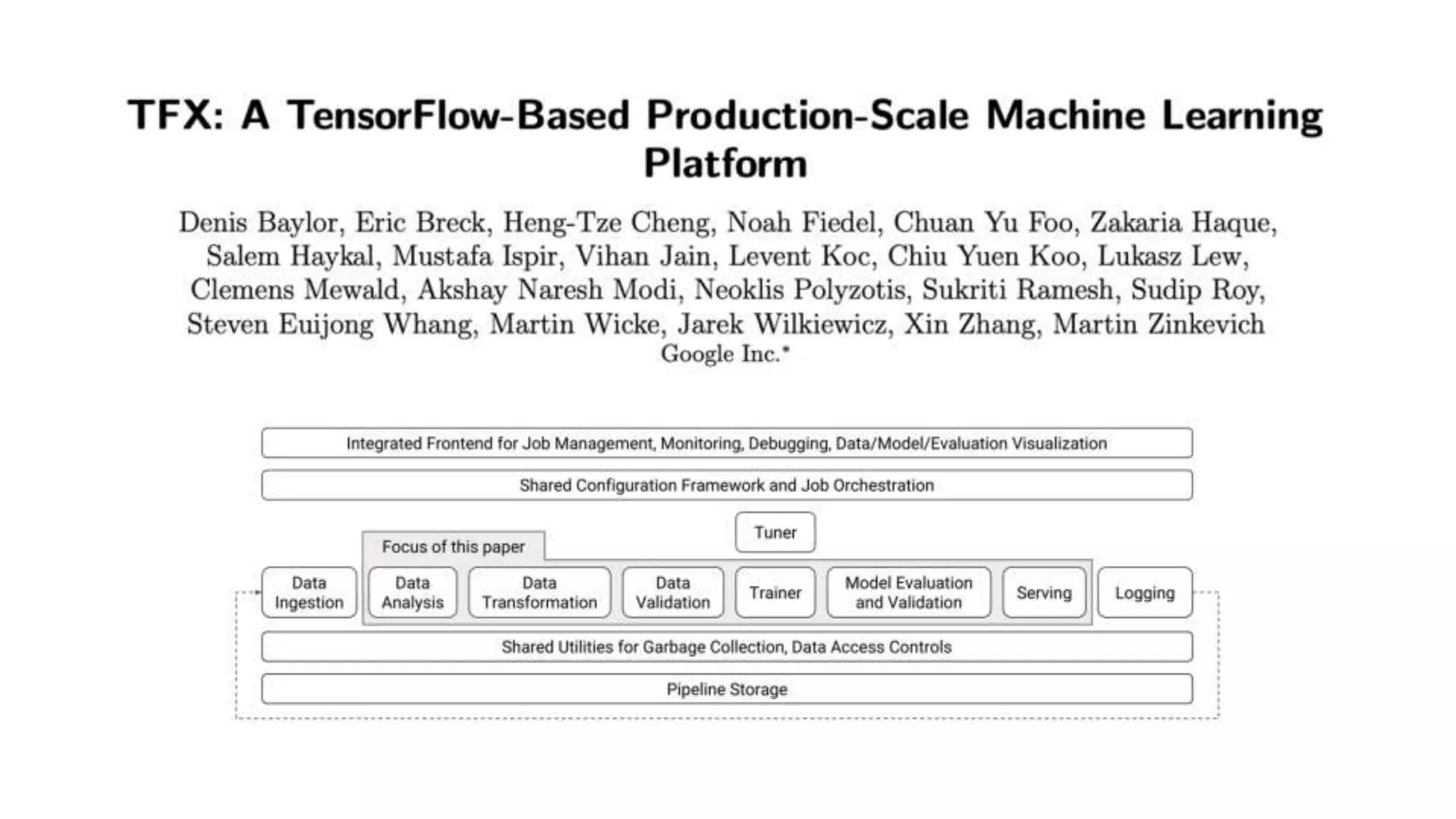
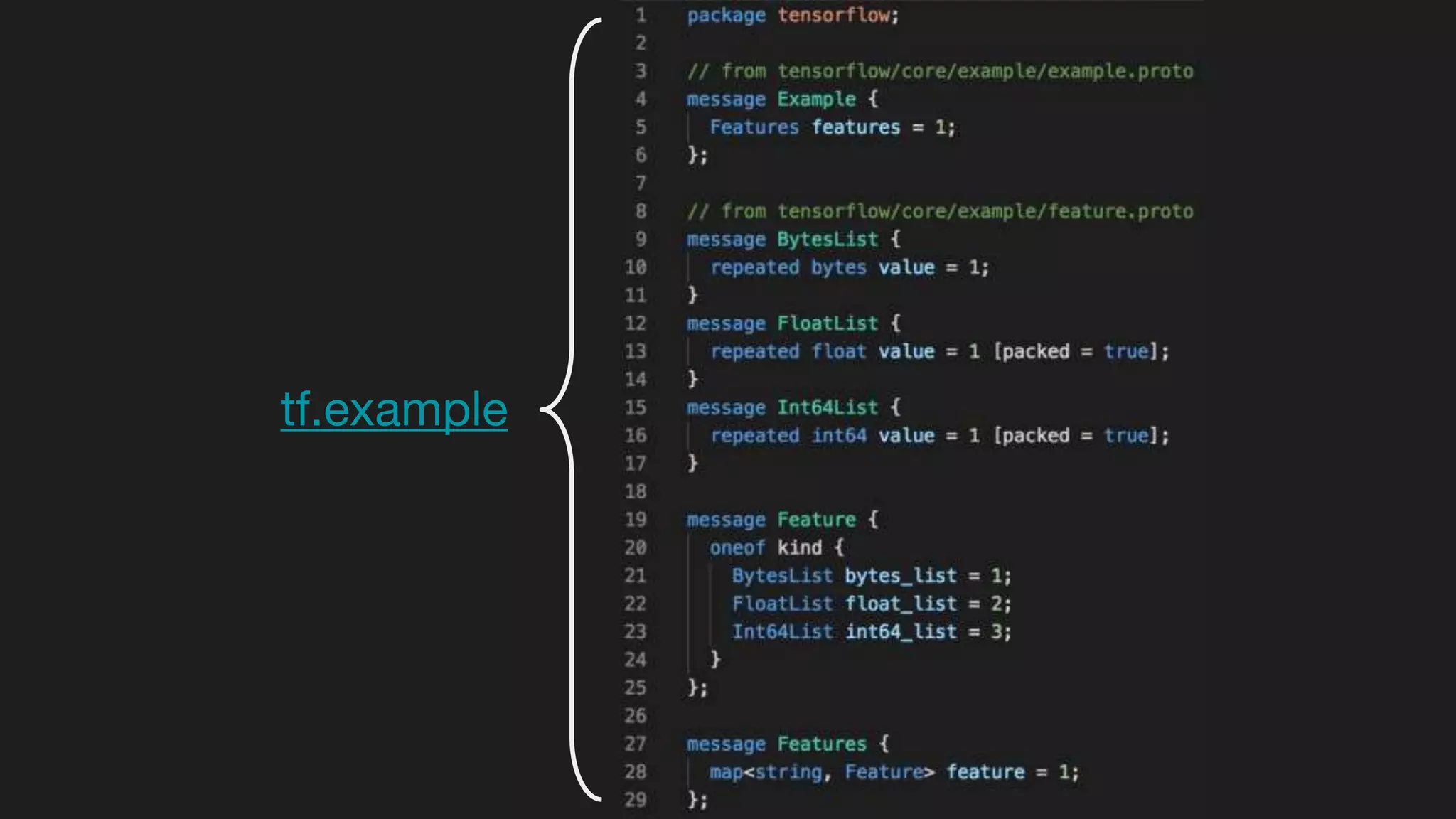
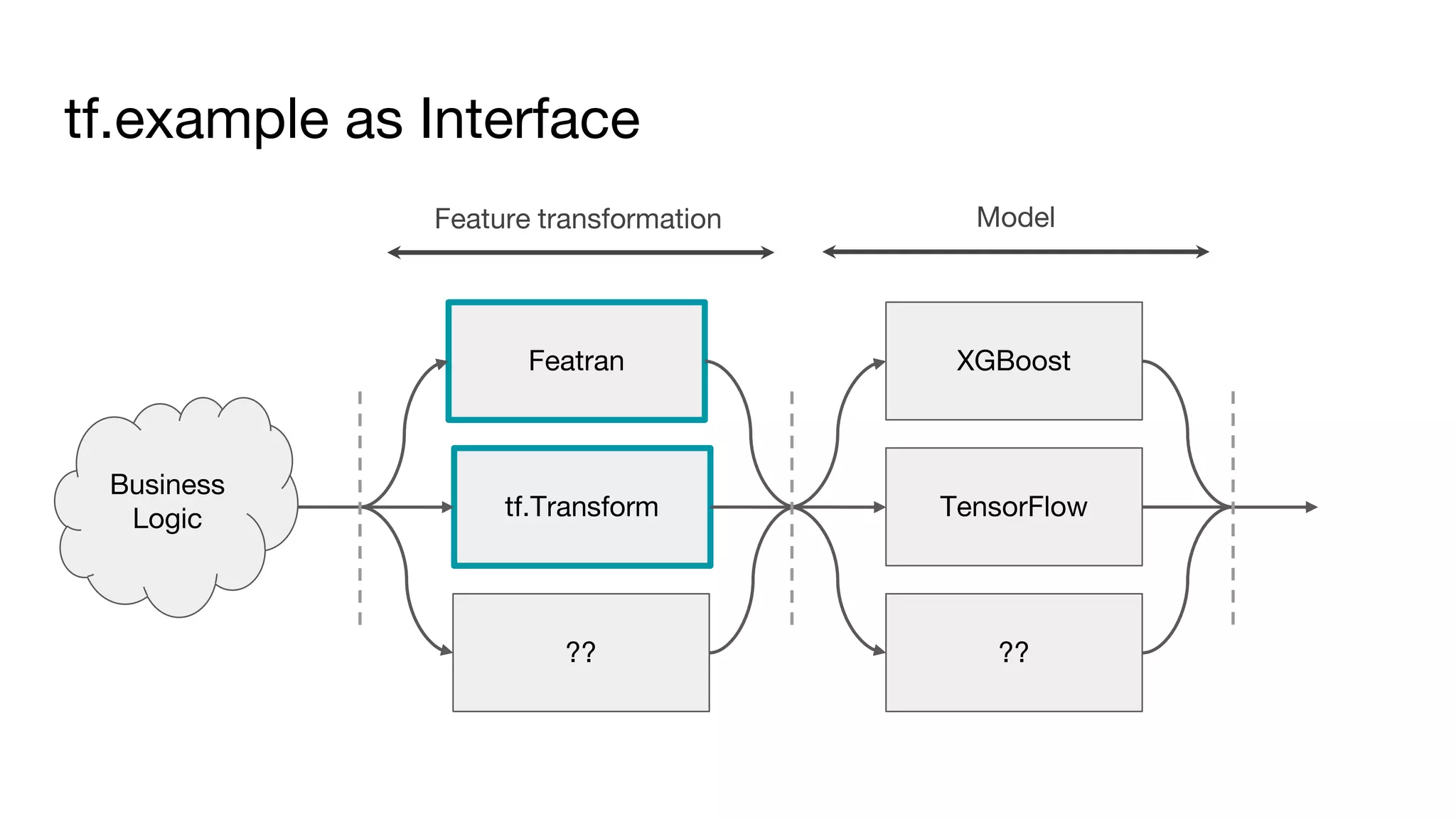
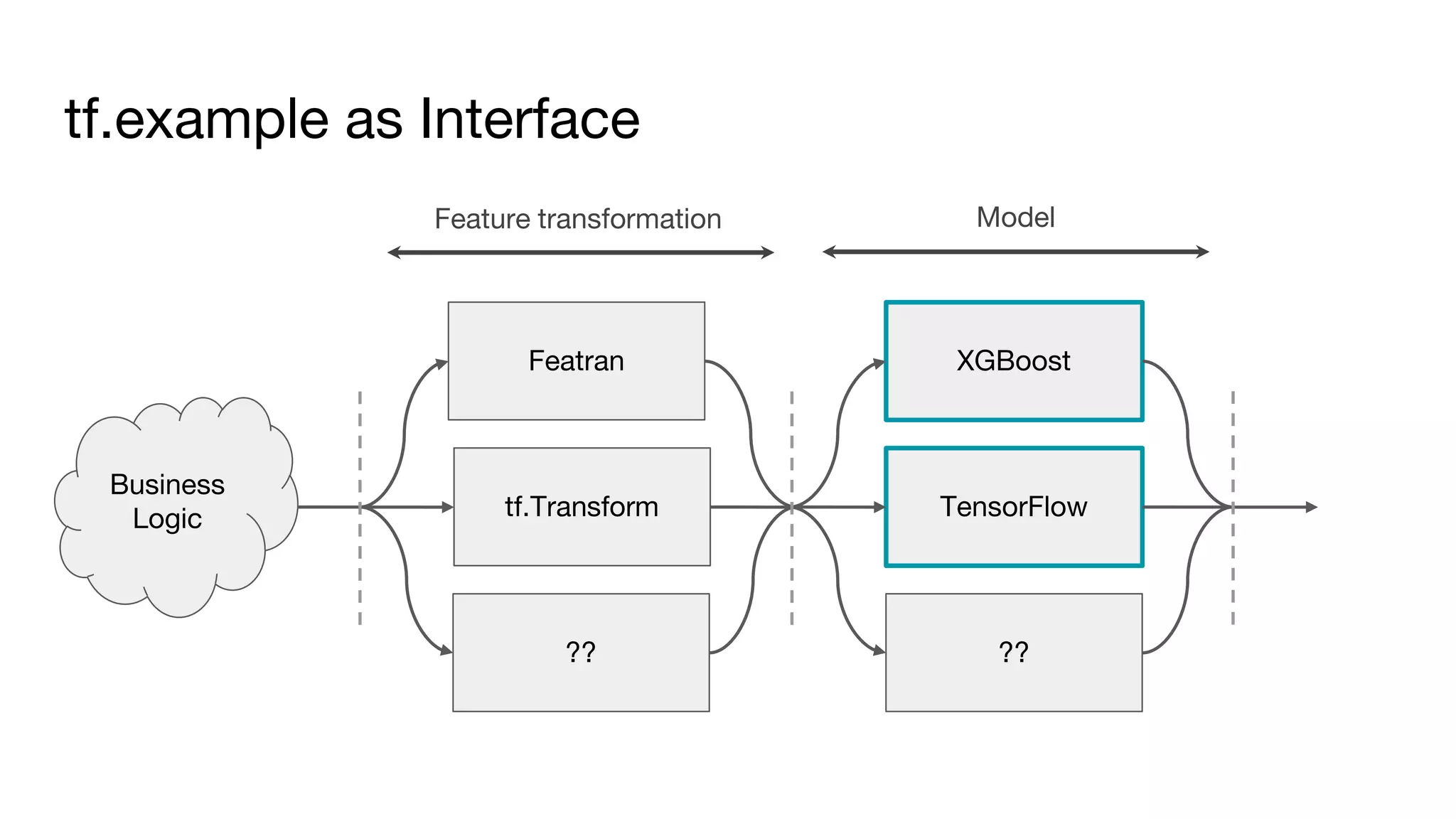
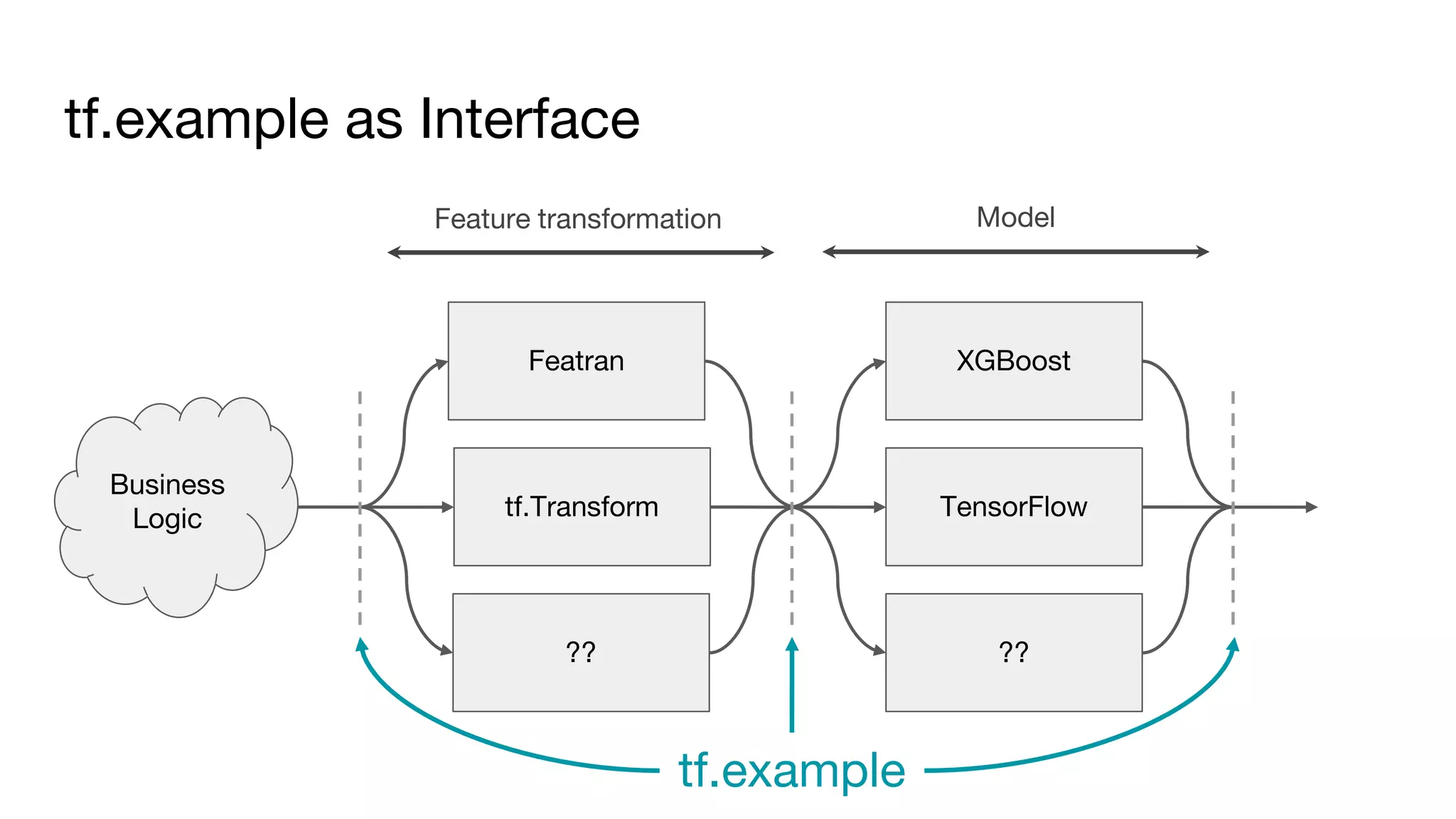
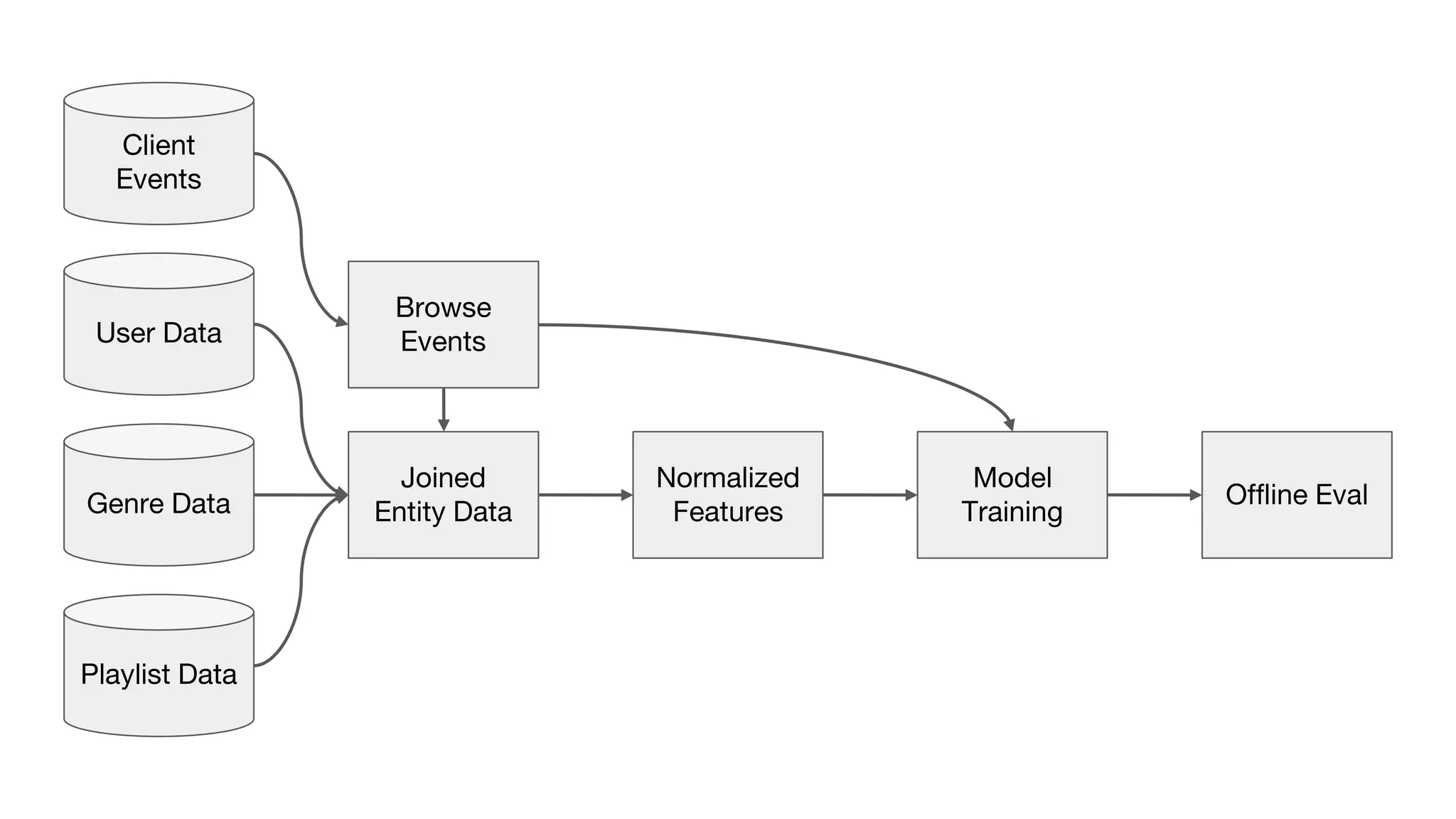
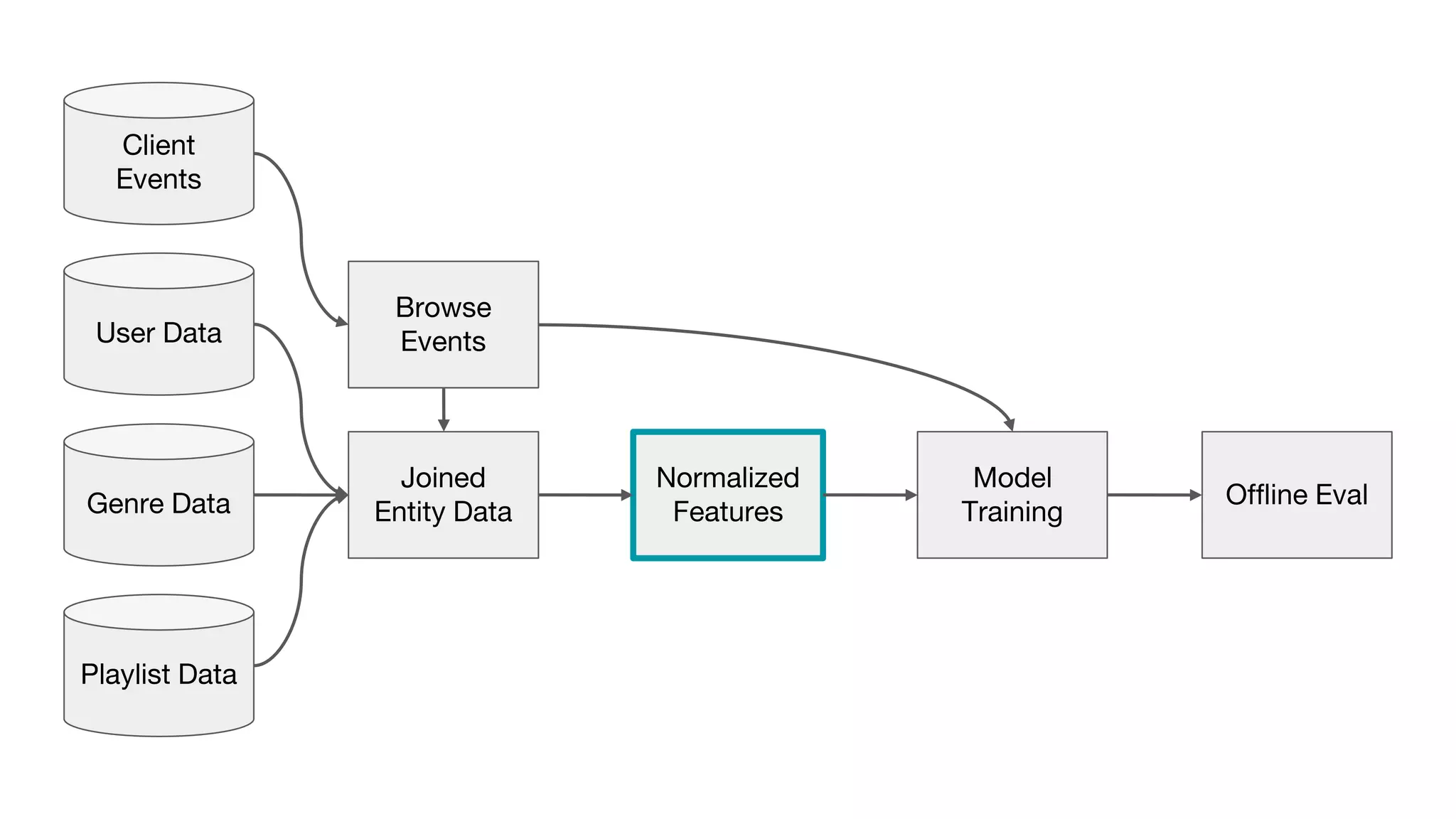
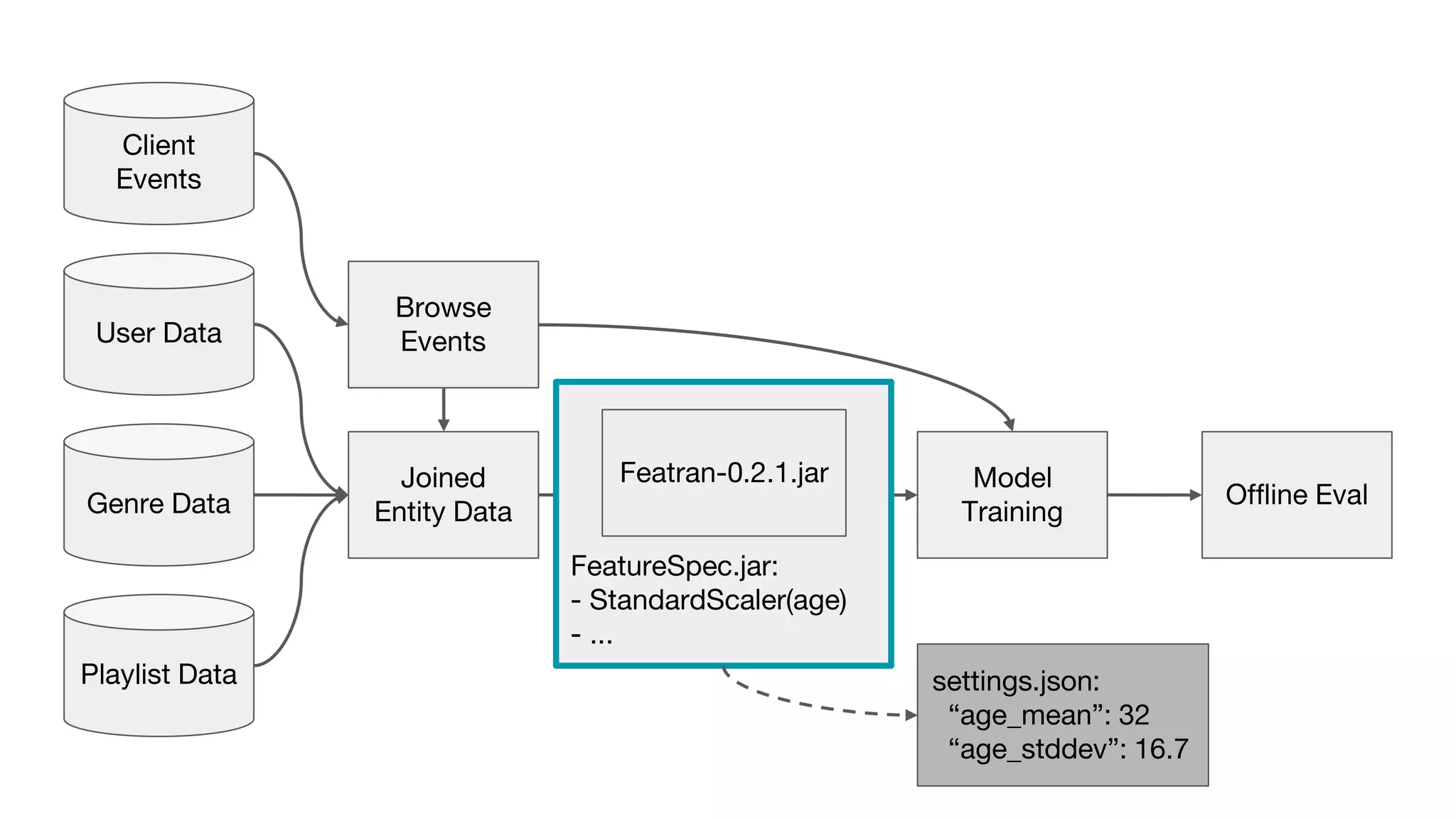
