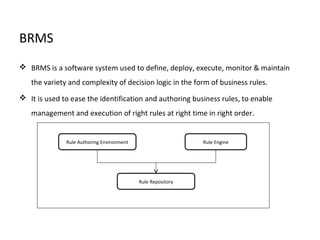
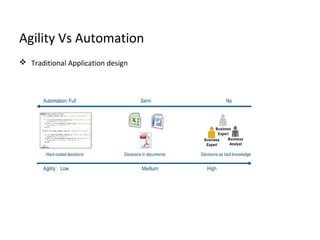
This document provides an overview of BRF+, SAP's business rule management system. It discusses BRF+ prerequisites and history, how it enables business rule management systems (BRMS) through rule authoring, repositories, and engines. The document contrasts BRF+ with its predecessor BRF, noting improvements like enhanced user interfaces, data types, APIs, and persistence. It concludes that BRF+ allows for business user empowerment, rapid development, centralized rule management, and automated yet agile systems.