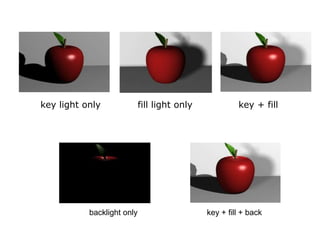
The document discusses the concept of mise-en-scene in TV drama. It defines mise-en-scene as the visual elements within a scene, including settings and props, costumes, lighting, positioning of characters, and facial expressions. It explains that these elements communicate meaning and help the audience understand characters' emotions. The document then examines each of the five elements of mise-en-scene in TV drama, providing examples of how they are used to convey meaning and influence the audience.