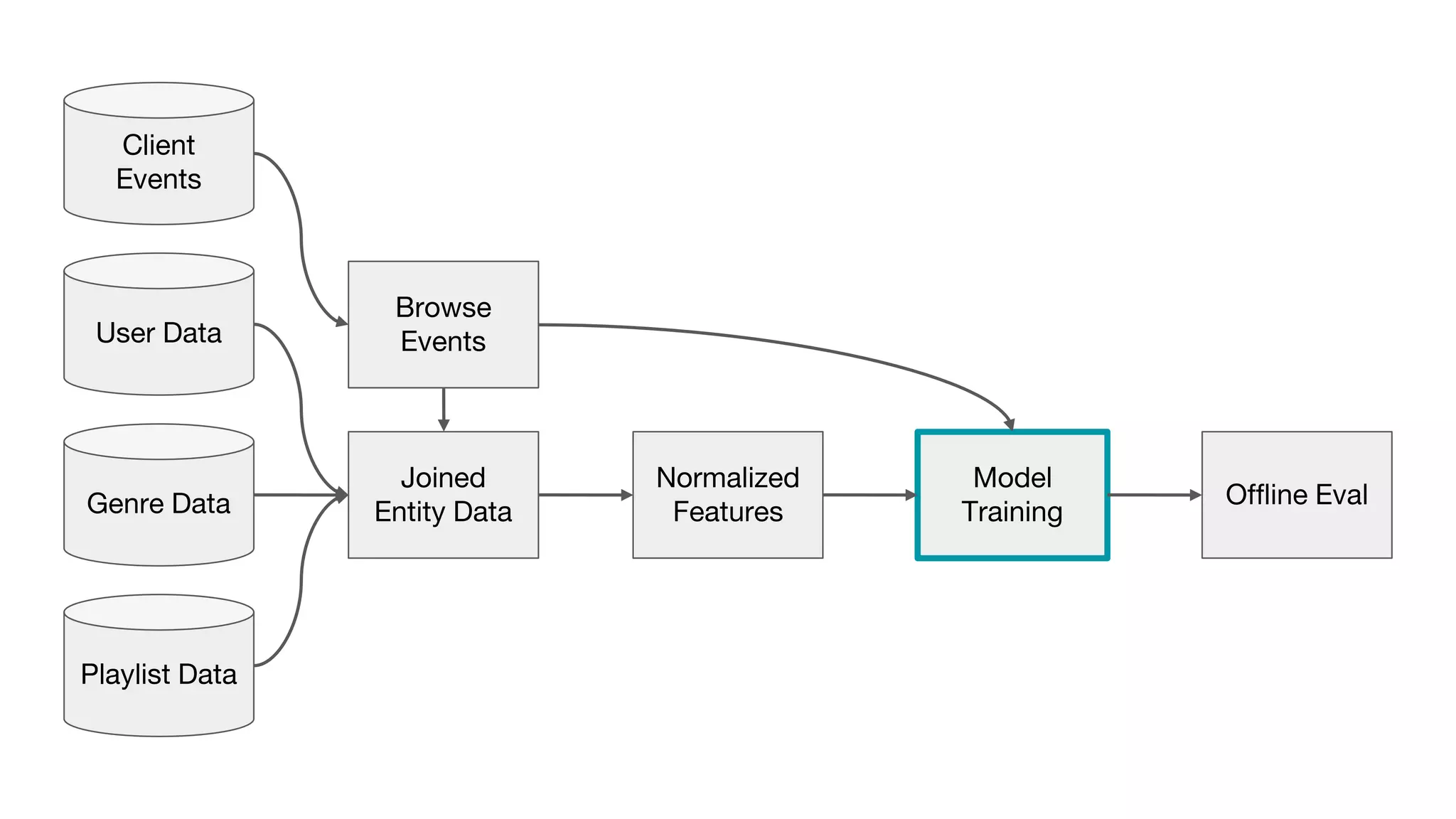
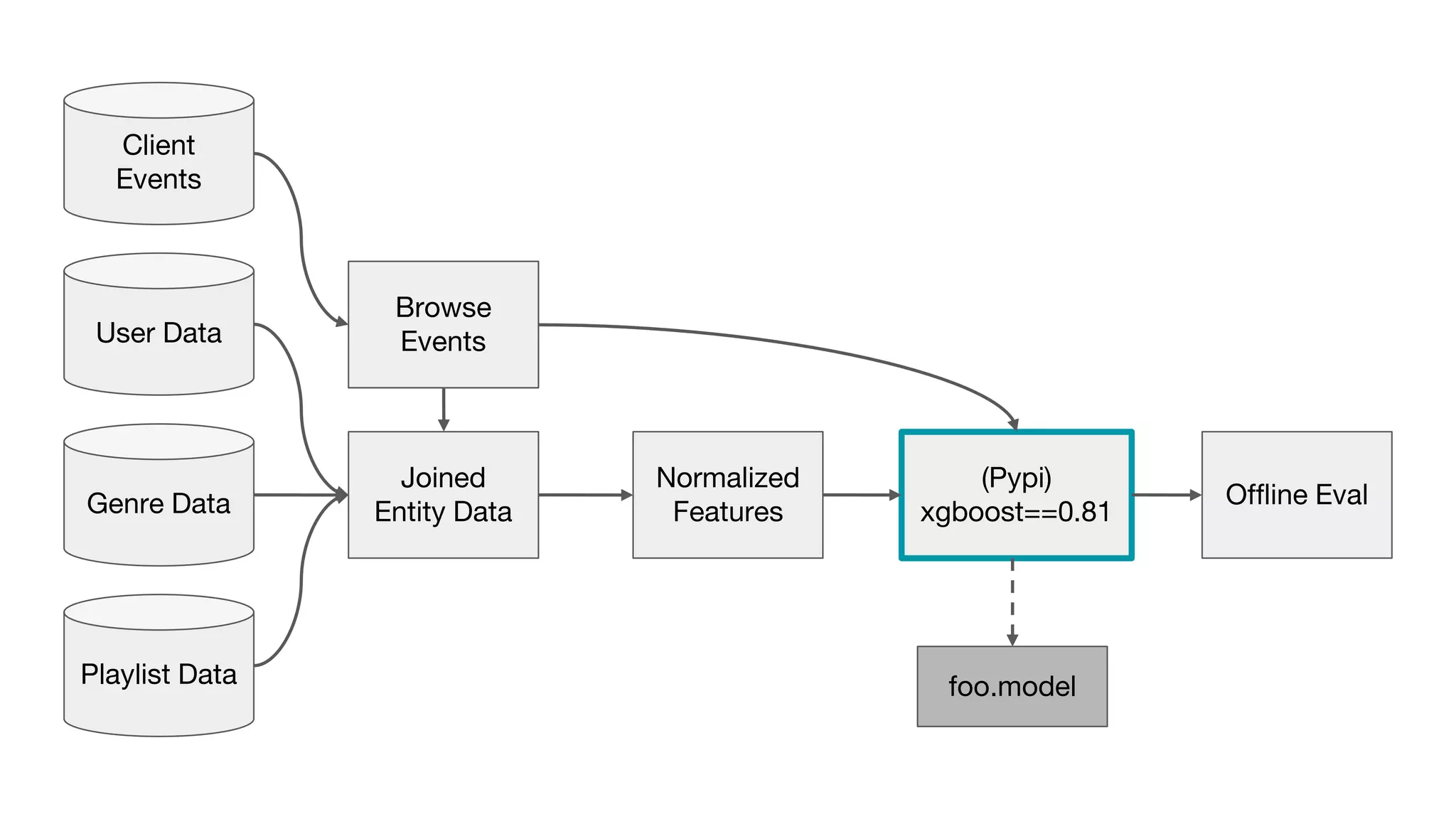
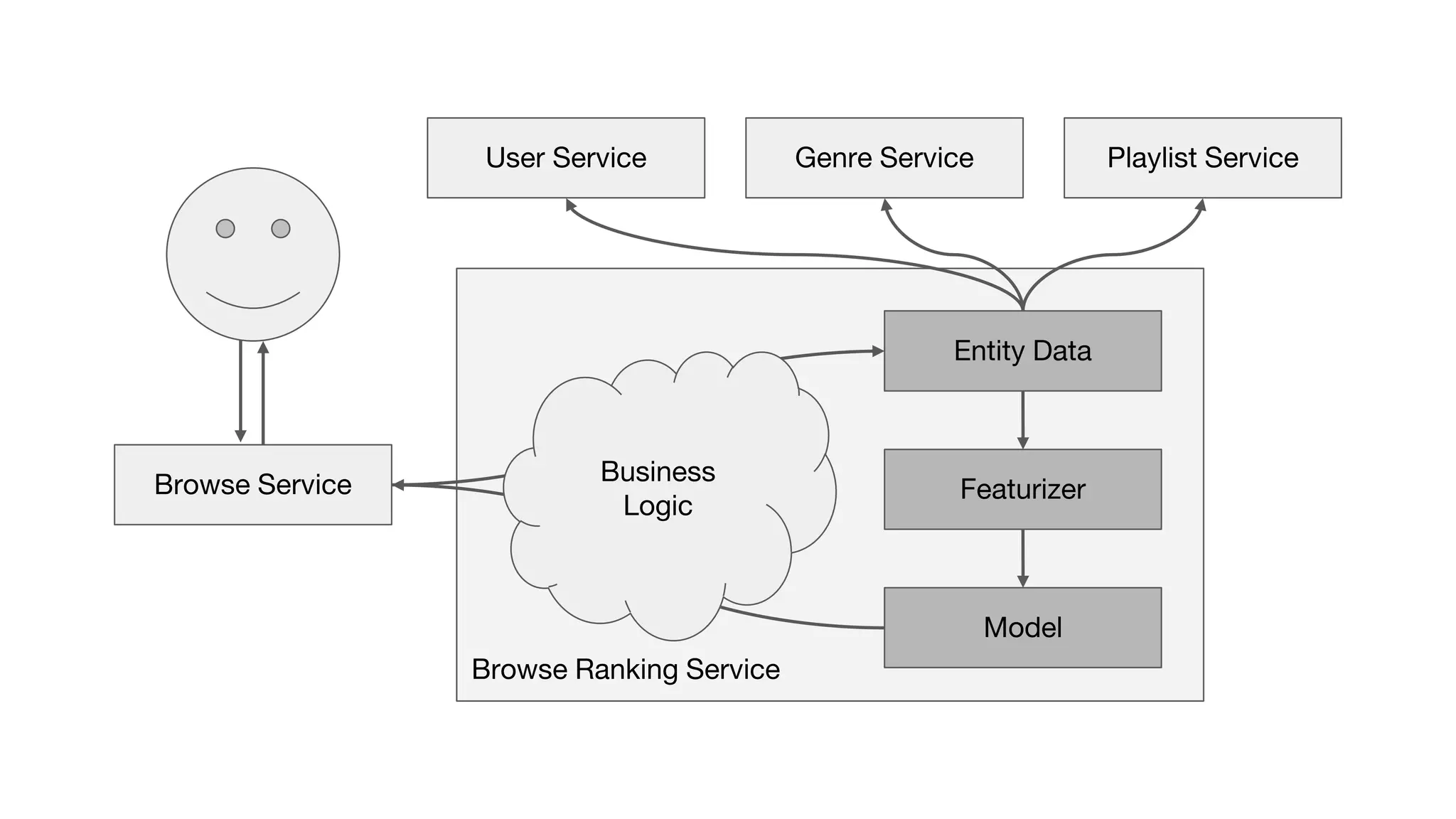
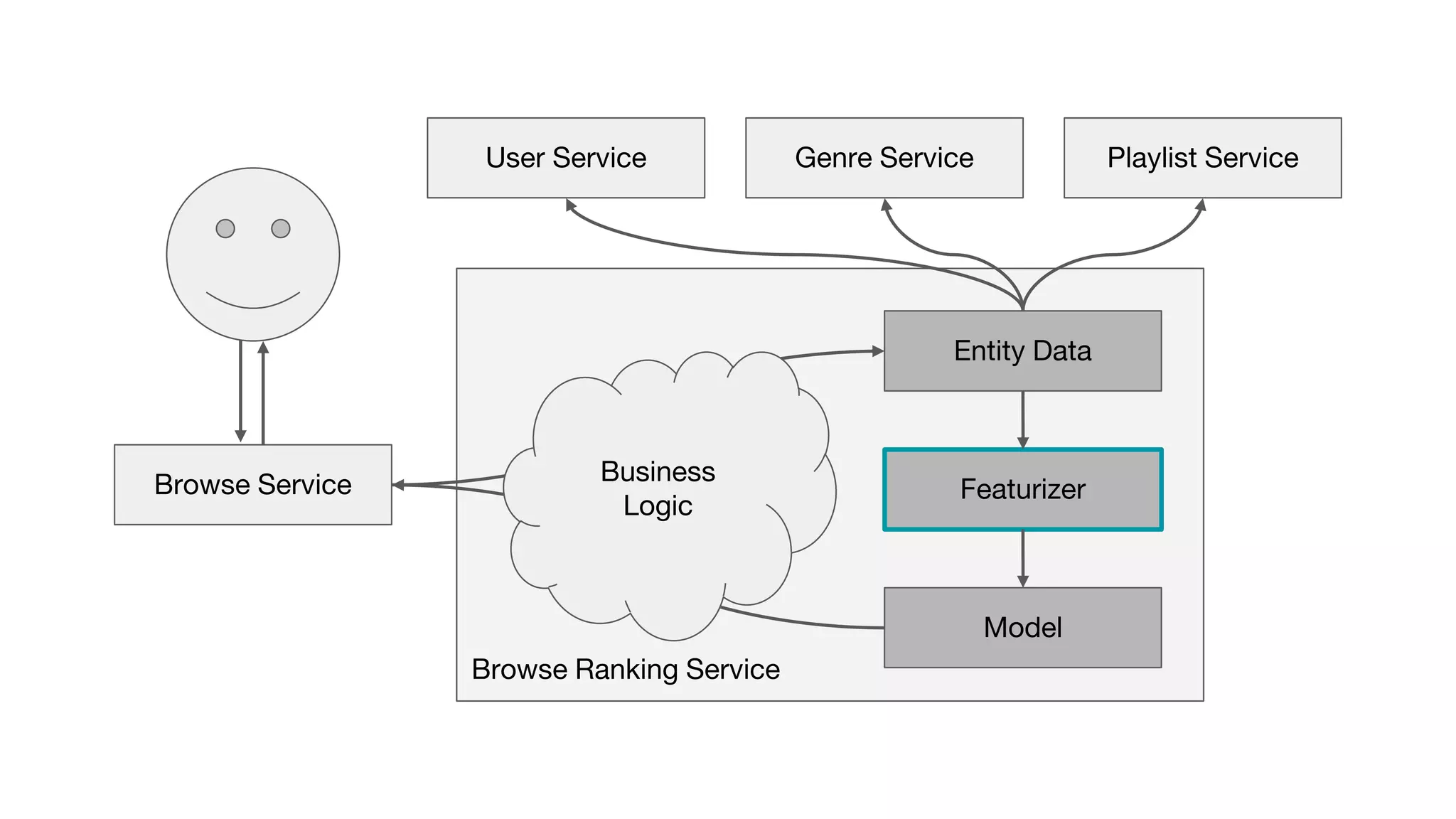
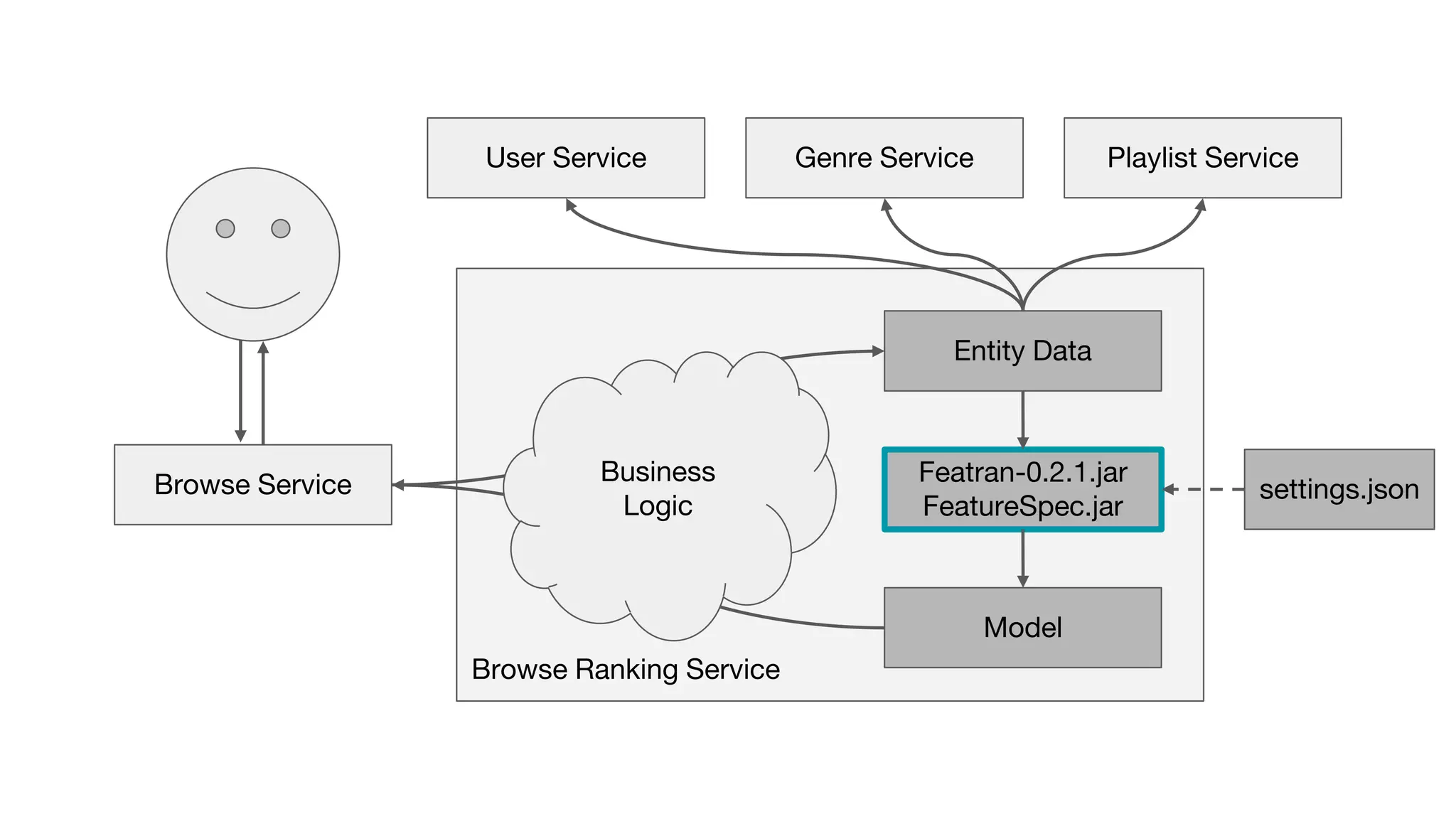
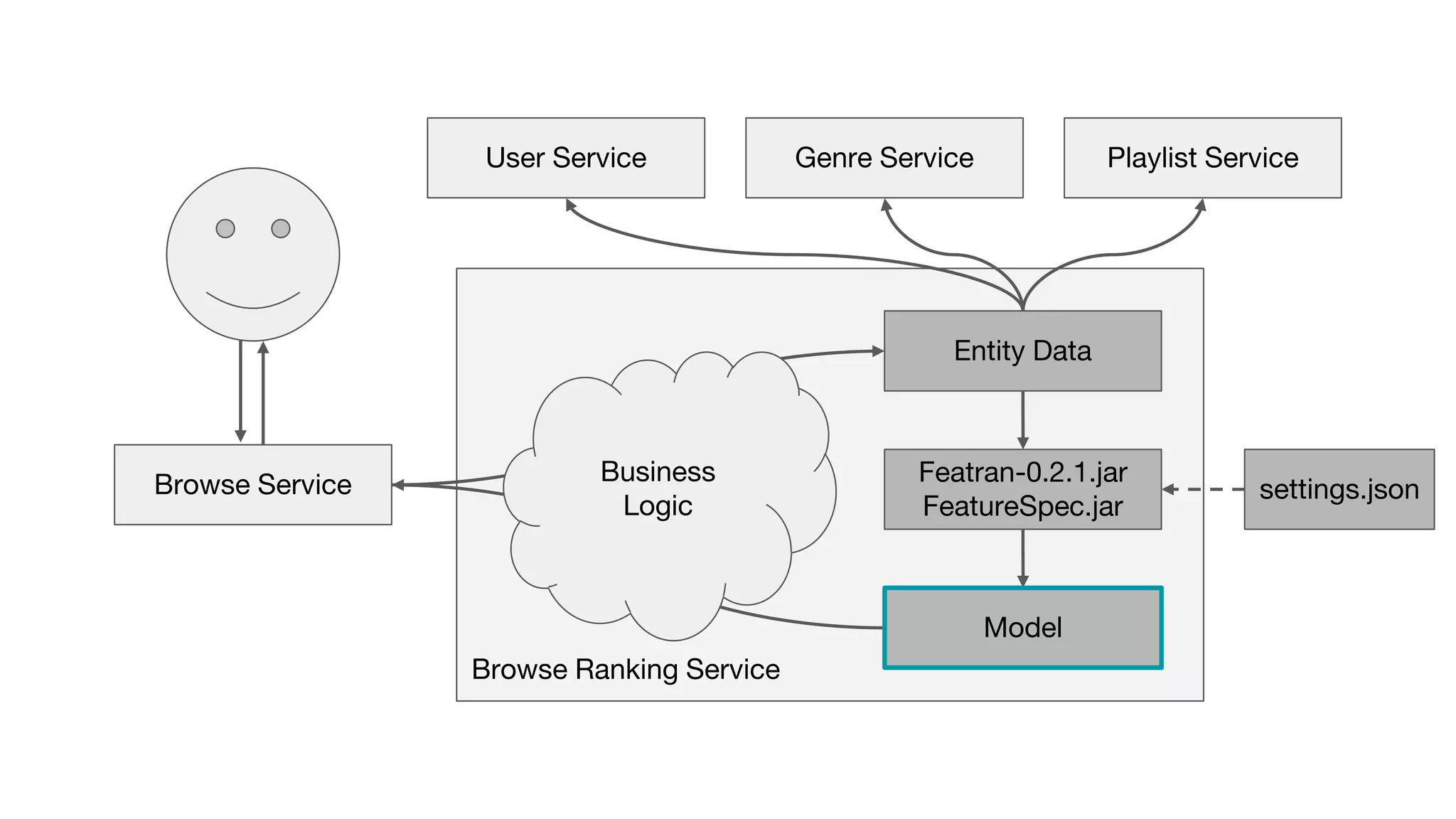
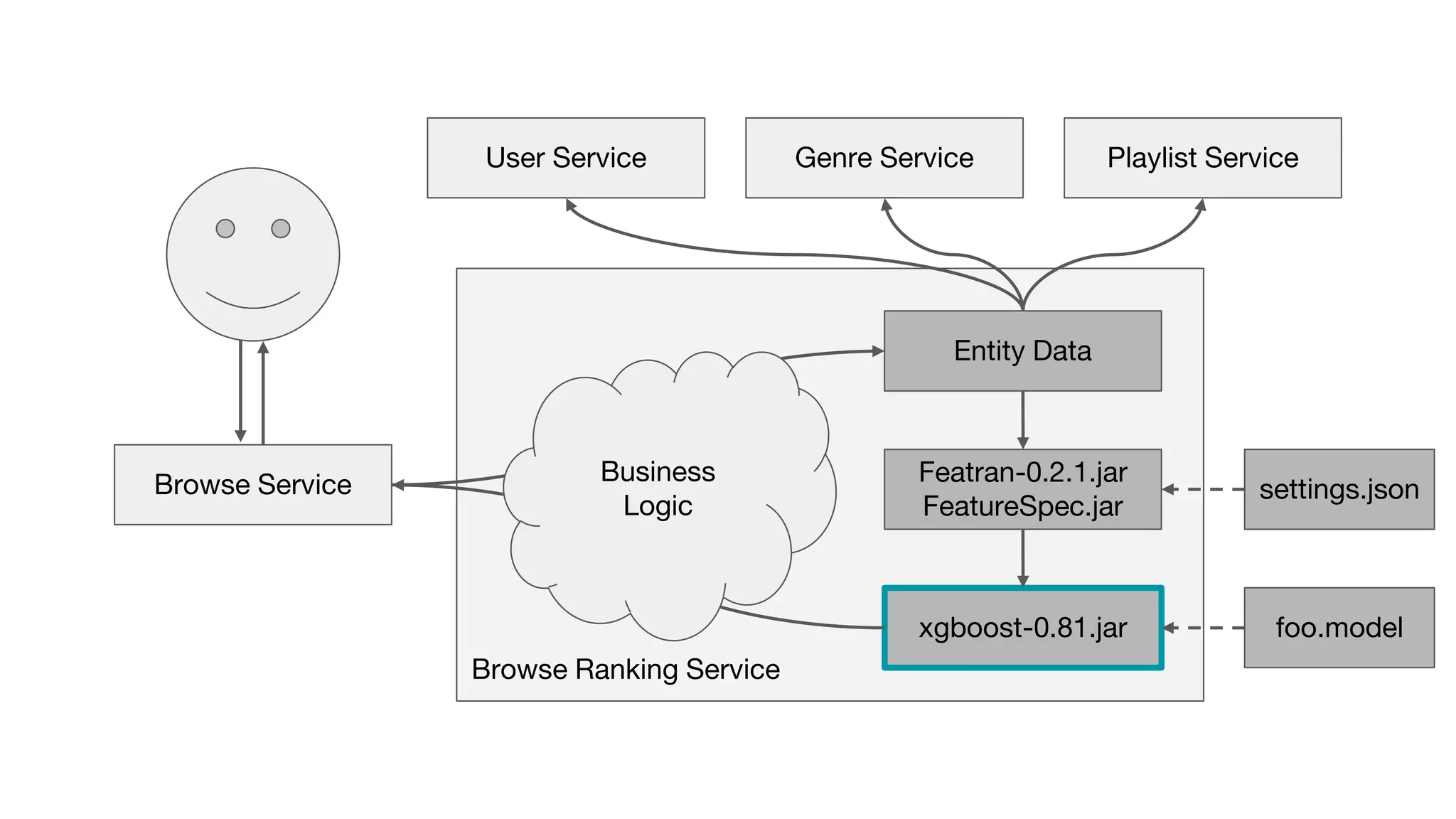
