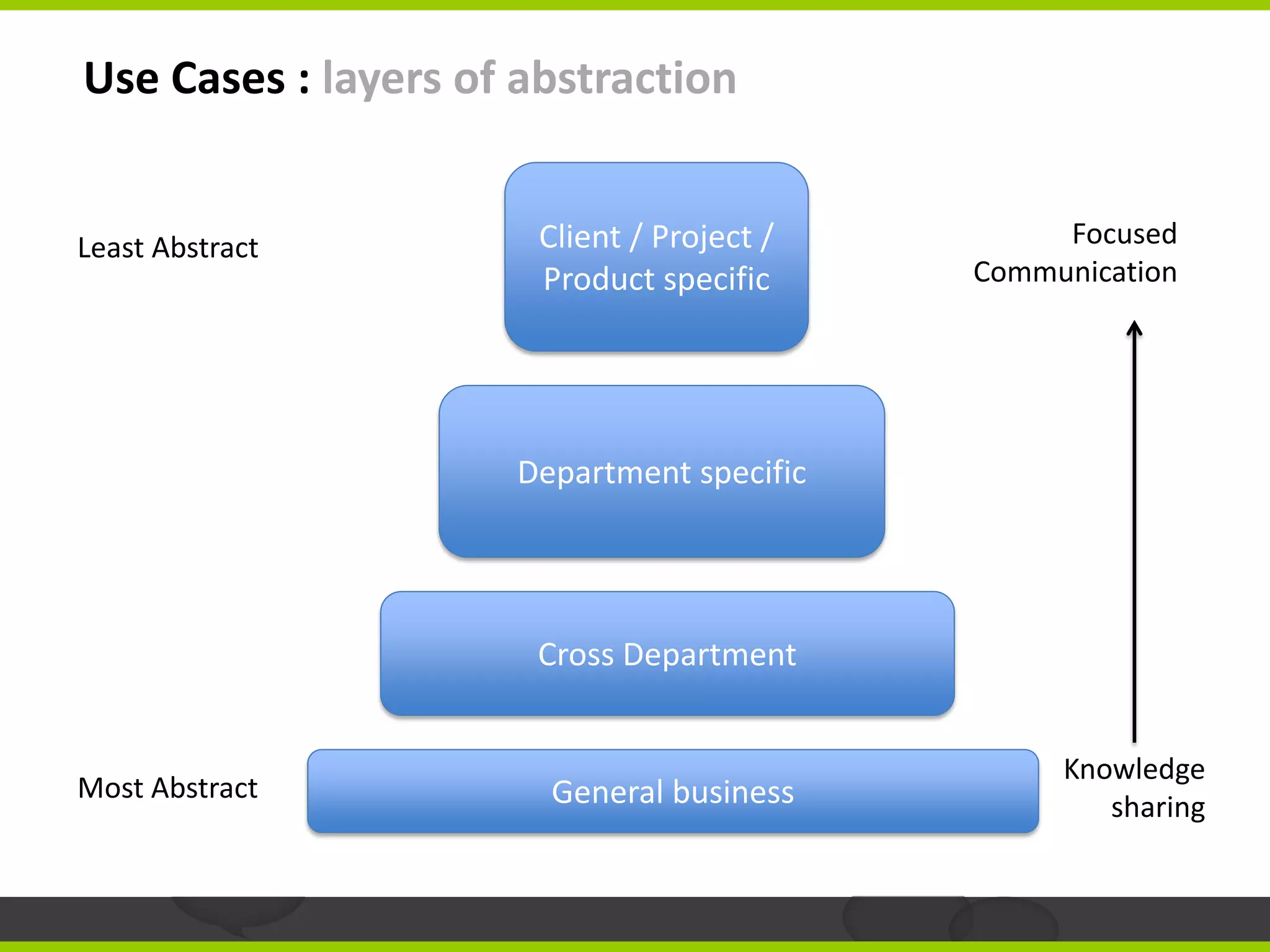
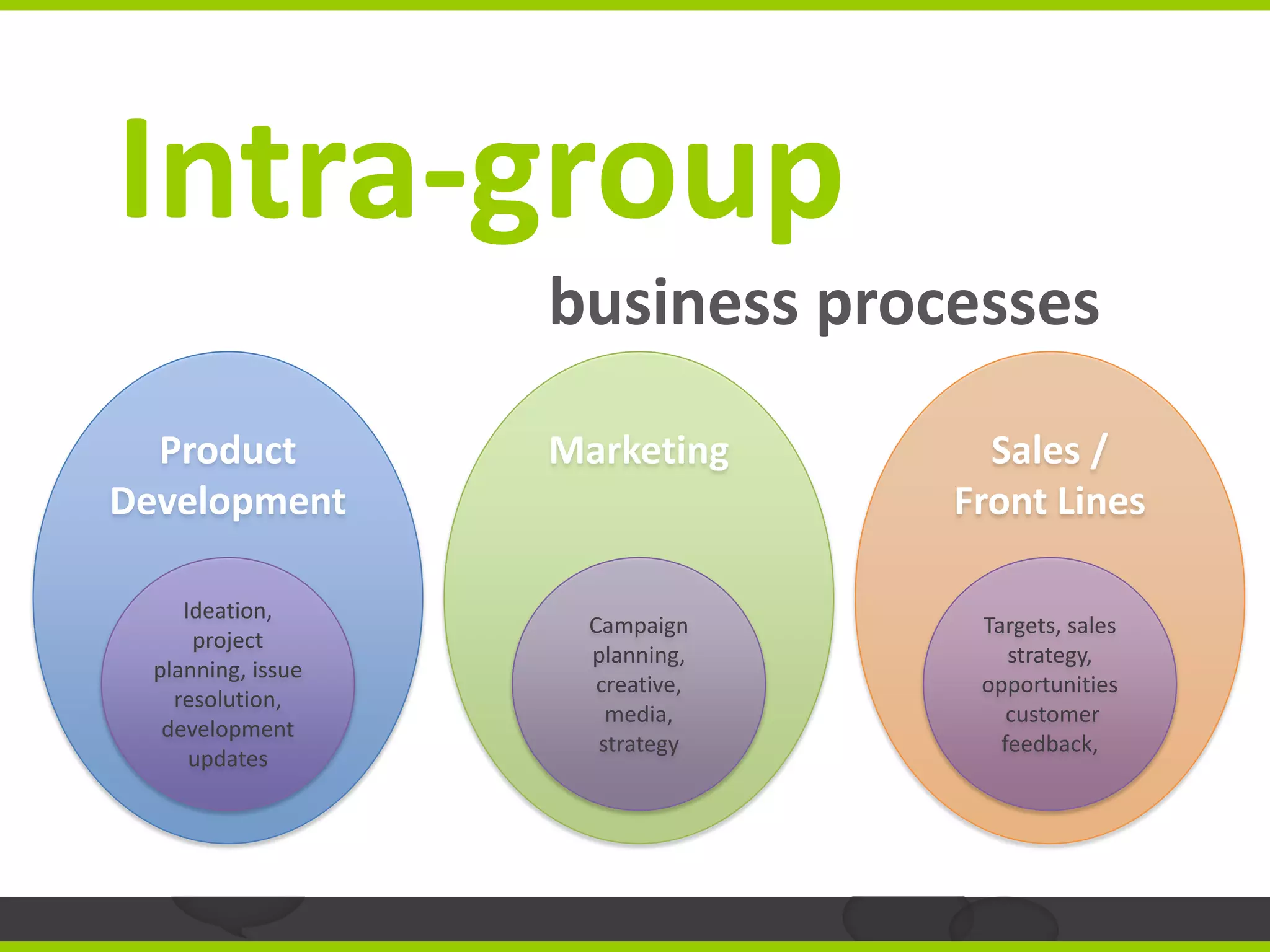
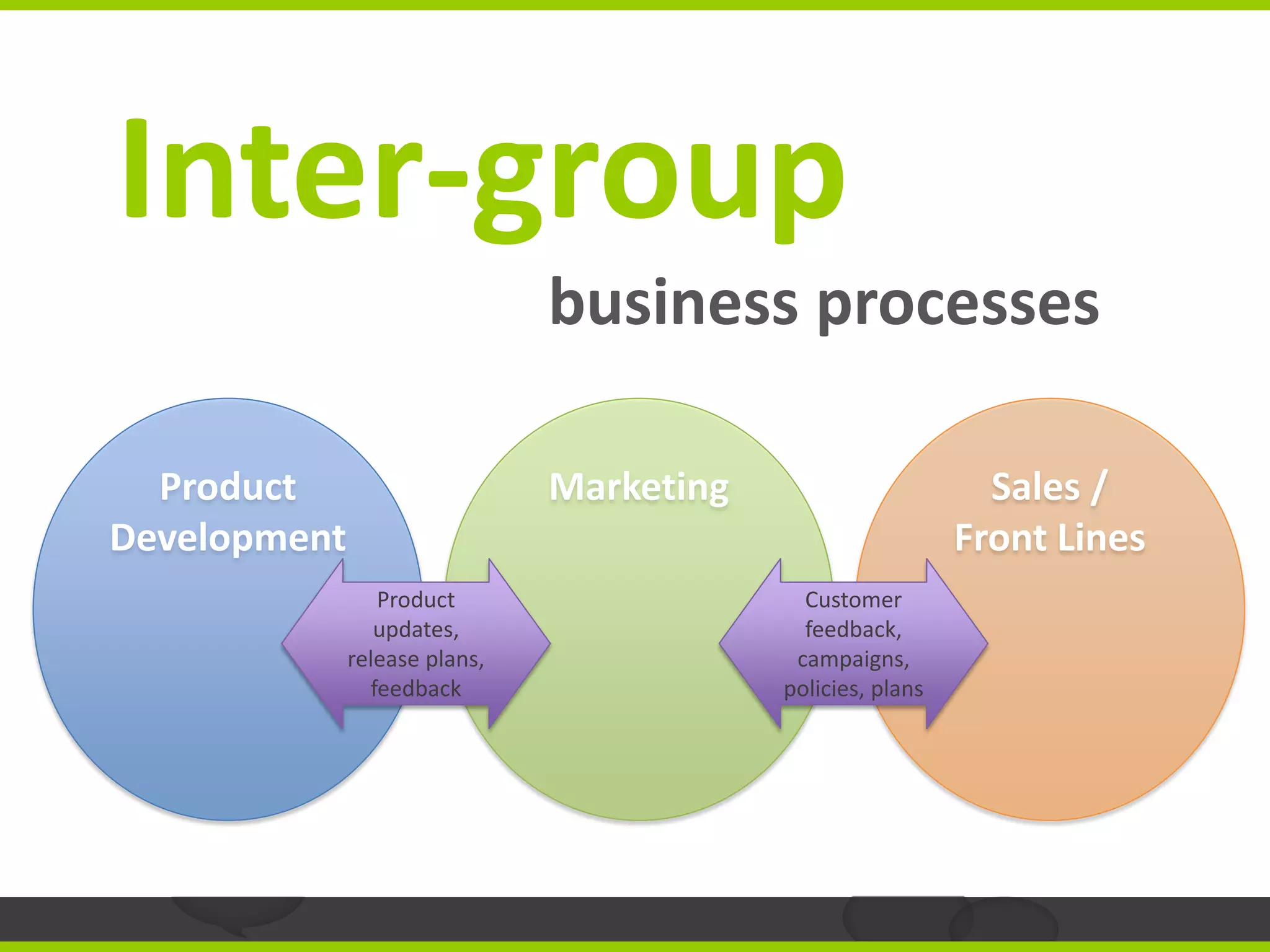
The document outlines a strategic approach to rolling out social software in organizations, emphasizing the need for clearly defined business use cases to ensure user engagement and contribution. It suggests starting adoption from core business processes, involving senior managers, and building immediate value to prevent user fatigue and facilitate sustainable content creation. The text also provides examples of successful implementations in different sectors, highlighting the importance of integrating external data to enhance collaboration.