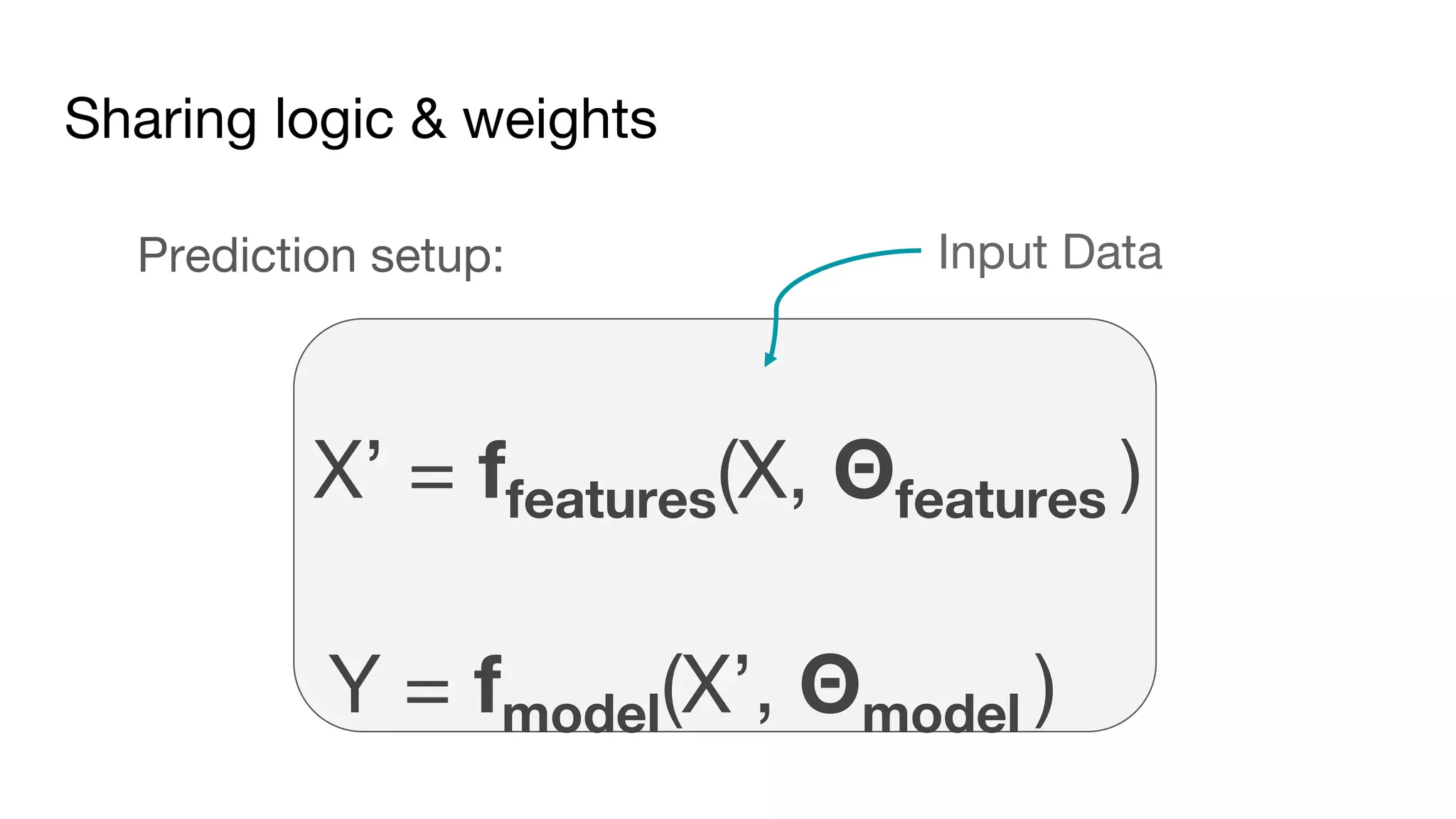
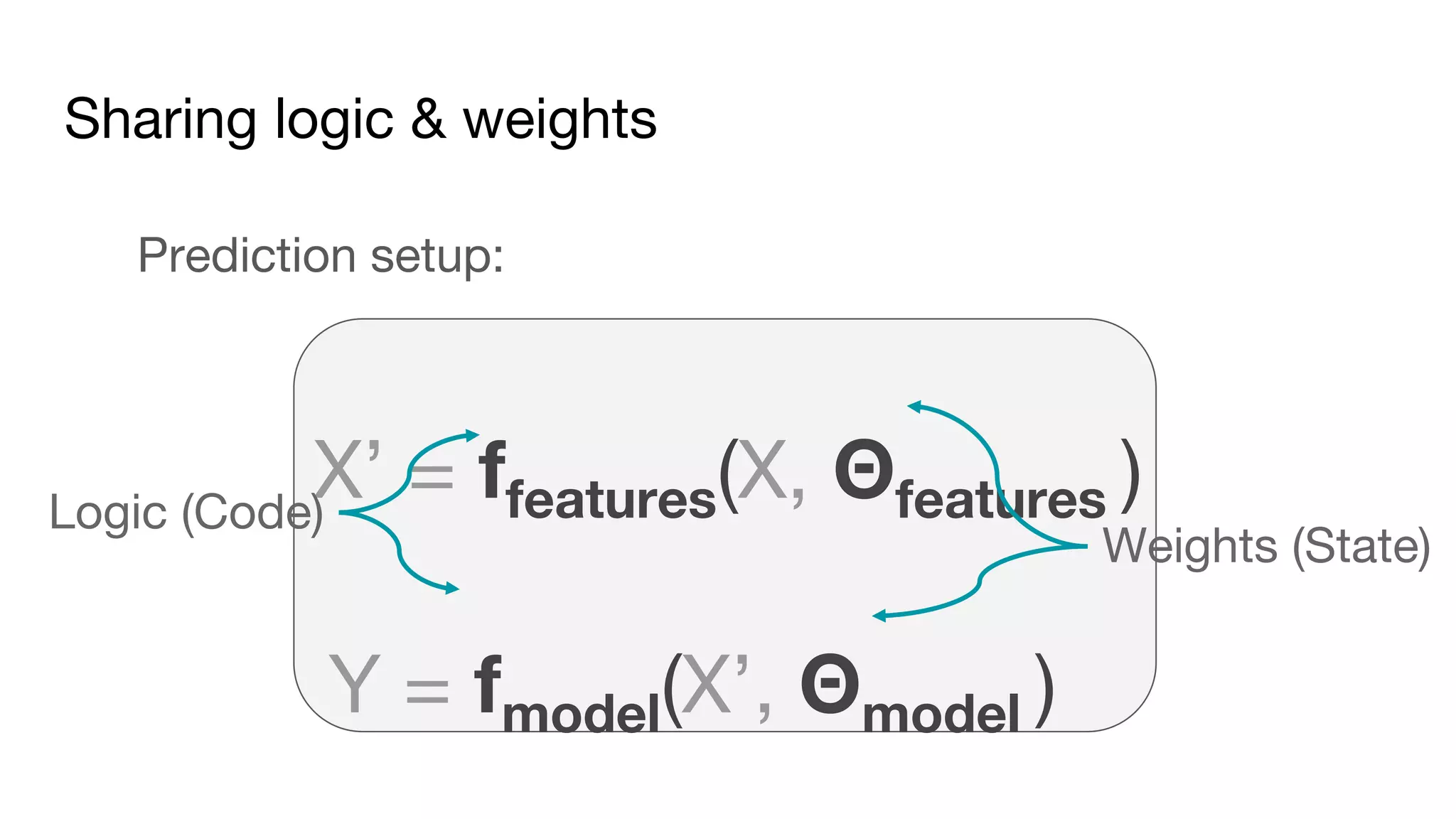
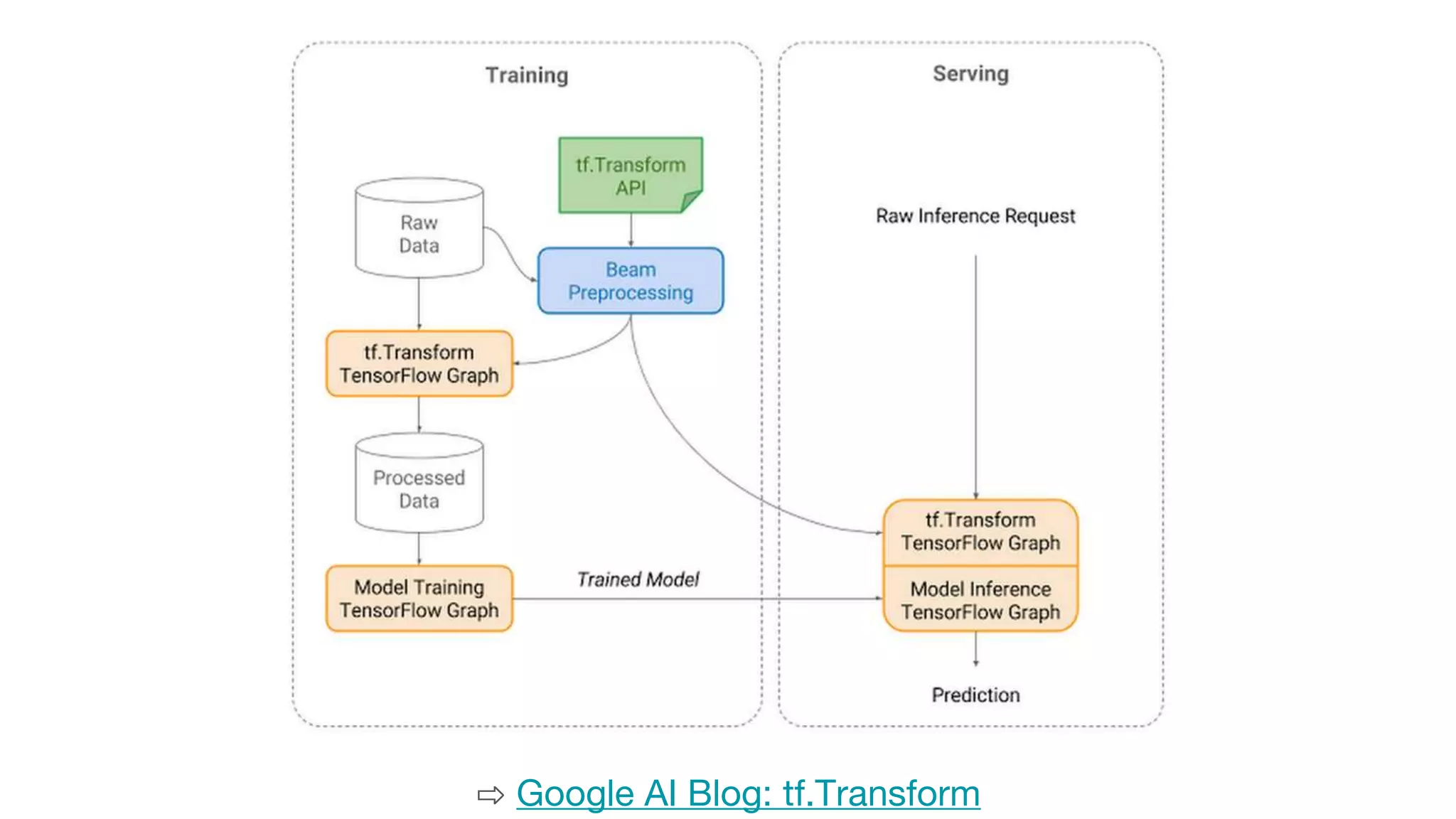
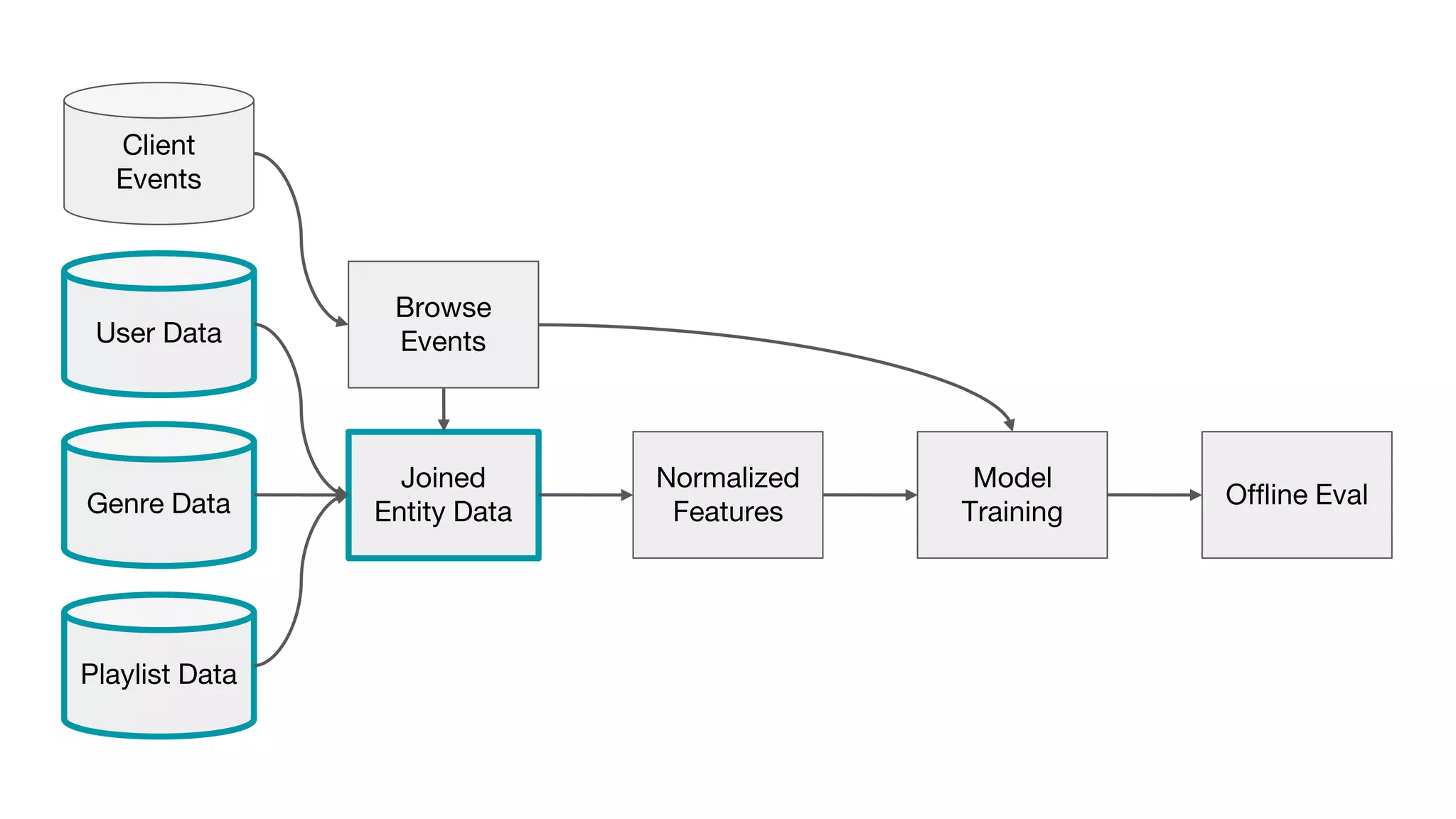
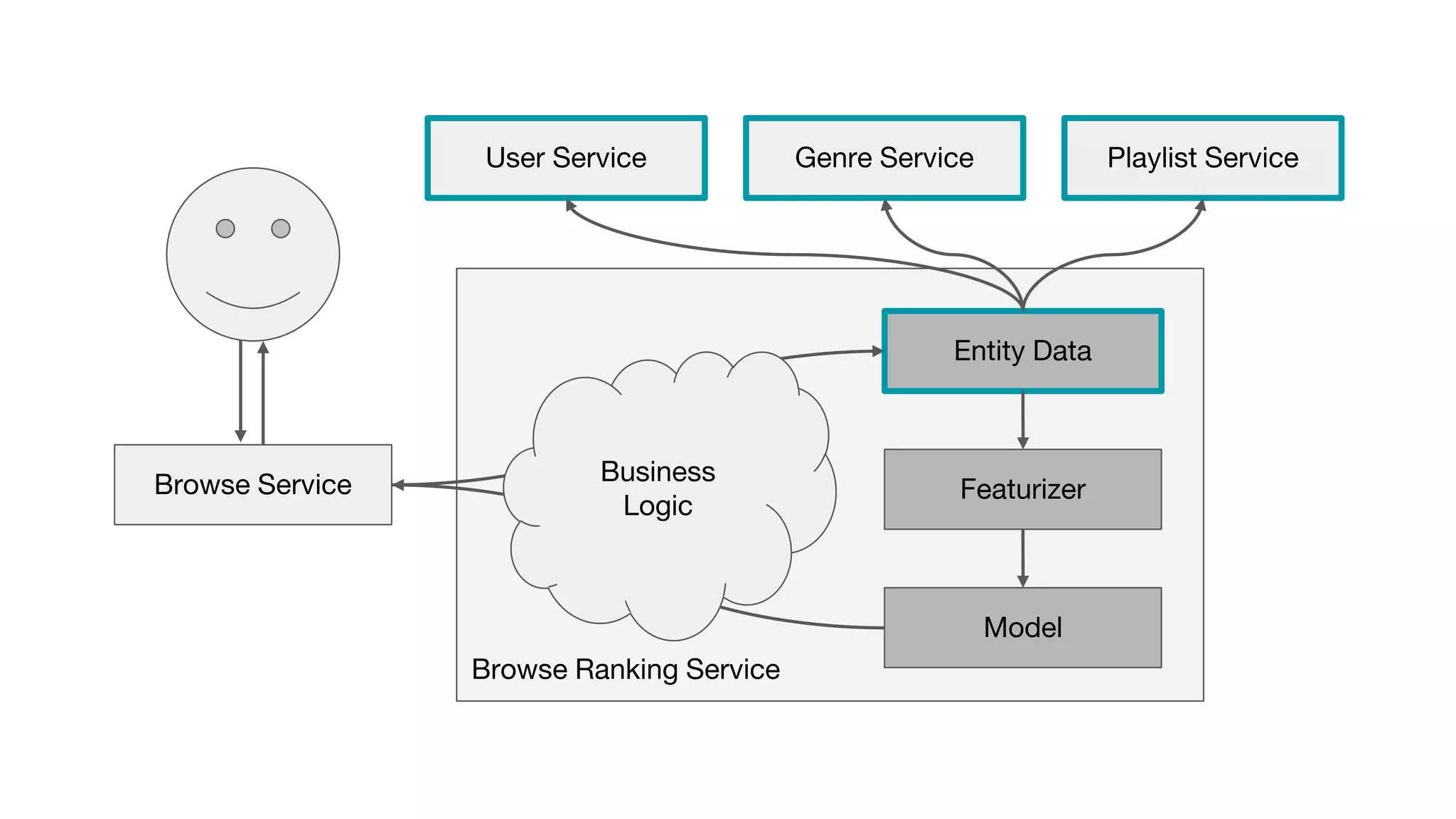
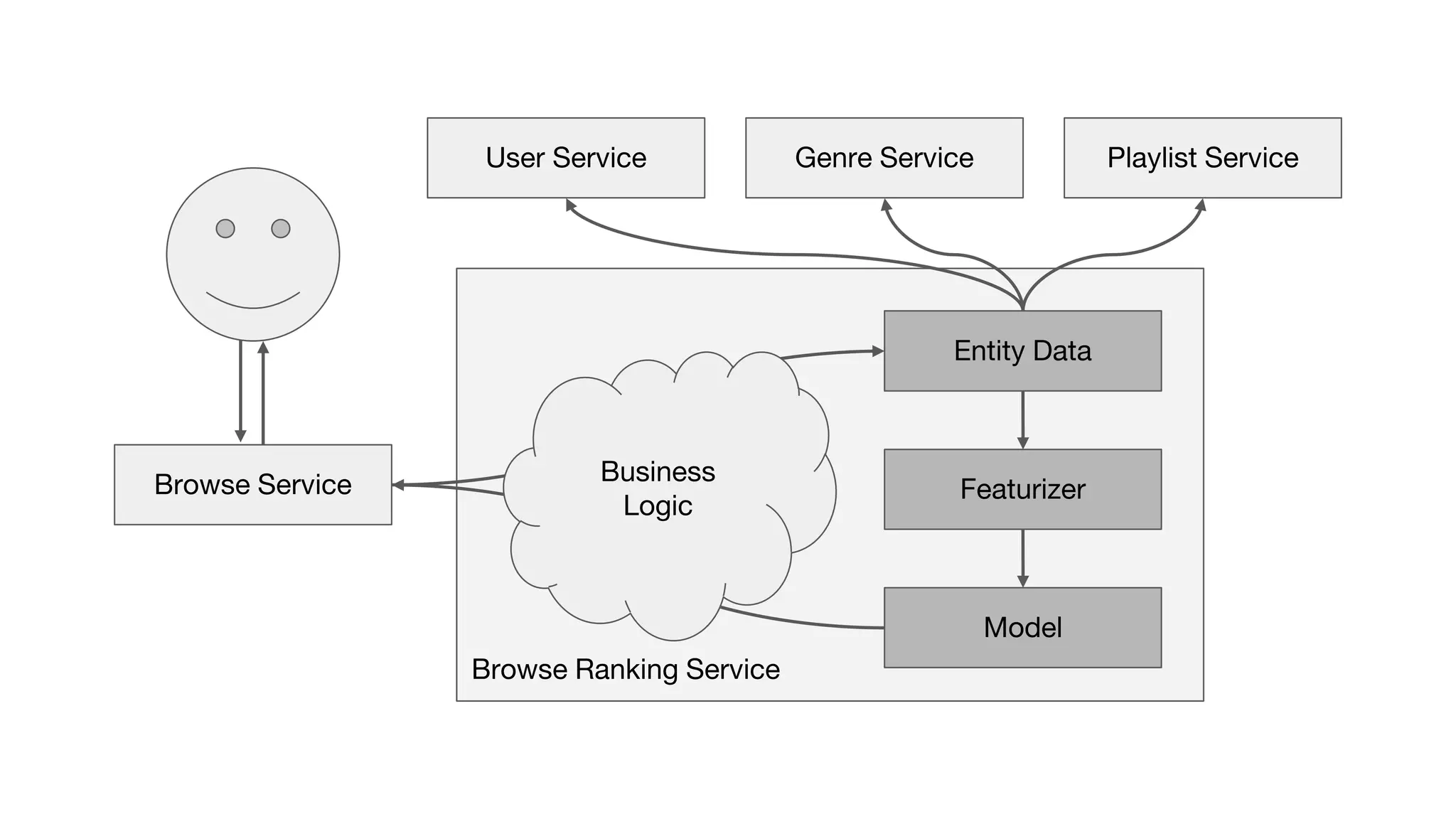
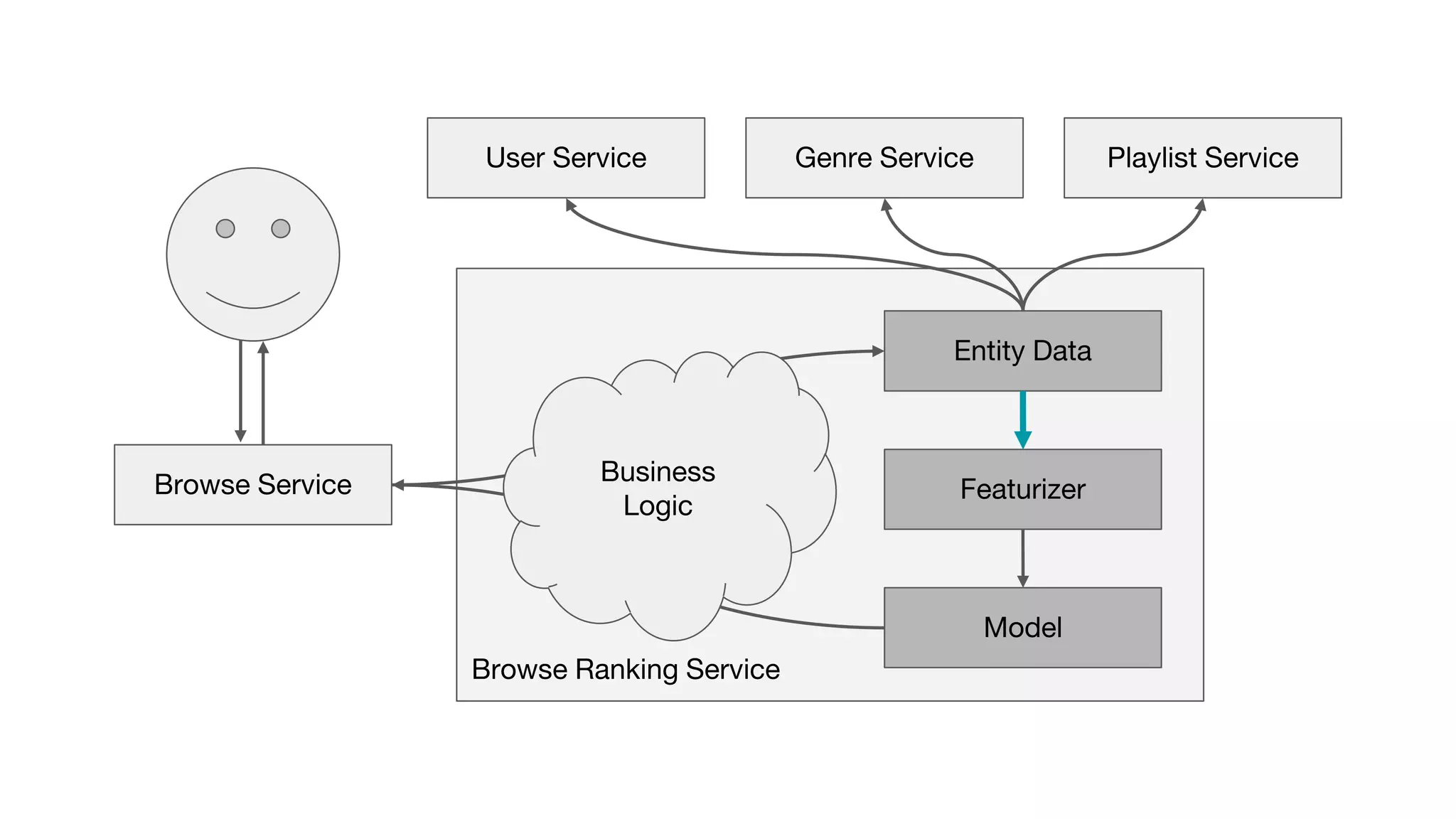
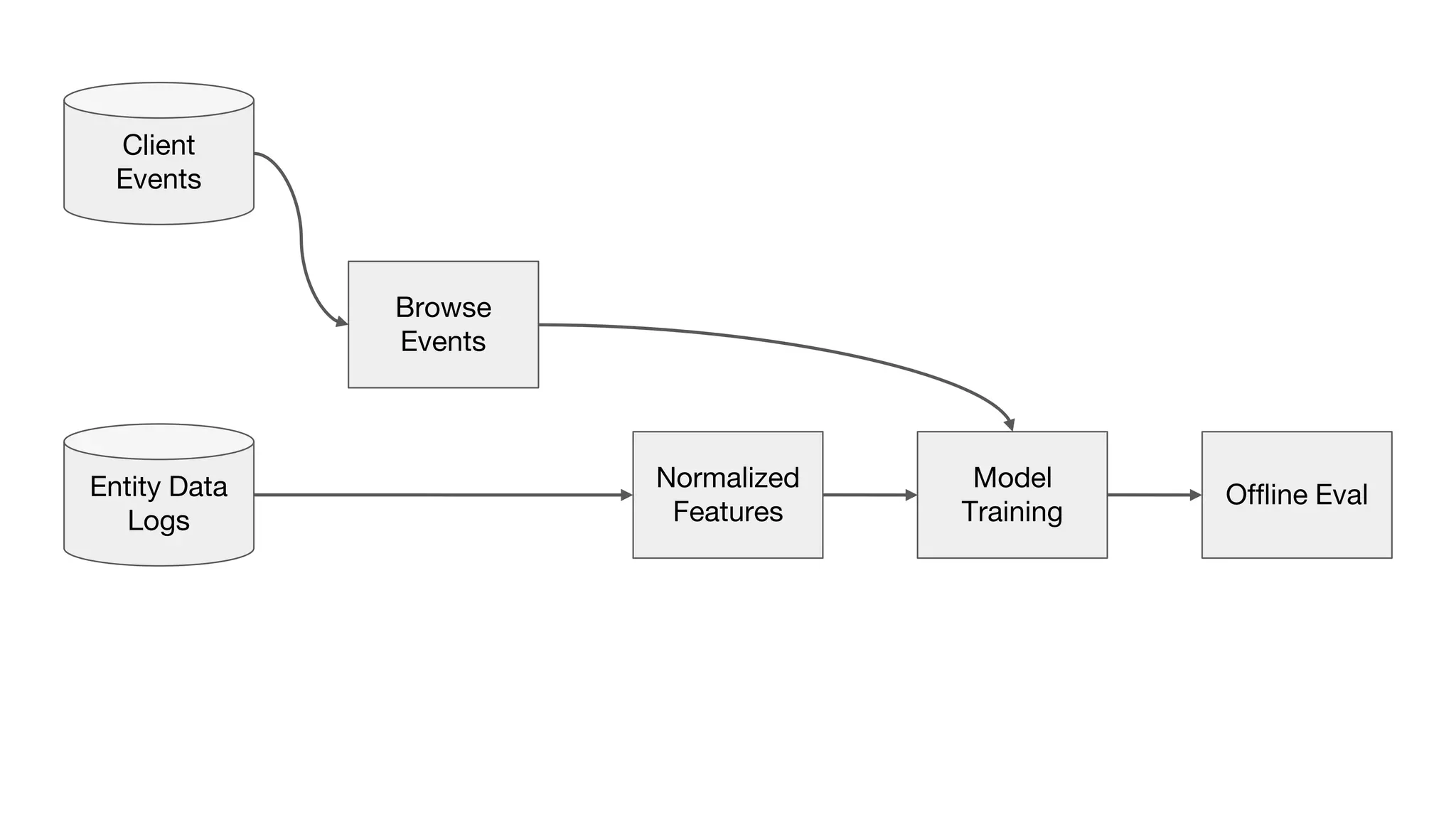
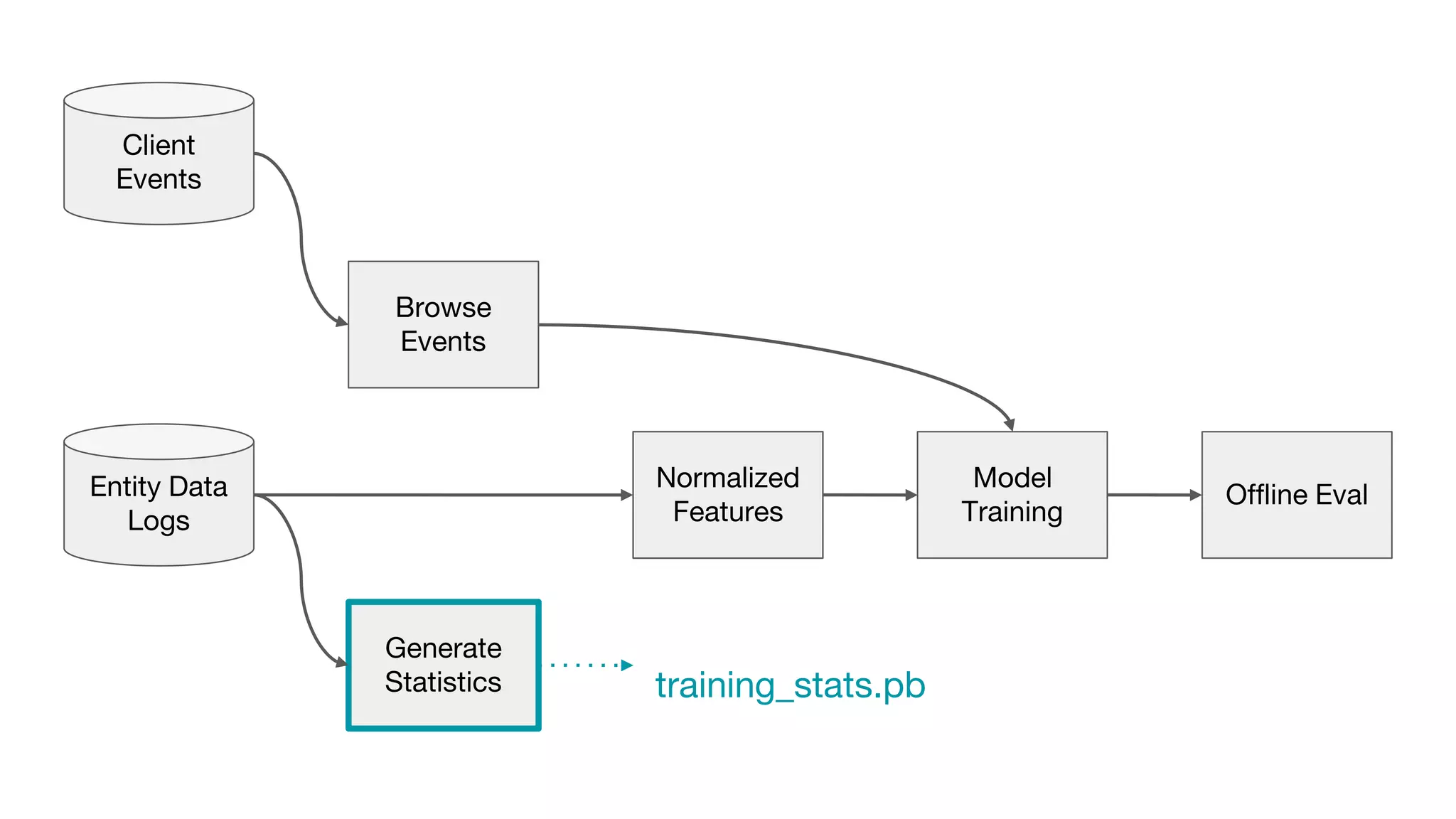
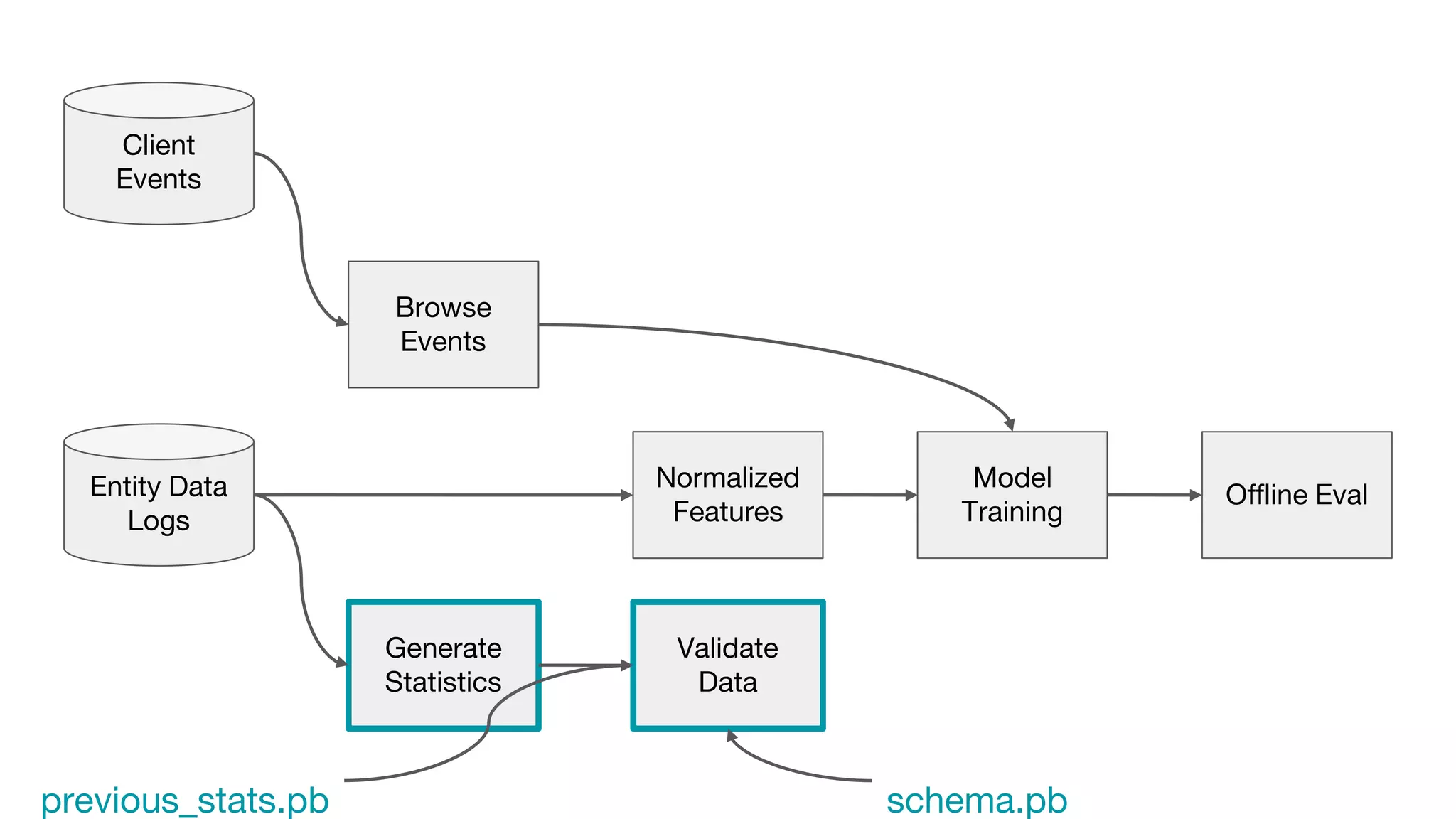
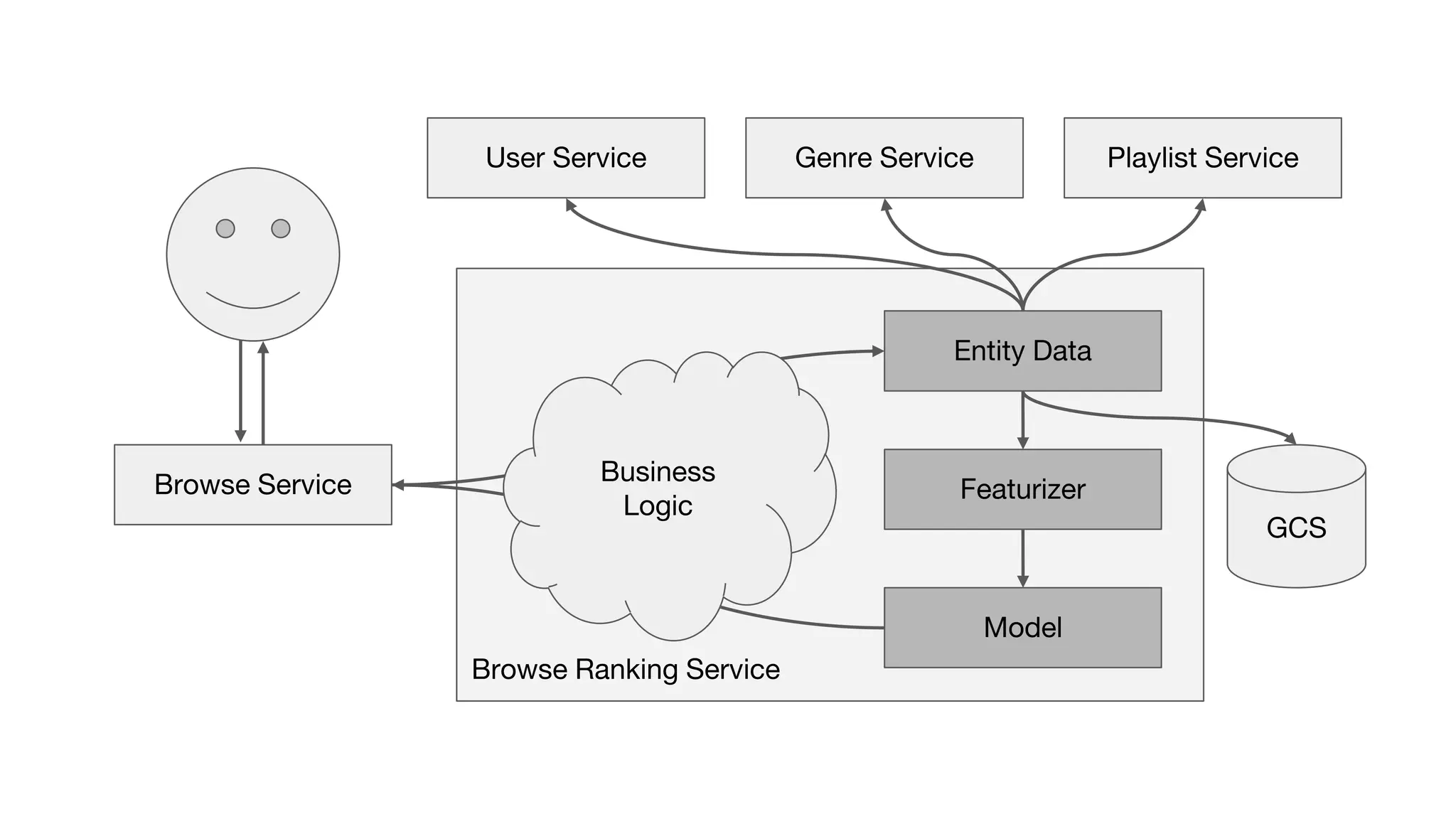
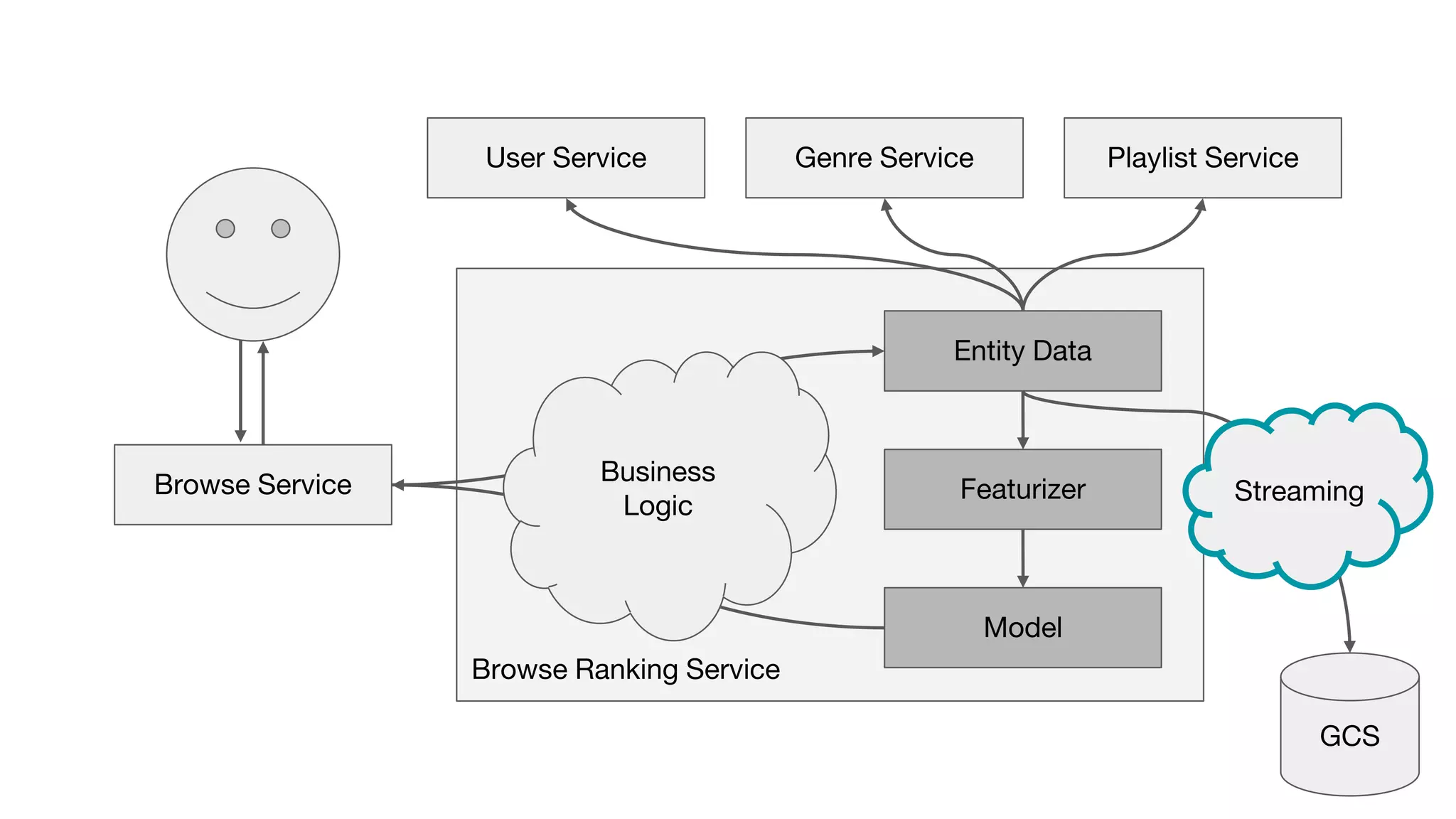
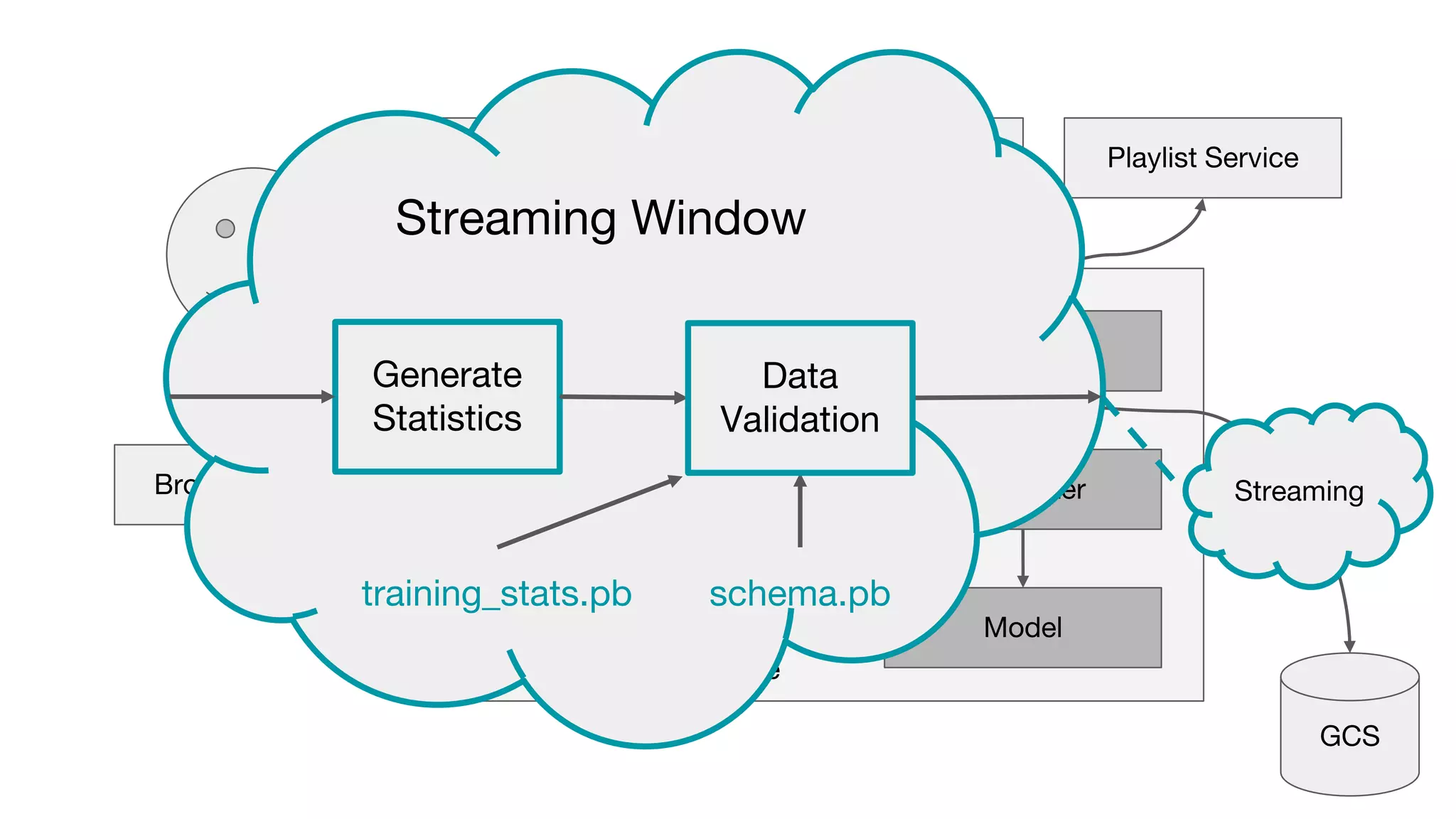
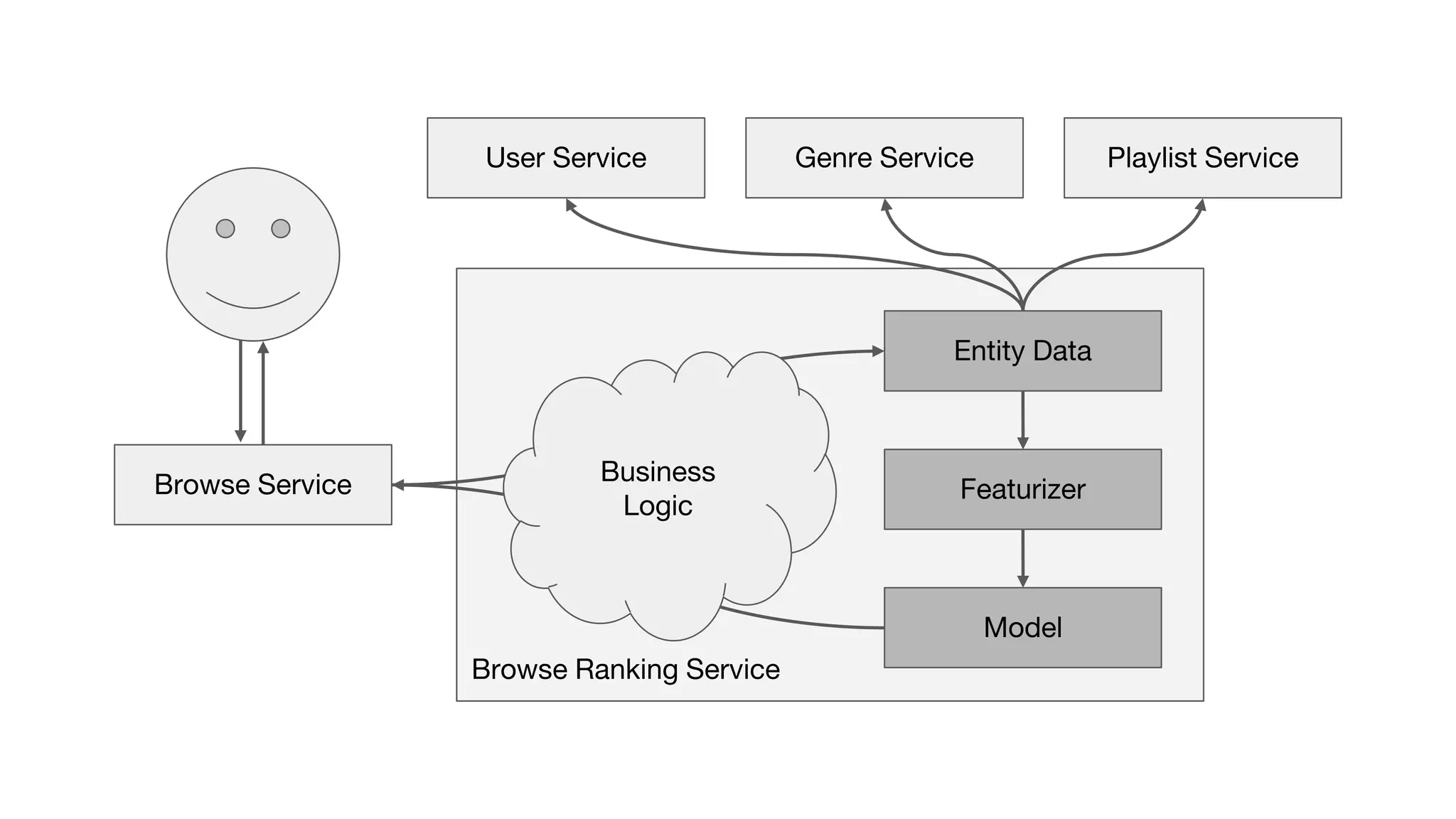
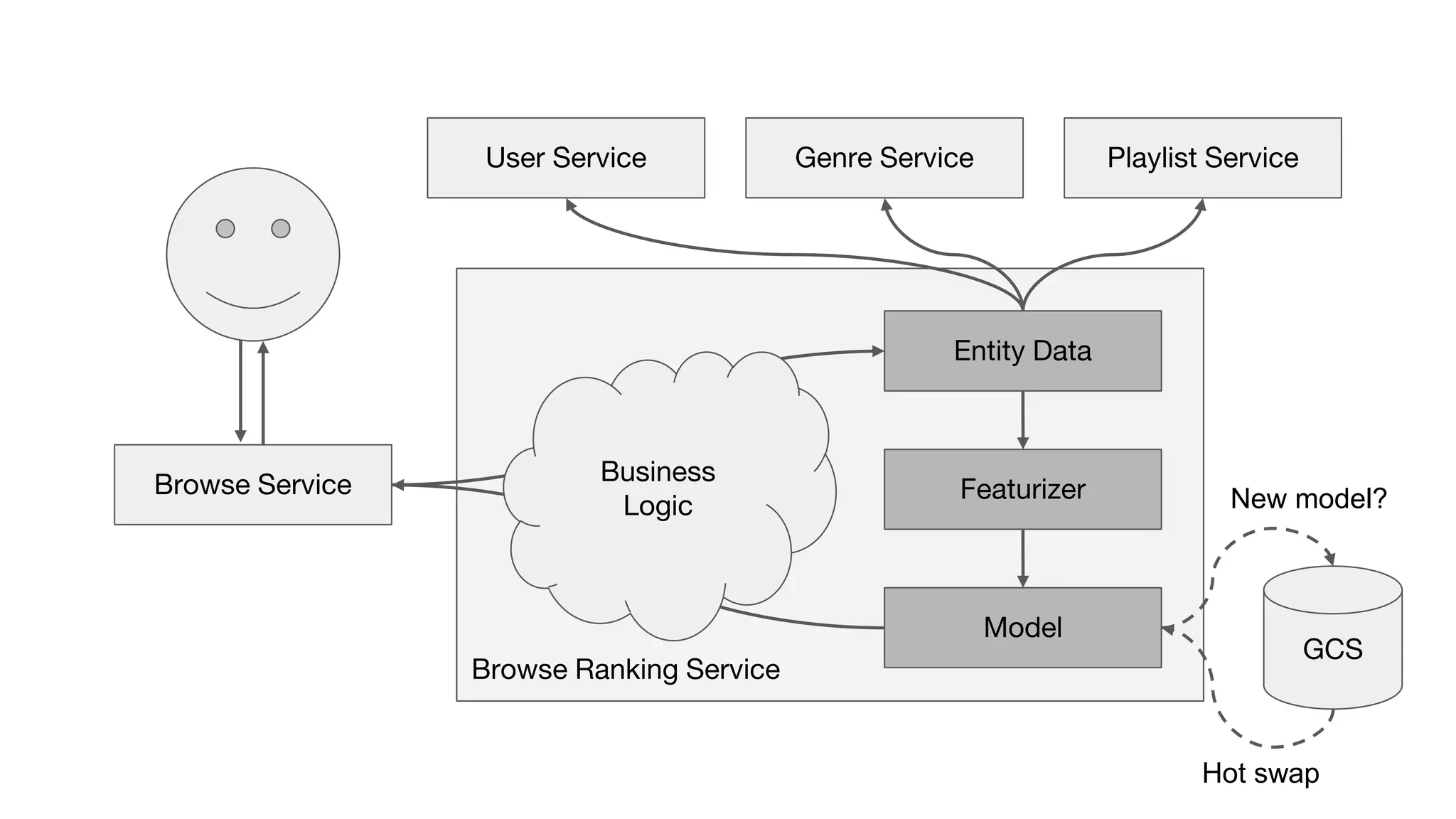
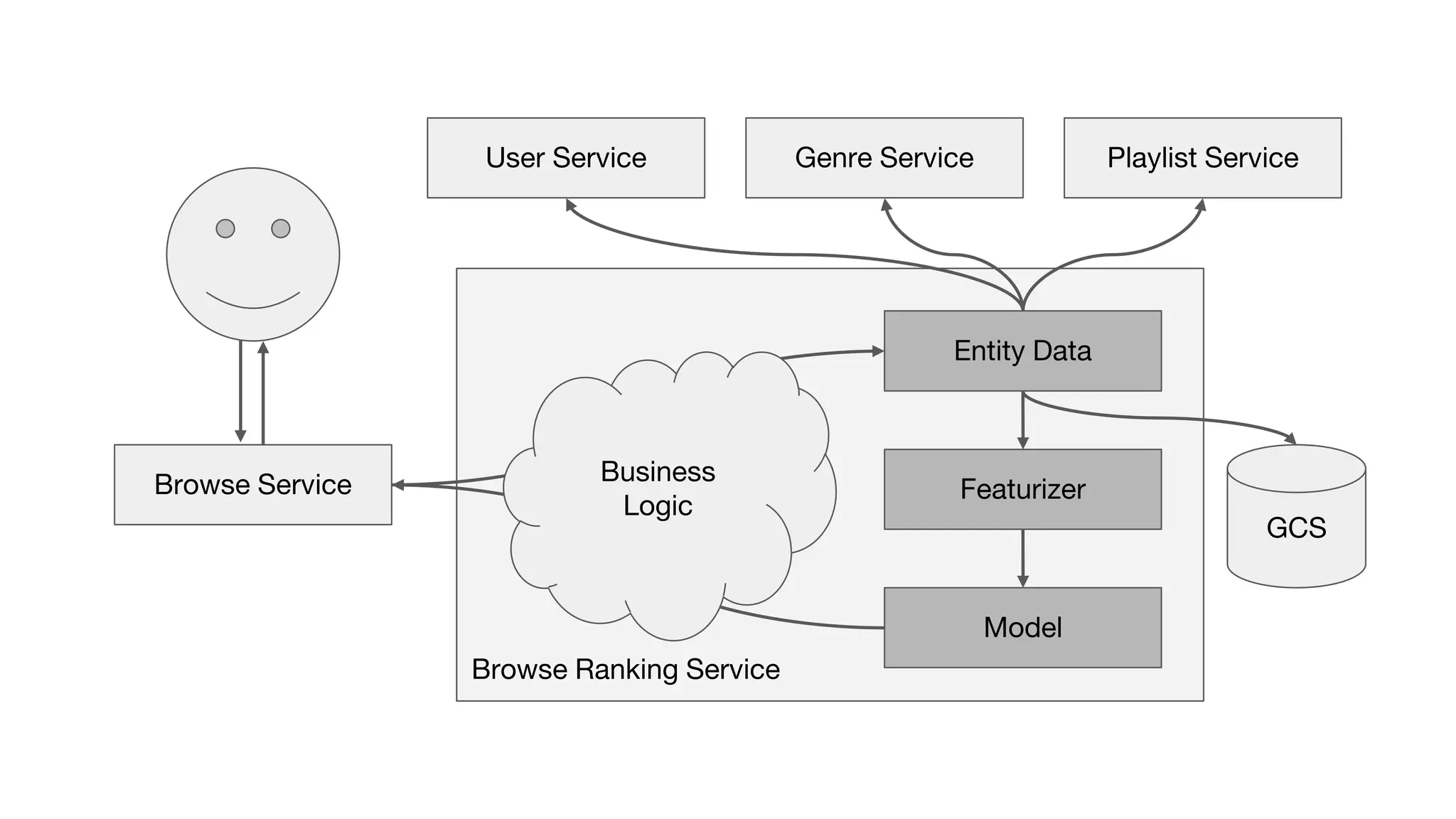
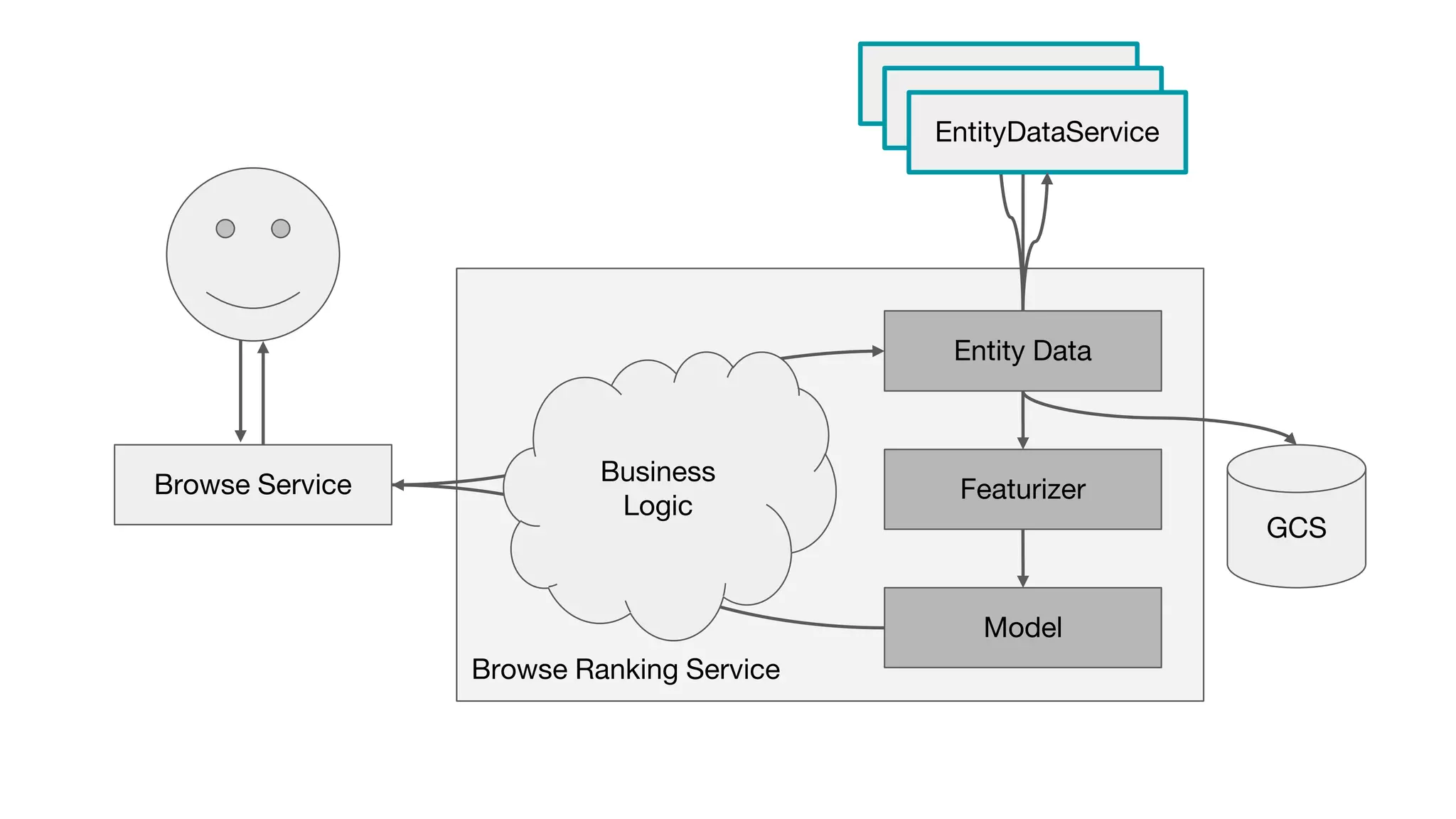
This document outlines the lessons learned from building machine learning infrastructure at Spotify, highlighting key issues, challenges, and strategies for effective ML deployment. It emphasizes the importance of data standards, sharing logic and weights, data validation, and maintaining reliability through continuous integration and delivery practices. The document also discusses the complexities involved in real-world ML production systems and provides guidance for sustaining high reliability.





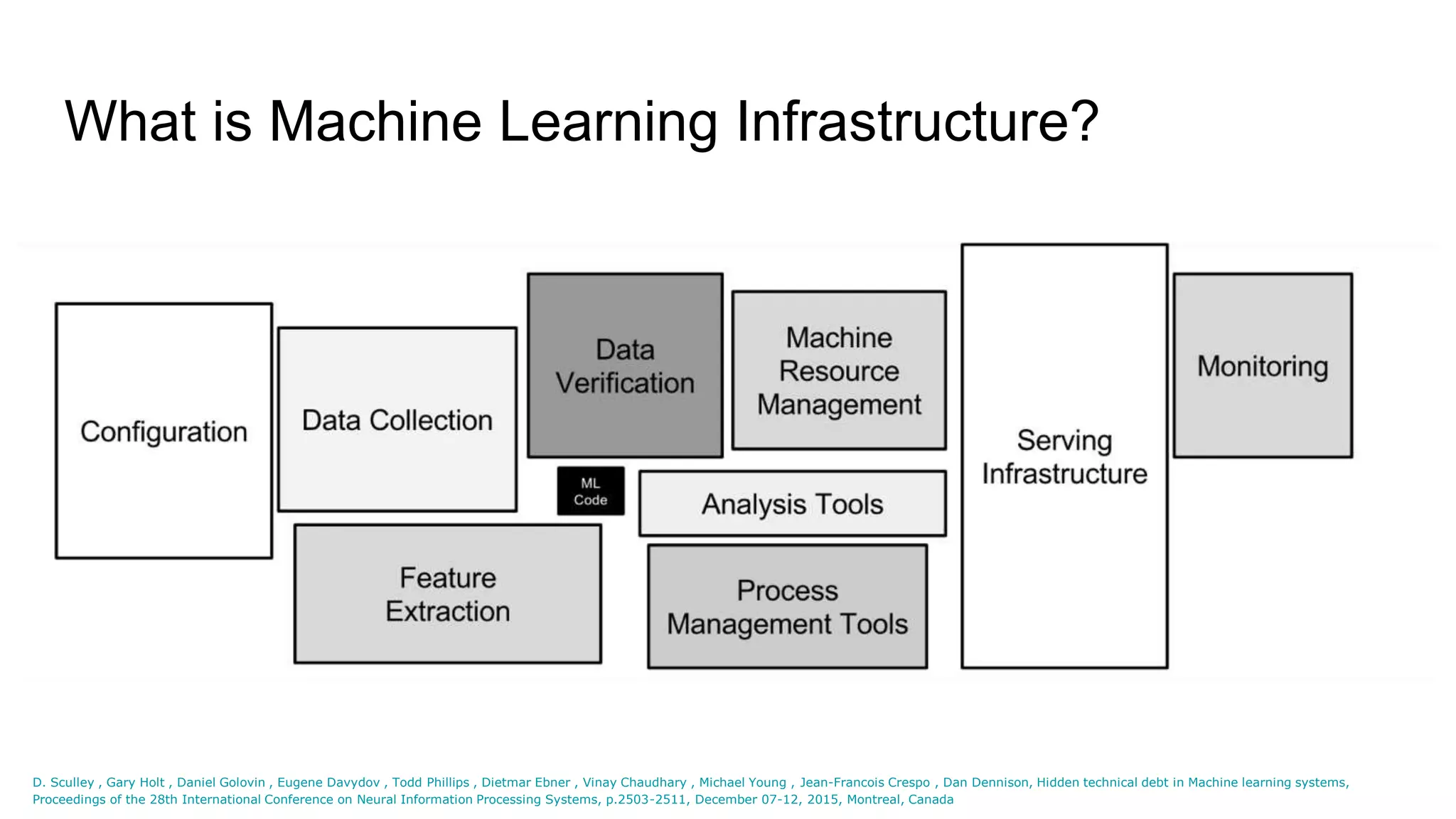
![ML systems have a special capacity
for incurring technical debt,
because they have all of the
maintenance problems of
traditional code plus an additional
set of ML-specific issues¹
[1] D. Sculley , Gary Holt , Daniel Golovin , Eugene Davydov , Todd Phillips , Dietmar Ebner , Vinay Chaudhary , Michael Young , Jean-Francois Crespo , Dan Dennison, Hidden technical debt in Machine
learning systems, Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, p.2503-2511, December 07-12, 2015, Montreal, Canada](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nycmlmeetup-181210231623/75/ML-Infra-Spotify-Lessons-Learned-Romain-Yon-NYC-ML-Meetup-11-2048.jpg)